At what age does Dissociative Identity Disorder develop?
DID can be diagnosed at any age; however, symptoms commonly develop during childhood.
Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID), previously known as multiple personality disorder, is a rare mental health disorder characterized by alternating between two or more identities.
A young adult with DID may hear different voices in their head that are trying to take control.
Each identity, or alteration, can have distinct names, characteristics, and mannerisms. They may also have different memories, experience different health conditions, or speak different languages.
DID is most commonly found in individuals who have experienced severe abuse and childhood trauma.
DID can be diagnosed at any age; however, symptoms commonly develop during childhood.
According to StatPearls, about 1.5% of the global population is diagnosed with DID.
Signs and symptoms of dissociative disorders in young adults can include:
Sandstone Care provides age specific care for those who struggle with substance use, mental health, and co-occurring disorders. We have treatment centers throughout the United States.
Yes, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders describes three different kinds of dissociative disorders that include:
Dissociative amnesia involves difficulty remembering significant information about one’s self. It can be centered around a specific event or even concern their identity and history.
Amnesic episodes can last anywhere from minutes or hours to years.
Depersonalization disorder is characterized by consistent feelings of detachment from actions, thoughts, or feelings. Someone struggling with depersonalization disorder can also feel that the people or things around them aren’t real, which is known as derealization.


Dissociation most commonly develops as a response to trauma at a young age.
Trauma can include childhood abuse, sexual abuse, emotional abuse, physical abuse, loss of a loved one, natural disasters, or any other stressful life event.
Sensory stimuli related to a person’s trauma commonly trigger dissociation, such as specific smells, people, noises, and objects.
Some research characterizes DID as a stress disorder and can be a form of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) due to repeated trauma over a long period.
People of any background can develop DID; however, it is most commonly seen in individuals who have experienced trauma.
Sometimes, a person may not know or remember trauma as it may have become “blocked out” in their brain.
According to Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience, the main feature of dissociation is a disruption of one or more mental functions.
Dissociation can disrupt a person’s consciousness, memory, identity, thinking, emotions, and behavior.
Signs and symptoms of dissociation can include:
A doctor will review a person’s symptoms and personal history to diagnose dissociative disorders.
To rule out any physical conditions, like a brain injury or sleep deprivation, they will also perform physical exams that may cause similar symptoms.
It is also important to note that cultural background can play a role in diagnosing dissociative disorders.
The Continuum of Care
Access a full range of treatments for mental health and substance use disorders. Whether you need a safe detox program, inpatient care, or outpatient therapy, we have a program to help.
5-21 days of 24/7 on-site medical supervision.
Our Medically-Assisted Detox and Inpatient Center offers private rooms and 24/7 medically supervised care to support a safe recovery from drugs and alcohol, followed by comprehensive treatment that addresses your physical, psychological, emotional, and spiritual needs.
4 weeks of on-site day treatment.
Our Young Adult Day Treatment Program, also known as Partial Hospitalization Program (PHP), is a highly structured level of care for young adults that offers five days of robust programming a week.
Our two distinct mental health and substance use tracks help young adults to stabilize, begin to understand their mental health and/or addiction struggles, and heal from them. We strive to help our clients become more like the person they want to be without using negative coping strategies or substances to get there.
12 weeks of on-site or virtual treatment.
Our Young Adult IOP, or Intensive Outpatient Program, offers two distinct tracks to address young adult needs, each track consisting of 3-4 days of weekly programming.
In our mood disorder track, we are able to focus on mental health, depression, trauma, and anxiety. In our dual diagnosis track, we are able to support young adults with substance use and mental health challenges. Each focuses on developing positive social, academic, and vocational habits while continuing with their job or school responsibilities.


Sandstone Care offers age-specific, individualized, and evidence-based treatment programs that help you regain control of your life and achieve lasting recovery.
Dissociative Identity Disorder is a complex condition, making treatment difficult at times.
A person diagnosed with DID may experience trust issues or fear rejection, making it hard for them to open up to a therapist or others.
When treating individuals with DID, therapists commonly see their patients weekly or biweekly for a number of years.

First, it is important to go to your healthcare provider to receive a proper diagnosis where they will review symptoms and personal history.
Your healthcare provider can then refer you to a mental health specialist.
Treatment plans should be made to meet the specific needs of the individual so that they get the best care and support they deserve.
The approach to treating DID in young adults differs from person to person. Sometimes, a person may have to try different forms of therapy to find what works best for them.

