Mental Health in Teens Statistics 2023


This report is all about teen mental health in the United States. Sandstone Care gathered insights directly from teens and their loved ones about their mental health experience. This overview can help teens, parents, healthcare providers, and journalists to be equipped with the information they need to effectively address mental health struggles in our communities.
By combining the results of Sandstone’s own original research with the latest findings from medical associations across the United States, this report provides unique insights into the mental health landscape in 2023.
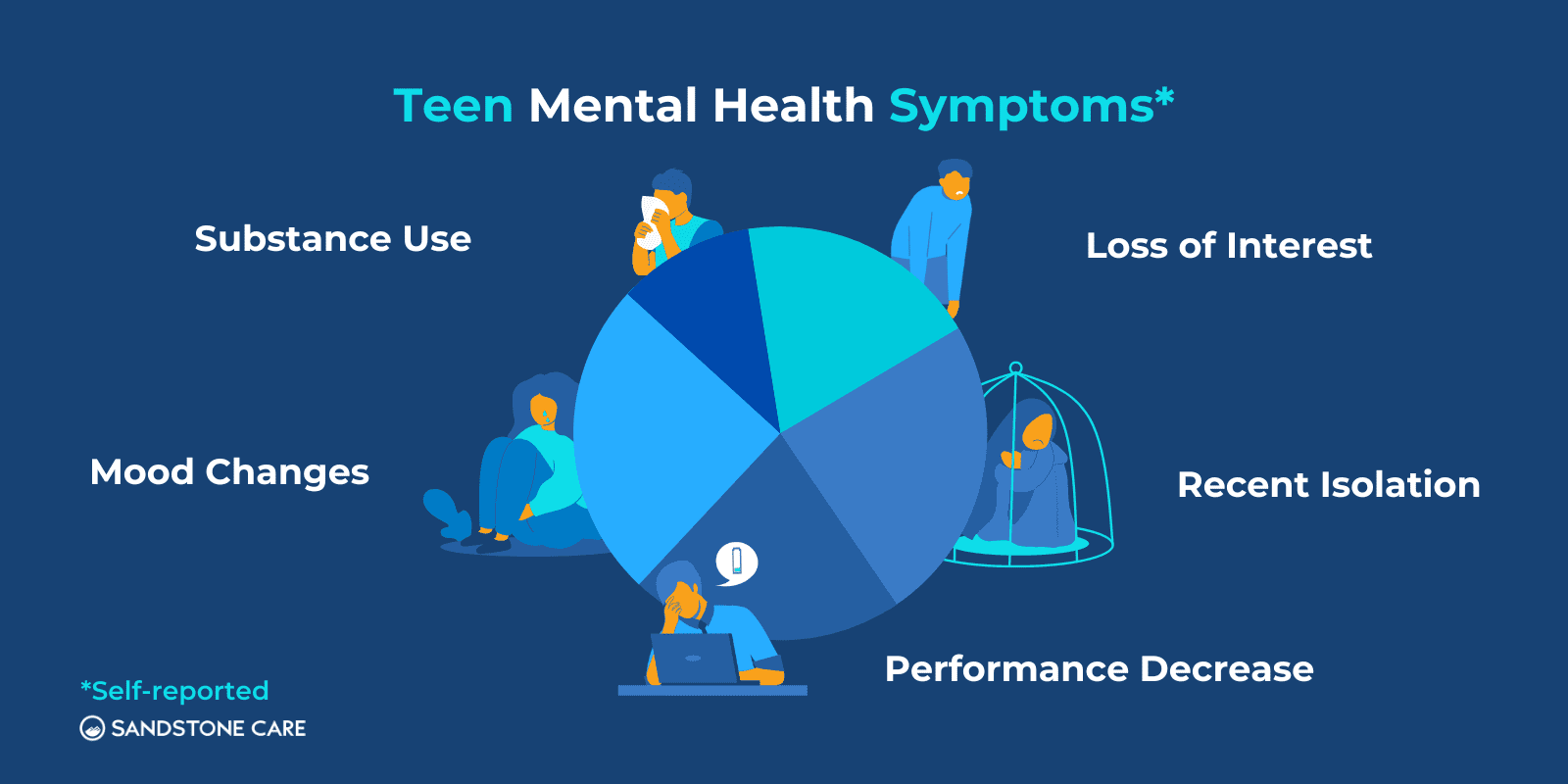
