Effects of Drugs on Adolescent Brain Development
The human brain is amazingly complex. Researchers have studied it for centuries, but they still don’t fully understand how it works. One aspect of the brain’s complexity is the way it develops.
From the moment a child is conceived, the brain begins to grow, becoming more and more complex with time. The full development of the brain takes years. In fact, our brains don’t stop developing until we reach our mid-twenties.
Because of the brain’s complexity and its primary role in a young person’s wellbeing, it’s important for them to get enough sleep, eat nutritious food and receive medical attention for any kind of potential trauma, such as a head injury.
It’s also crucial for young people to avoid substance abuse – drugs and alcohol dramatically impede the brain’s development and can cause long-term damage. In some cases, the effects are irreversible.
Why is Brain Development Crucial During the Teen Years?
Adolescence is a critical stage of brain development. During these years, teens’ personalities are emerging – they are effectively growing into who they will be for the rest of their lives. Teens are also learning many new skills and developing the capacities they need to become well-adjusted, responsible adults.
Teenage brains are more adaptable to all types of experiences, and it’s easier for them to learn new things at this stage than it will be for them as adults. But this also makes them more driven to try mind-altering substances – and more vulnerable to sustaining harm as a result.
What is Normal Brain Function For Teenagers?
One aspect of a healthy brain’s complexity is its delicate balance of chemicals that keep the body and mind functioning normally. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters, and they carry messages between nerve cells and neurons, or nerve endings.
Everything a person thinks and feels – including their mood, energy level, consciousness, memory, ability to feel pleasure and need for food and rest – is affected by neurotransmitters, so it’s important to keep your child’s brain healthy as they grow.
Some examples of neurotransmitters are:
- Glutamate, which affects your memory and thinking abilities.
- Dopamine, which is responsible for your feelings of pleasure and reward. When you laugh or feel good, that’s your dopamine at work.
- Serotonin, which helps you sleep, and also affects your appetite, arousal level and mood.
- Norepinephrine/ noradrenaline, which helps you deal with stress.
- Epinephrine/ adrenaline, which interacts with norepinephrine/ noradrenaline, also helping you deal with stress.
- Oxytocin, which helps you relax, socially bond and maintain a reproductive drive.
- Endorphins, which reduce your feelings of pain and stress.
Overall, these chemicals help you stay healthy and have feelings that are appropriate for whatever experiences you’re exposed to. When you’re in danger, your brain should make you feel scared, and give you a burst of energy – the “fight or flight” response.
When you’re with friends, your brain chemicals should help you feel a sense of relaxation and trust. When your body needs food, your brain should make you feel hungry. And when your body needs rest, your brain should help you feel tired and ready to go to sleep.
Overall, these brain chemicals are designed to help you take care of yourself – to eat right, sleep right and form social connections. Your brain chemicals, when working correctly, provide you with motivation to do the things required for your survival and happiness.
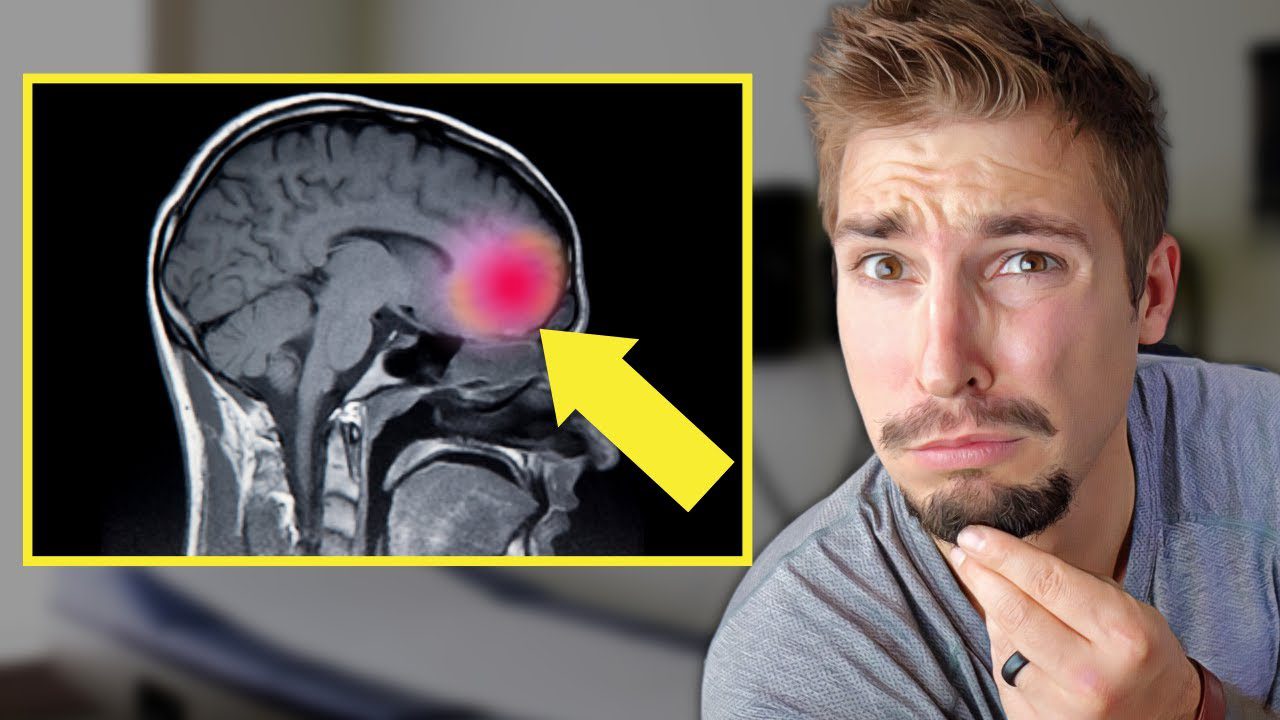
Why Are Young People More At Risk For Brain Damage From Substance Abuse?
The human brain is made up of cells called neurons. These cells are protected by a substance called myelin, which acts as a sort of insulator to the messages that come to your brain. The older you are, the more “insulated” you are from brain messages – that is, the better you’re able to handle them.
But in teens, the protective properties of myelin haven’t been fully developed, so they receive more intense messages. When teens experience pleasure, that sensation is more intense in their brain than in the brain of an adult. Conversely, when teens feel sadness, it’s also experienced more intensely.
And because of the myelin level of the teen brain, drugs have more intense effects on teens than they do on adults. So when they use substances like marijuana, opioids or amphetamines, their brains’ reward systems are triggered more powerfully – which also puts teens at greater risk for addiction.
How Do Drugs Affect Brain Function?
What are the Cognitive Effects of Drug Use in Teens and Young Adults?
How Can The Brain Recover From Damage Due to Drug Use?
How Does Healing the Brain Impact Short and Long Term Recovery?
How To Get Help For Substance Abuse?
If you suspect that your teen is abusing drugs, it’s important to help them as soon as possible, because the risk of impaired brain development is too great. If they have developed dependence or addiction to drugs, it’s urgent that they get professional treatment as soon as possible.
At Sandstone, our caring, compassionate staff has experience helping countless teens get back on track. We provide a safe, nonjudgmental space for teens and their parents to open up about their problems – call us today at (888) 850-1890 to learn how we can help.