CBT and other therapy can help treat young adults with DID. Sandstone Care supports teens and young adults with substance use and mental health disorders.
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is the best and most effective approach for treating dissociative identity disorder.
Psychotherapy refers to a variety of different treatment techniques that can help a person identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors.
Psychotherapy can be used in combination with medication or as an alternative.
Talk therapies can help people increase their awareness, learn how to cope with stress, improve their social and communication skills, and teach mindfulness and relaxation techniques.
Medications, such as antidepressants may also be prescribed along with psychotherapy for individuals with DID.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of talk therapy commonly recommended for individuals struggling with DID.
Through CBT, the therapist may communicate with the different alters to better understand each one and how they can help.
In CBT, a therapist may try to teach relaxation exercises so that they can figure out a way to cope with the stress that doesn’t involve switching.
CBT can help young people learn new coping mechanisms and skills they can use for managing stress and symptoms related to DID.

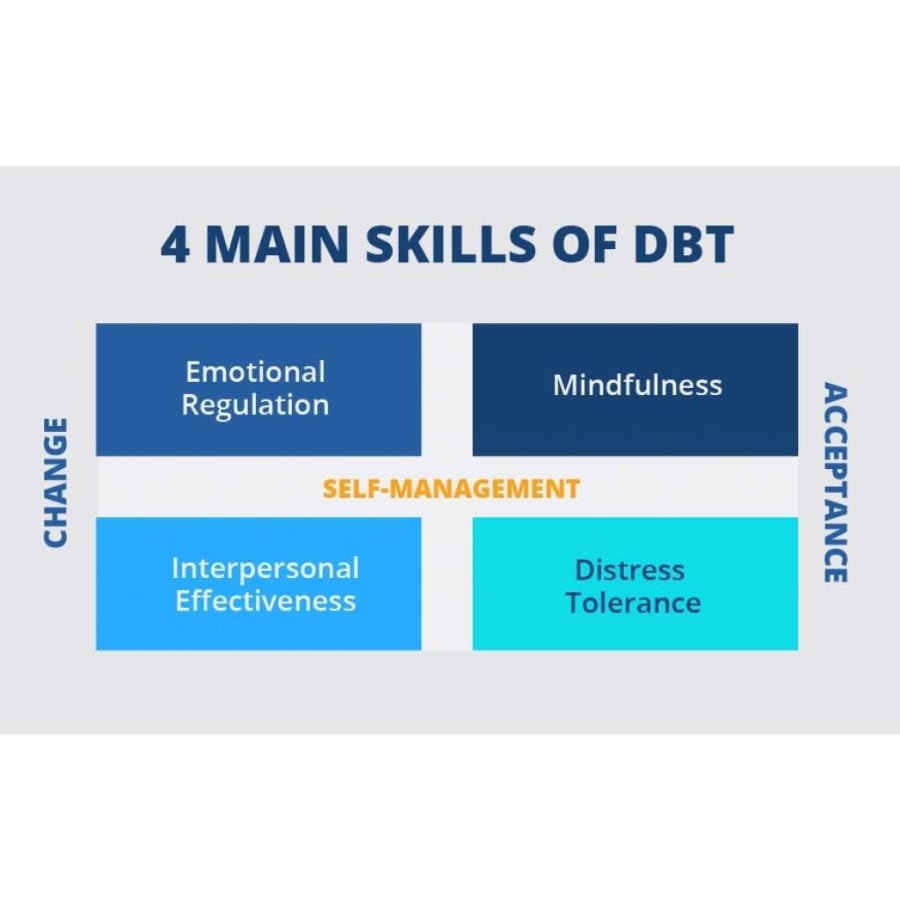
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), is a form of psychotherapy originally designed for individuals struggling with a borderline personality disorder or who were chronically suicidal.
Now, DBT is used for a variety of different mental health conditions.
DBT focuses on four main skills: mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, emotion regulation, and distress tolerance. Each of these skills works to help balance acceptance and change.
DBT can be helpful for teens and young adults because it targets the unique thoughts and feelings that can lead young people to destructive choices and behaviors.

11820 Parklawn Dr. #403, Rockville, Maryland, 20852
(301) 321-7362
5040 Corporate Woods Dr., Virginia Beach, Virginia, 23462
(757) 585-3518