Sandstone Care’s 2023 research project was conducted through an online survey that focuses on assessing symptoms of mental illnesses and substance use. Questions surrounding mental health concerns centered on subjects like isolation, loss of interest, and mood changes. Participants had the option to fill out the survey as a self-report, or on behalf of a loved one.*
*Responses were tracked and separated into self-reports and loved-one reports
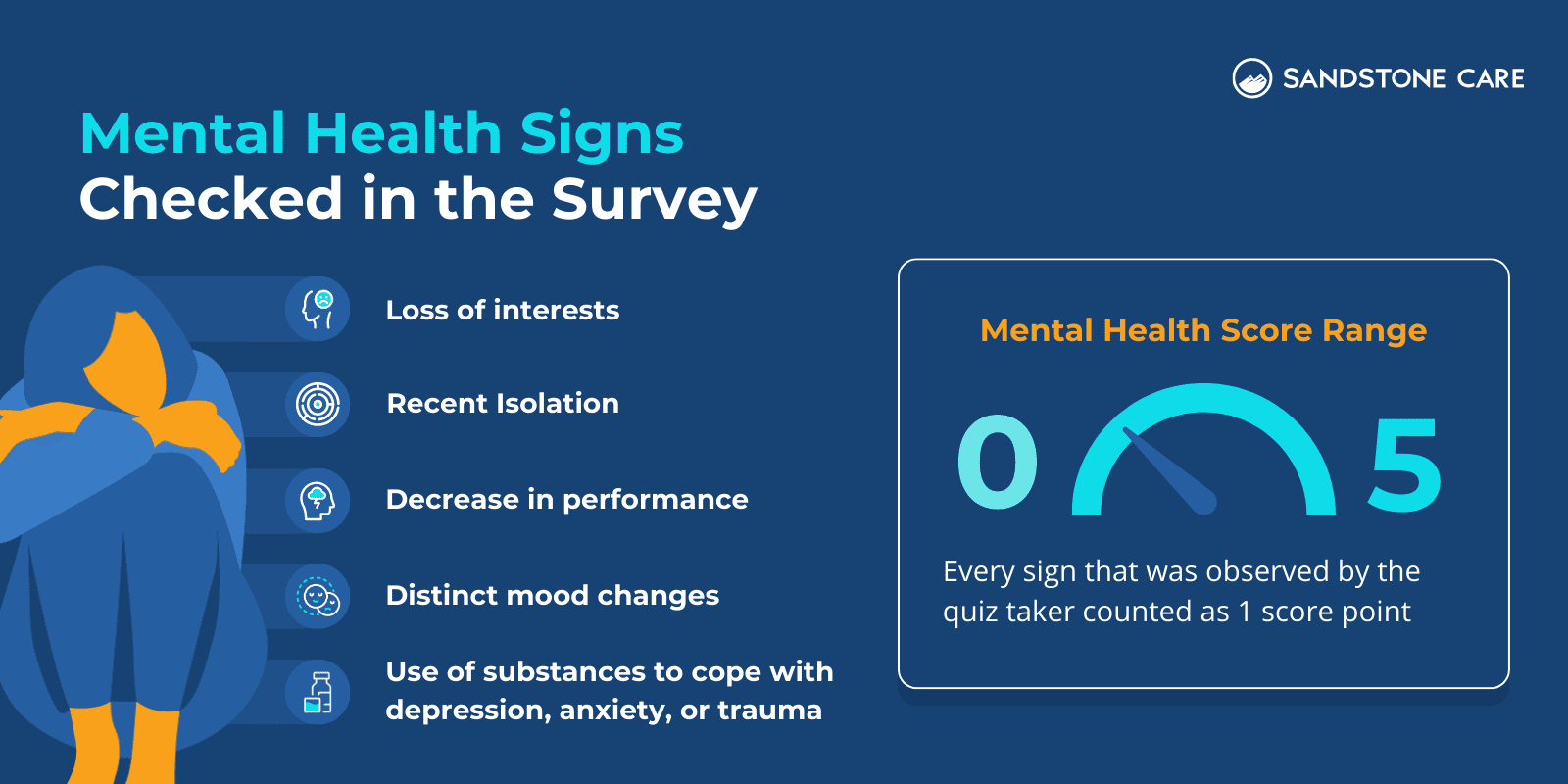
The survey was designed to assess teen mental health struggles by using a five-point scale. The scale ranged from least concern (one) to most concern (five).
Sandstone’s clinical team suggests that answering “yes” to 2 or more of the 5 questions below suggests the need for teenagers and their parents to consider treatment options.
Our research focuses on the personal observations of adolescent participants, which allows unique insights into the mental health needs of the teenagers in our community. While intake statistics and hospitalizations provide essential information, those numbers are limited to identifying severe cases.
By allowing participants to provide responses about the social and emotional changes they have observed in themselves or in their loved ones, Sandstone’s research can collect results from across the spectrum of youth mental health experiences.
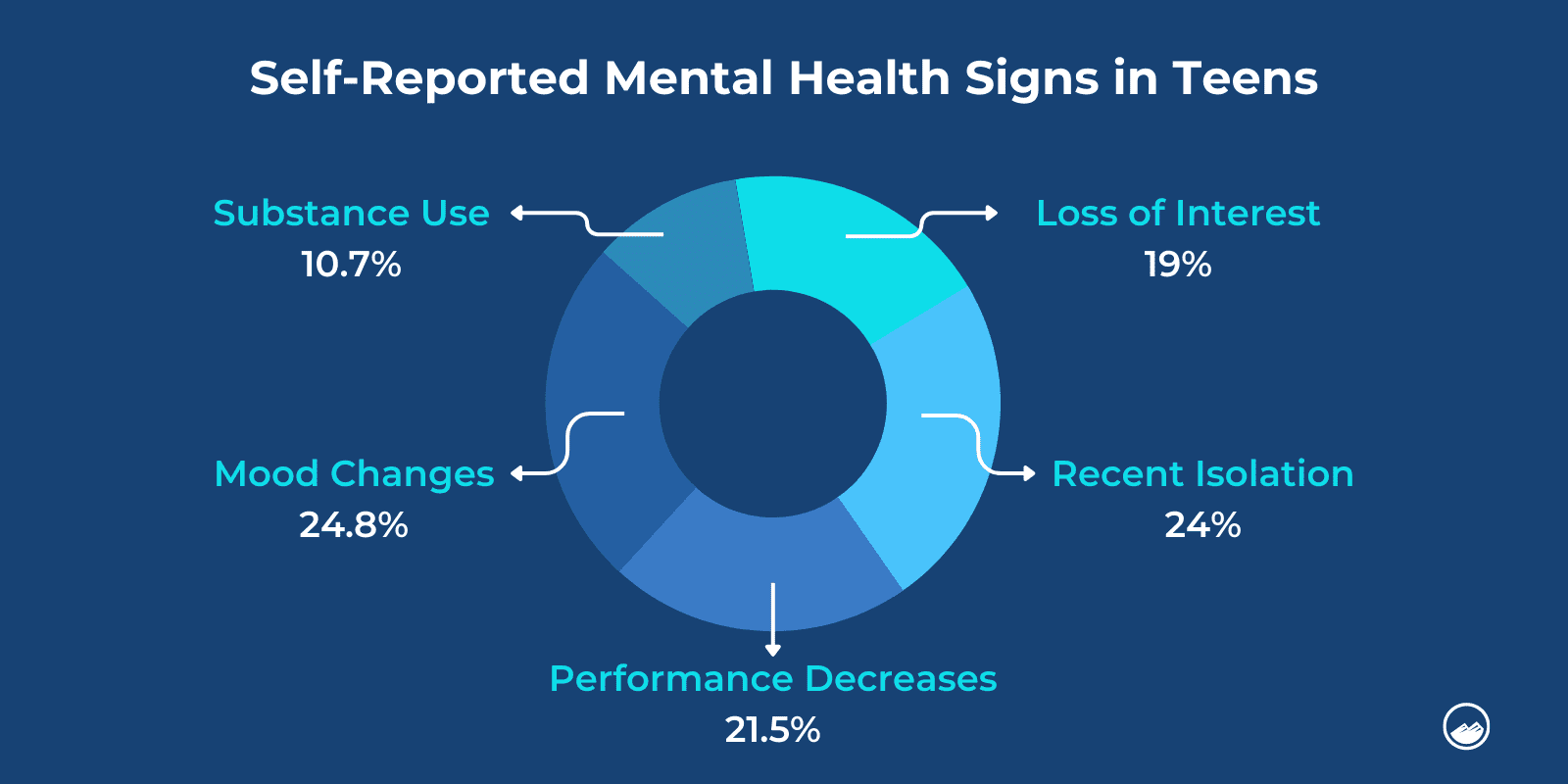
Our survey found that mood changes were the most commonly reported symptom among teenage respondents. This finding aligns with the NIMH’s findings on the prevalence of mood disorders among teenagers.
Isolation was the second most common symptom reported by teenagers. Sandstone’s findings align with existing research that indicates that teenagers experience higher rates of major depression and anxiety, which can be related to social rejection and feelings of loneliness.
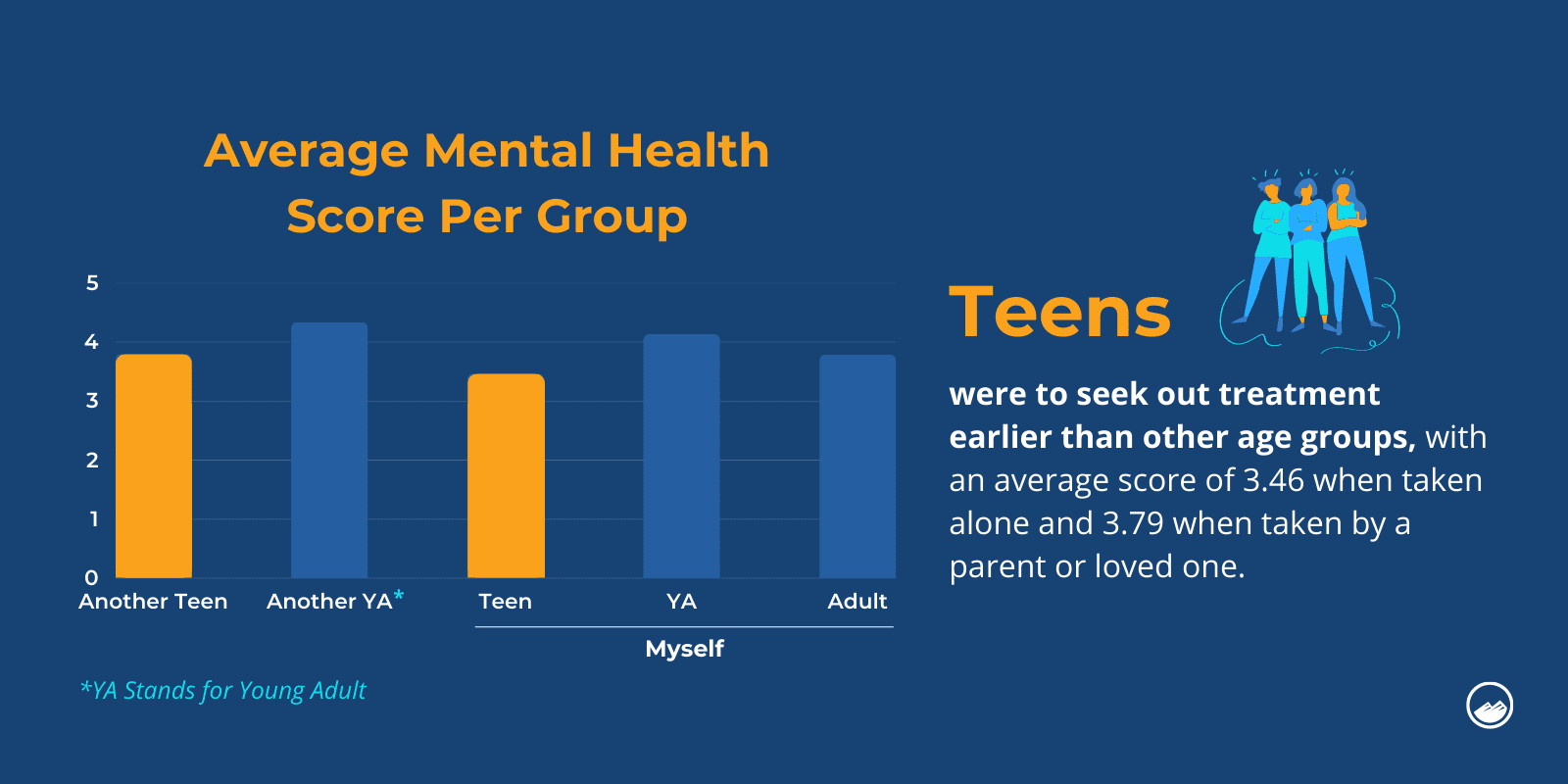
Sandstone’s research also found that teens were quicker to take the mental health quiz than adults, with an average score of 3.46 when taken alone and 3.79 when taken by a parent or loved one. This suggests that teens may be more willing to assess their mental health problems before they become severe compared to other age groups.
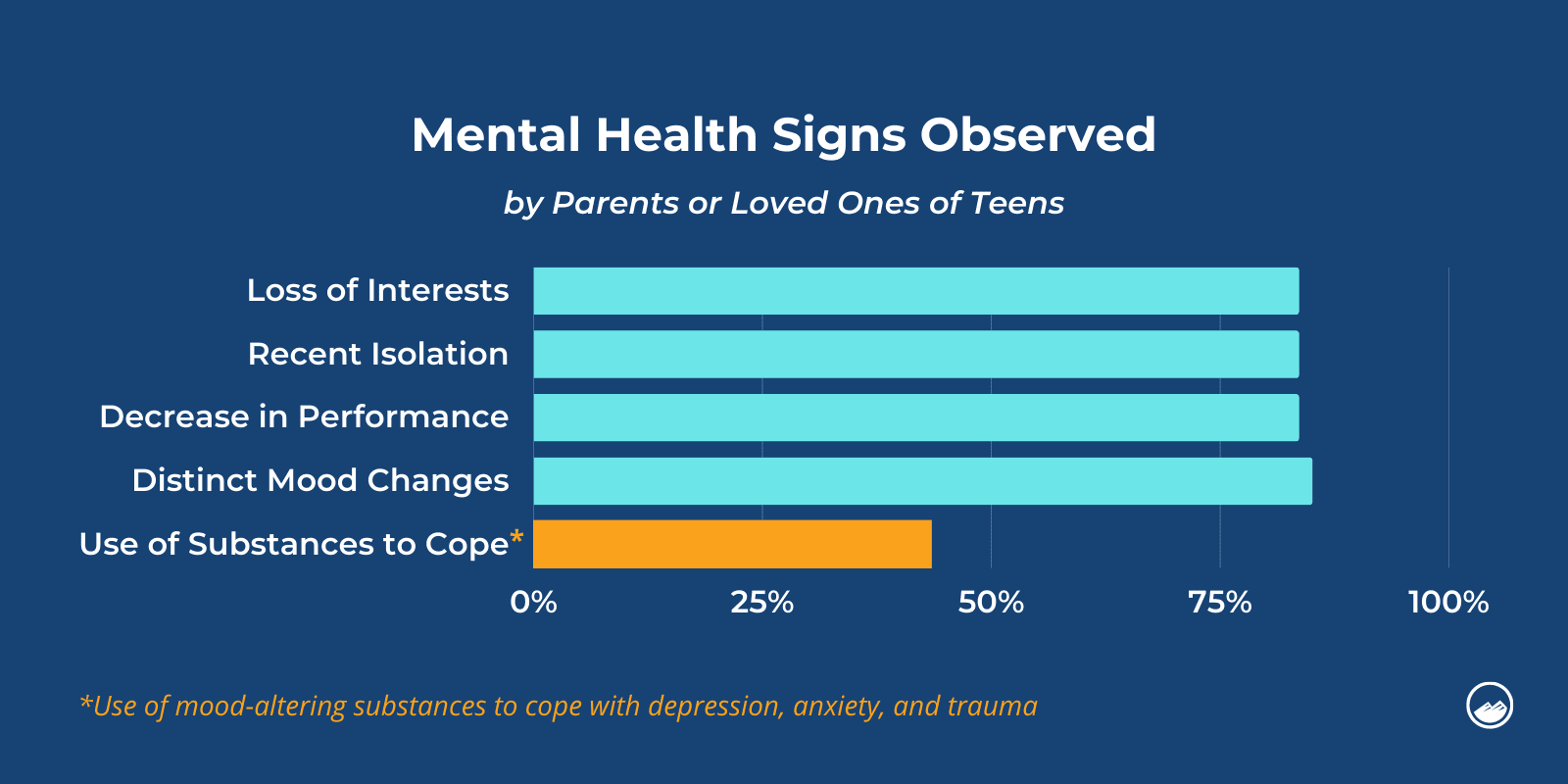
Finally, Sandstone’s research found that parents or loved ones of teens typically observe distinct mood changes, loss of interest, recent isolation, and a decrease in school/work performance equally.
When teenagers enter adolescence, they are hurled into a period of drastic transition and self-discovery that involves a great deal of change. Adolescents often face social, emotional, and physical challenges as they navigate their way from childhood to adulthood.
Teens may struggle with issues such as identity formation, peer pressure, and feeling misunderstood, all of which can impact their mental health. According to the World Health Organization, teens have high rates of depression, anxiety, and behavioral disorders.
Additionally, research by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) has found that nearly 50% of adolescents in the United States have experienced a mental disorder at some point in their lives.
There are several factors that are unique to teenagers beyond their physical and cognitive development. For example, some research indicates a link between social media use and mental health crises in young people.
Current research suggests that mental health in teenagers is a point of concern for public health. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), suicide is currently the fourth leading cause of death for American teens from 12-19 years old.
Research conducted by external organizations such as the WHO, NIMH, and the CDC also found that isolation, mood changes, and loss of interest were among the top symptoms experienced by adolescents in the last few years, which corroborates the data collected by Sandstone Care.
Teenagers and high school students face unique circumstances that can challenge their well-being and development. Adjusting socially, navigating complex emotions, and feeling misunderstood are common during adolescence. These distinct experiences can dramatically impact the relationship between teens and substance use. Young people are particularly susceptible to developing Substance Use Disorder due to a combination of factors. The influence of new social circles and the desire to fit in can drive them to experiment with substances. Teenage brains are still developing, leaving them vulnerable to developing dependencies and addictions that can last well into adulthood.
Some prominent risk factors observed among adolescents were the experiences of isolation and loneliness. Sandstone Care’s findings revealed that feelings of isolation ranked as the second-highest recorded symptom among teen participants. Adolescents who feel disconnected from their peers and support systems are more vulnerable to seeking solace through substance use.
Sandstone Care’s research revealed that out of the teens who reported using altering substances, over 65% of them also reported experiencing all signs of mental health struggles. This highlights the intricate connection between substance use and adolescent mental health challenges.
Sandstone Care’s findings indicated that parents and caregivers, on average, identified the most signs of substance use issues in their teens, with an average score of 5.35 out of 6.
However, it is important to note that while self-reported instances of substance use were lower than other symptoms, factors such as isolation and mood changes were more prevalent across the board. When the test was completed by a concerned loved one, all findings—whether related to substance use or other symptoms—were given equal weight.
This underscores that the perspectives of loved ones can provide valuable insights into an adolescent’s overall well-being.
Studies have shown that the teenage years are a critical period when it comes to substance use. Research from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that most adults with substance abuse disorders actually started using during their teenage years. Additionally, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) discovered that about 15% of high school students reported using drugs like cocaine or heroin. Shockingly, the CDC also revealed that 14% of teenagers were misusing prescription opioids, which has been linked to higher rates of risky behaviors, dating violence, and even suicide attempts.
The COVID-19 pandemic had some unexpected effects on substance use among teenagers. According to the NIH, overall substance use rates decreased among middle and high school students during the pandemic. As in-person instruction resumed over the past year in 2022, substance use rates remained lower than before the pandemic. However, there was a concerning increase of nearly 300% in opioid use among teenagers, as reported by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
It is crucial to address misconceptions and educate teenagers about the risks associated with substance use. A study by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) found that 57% of high school students do not perceive excessive drinking as harmful.
Generation Z has grown up in an era defined by social media. Social media has become an integral part of modern life and modern communication, and teenagers have grown up in the heart of it. However, research has consistently linked increased social media involvement to various mental health concerns, including social media addiction.
In addition to the effects of the 24/7 news cycle, the APA has found that social media can contribute to feelings of inadequacy, comparison, and anxiety among Gen Z. The constant exposure to curated and idealized versions of others’ lives can have a detrimental impact on self-esteem and well-being.
The CDC found in February 2023 that anxiety, depression, and suicidal thoughts among teen girls are at the highest rates the country has seen in over a decade. Major depressive episodes were recorded Recognizing the influence of social media on mental health is crucial in supporting teenagers and promoting healthy digital habits that prioritize well-being and balance.
The global pandemic has had a profound impact on mental health worldwide. Teenagers, in particular, faced unique challenges as they navigated this period.
Adolescence is a critical stage of development, and researchers suspect that the circumstances of the pandemic further exacerbated issues such as isolation, anxiety, and depression. With limited in-person interaction (which began to slowly return to normalcy last year) teenagers experienced disruptions in their social support networks and may have missed out on crucial developmental milestones.
Beyond the COVID-19 pandemic, the national landscape during the last three years has been rife with anxiety that may have an impact on the mental health of young people. Social media presents constant news coverage of school shootings, climate change disasters, and civil unrest. The American Psychological Association found that events like mass shootings can cause a “cascade of collective traumas” that increases anxiety, depression, and suicide rates.

The unique circumstances faced by teenagers, coupled with the increasing rates of mental health issues, emphasize the critical need for professional care and treatment from health care providers and primary care physicians tailored to their specific age group.
Relying solely on general mental health care approaches may not effectively address the distinct needs of this generation. Age-specific treatment becomes crucial in providing the necessary support and interventions to promote the well-being of young people.
By understanding the specific challenges and developmental stages faced by teenagers, mental health professionals can tailor their approaches and interventions to address the unique circumstances and experiences of this age group.
Earlier findings in this report have highlighted the prevalence of mental health conditions among teenagers, such as anxiety disorders, depression, behavioral health challenges, and ADHD. These conditions can have a significant impact on their daily lives, relationships, and overall quality of life. By offering age-specific treatment options, mental health professionals can better address the specific symptoms and challenges faced by young people, helping them manage their symptoms, improve their well-being, and enhance their overall functioning.