Young Adult Opioid Addiction
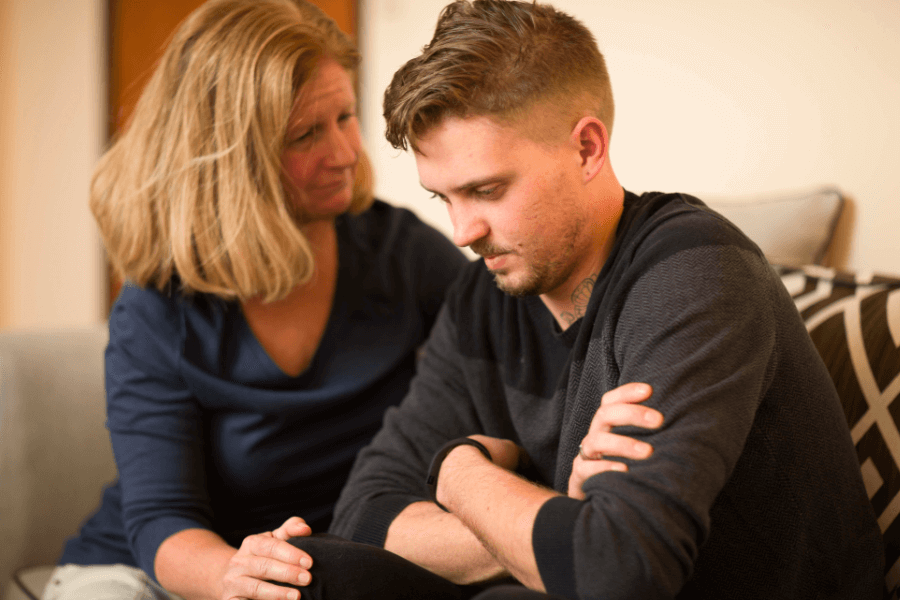
Young adult opioid addiction can be treated through individualized, age-specific care. Sandstone Care is here to support teens and young adults with mental health and substance use disorders. If you or a loved one needs substance use treatment, Call (888) 850-1890.
What Are Opioids And How Common Is Young Adult Opioid Addiction?
Opioids are a class of drugs that are used for pain.
Opioids can include illegal drugs like heroin, synthetic opioids such as fentanyl, and prescription pain relievers such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, codeine, and morphine.
Although they can be useful when prescribed, opioid misuse puts people at high risk of dependence and addiction.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services declared a public health emergency in 2017 regarding the opioid epidemic.
According to the HHS, in 2019, 1.6 million people had an opioid use disorder.
Many young adults who have used opioids also report getting them from friends or family members.
Opioid use and addiction are extremely dangerous for young adults and can lead to permanent health damage, overdose, and fatality.

How Serious Is Young Adult Opioid Addiction?
Young adult opioid addiction is extremely dangerous and serious.
According to the NIH, in 2019, almost 50,000 people in the U.S. died from opioid-involved overdoses.
When used, opioids block pain signals sent from the brain to the body, releasing high levels of dopamine. The release of dopamine can give the user a stronger urge to take the drug repeatedly to achieve the same effects.
However, over time, a person will need more of the drug to feel the same way, leading to dependence and, shortly following, an addiction.
Opioid misuse can also cause slowed breathing, which may lead to hypoxia. Hypoxia is a condition that happens when too little oxygen is in the brain.
Hypoxia can lead to permanent brain damage, coma, or death.
The dangers of opioids also become heightened when mixed with other substances such as benzodiazepines or alcohol.

Why Do Young Adults Abuse Opioids?
There are various reasons why a young adult may abuse opioids.
One could be as a way to fit in or experiment. They may experience peer pressure from the people around them to try it or be under the false impression that everyone else is doing it.
Some young adults may also misuse opioids because they can be easier to get compared to other drugs.
Many young people who obtain opioids report getting them from a family member or friend who was prescribed them.
Mental illness is most common among teens and young adults, and many turn to substances, such as opioids to self-medicate.
Young adults may also abuse opioids as a way to enhance the effects of other substances.
According to PLoS Med, individuals who reported prescription opioid misuse also reported a high prevalence of use of other substances such as cocaine, hallucinogens, and inhalants.
However, when a person mixes opioids with other substances, it can increase the likelihood of an accidental overdose.
How Fast Can A Person Become Addicted To Opioids?
Opioids have a high potential for causing addiction.
Drug abuse alters the natural chemicals and functions in the brain. Teens’ and young adults’ brains are more susceptible to becoming addicted because they are still going through major development.
It can take as little as a couple of weeks to become dependent on an opioid, which can quickly become an addiction.
What Are The Signs A Young Adult Needs Opioid Addiction Treatment?
Some signs that a young adult may have an opioid addiction and need treatment can include:
- Constantly changing friends
- Isolating themselves or losing interest in things they used to enjoy
- Extreme changes in eating or sleeping habits
- Poor hygiene
- Extreme mood swings
- Saying things that don’t make sense
- Drowsiness
- Getting in trouble with the law
- Being caught using substances
- Underlying mental illness
- Finding prescription medications that were not prescribed to them
What Is The Most Common Type Of Opioid Addiction In Young Adults?
The majority of misuse and most common opioid addiction in young adults is prescription opioids.
This can include drugs like oxycodone, hydrocodone, codeine, and morphine.
According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, after marijuana and alcohol, prescription drugs are the most commonly used substances in Americans over the age of 14.
How Does Addiction Affect Your Mental Health?
Addiction can cause serious, long-lasting effects on your mental health.
Over time, repeated drug use can alter the functions and chemical levels in the brain.
According to the NIH, drugs can work in two ways in the brain, including; imitating the brain’s natural chemical messengers and overstimulating the “reward circuit” of the brain.
Repeated substance use causes the brain to send out urges to seek the drug over and over again to feel pleasure.
However, over time the ability to feel pleasure goes down. It is difficult to enjoy things you once loved to do, and you can feel depressed, lifeless, and empty. The drugs no longer create feelings of pleasure but allow someone to feel “normal” again.
Mental health and substance abuse disorders commonly co-occur.
Substance abuse and addiction can worsen the symptoms of mental health illnesses and contribute to feelings of sadness, loneliness, irritability, and anger.
What Is Young Adult Opioid Addiction Treatment?
The goal is to help adolescents and young adults gain freedom from dependence on opioids.
The Sandstone Care approach to treating young adult opioid addiction includes:
- Thorough assessment
- Treatment for co-occurring disorders
- Adolescent-specific treatment considerations
- Academic and vocational support
- Individualized treatment plan
- Opioid-specific treatment considerations
- Focus on family involvement
The Continuum of Care
Care for wherever you are in your journey.
Access a full range of treatments for mental health and substance use disorders. Whether you need a safe transitional living program, inpatient care, or outpatient treatment, we have a program to help.
In Network With All Major Insurance
How Can Opioid Treatment Be Tailored To Young Adults?
Opioid treatment can be tailored to young adults by providing age-specific care.
Age-specific care involves the understanding that teens and young adults need a healthy, welcoming, and accepting environment to help get the most positive treatment outcome.
Opioid treatment for young adults can also involve academic and vocational support. Opioid abuse or addiction can be both a cause or a contributor to problems at school or work.
When receiving help for an addiction, it could be difficult to envision a life without drugs or alcohol. Many people can begin to develop a sense of self-centeredness around drug use and not be sure of who they are outside of it.
By providing academic and vocational support, teens and young adults can gain a sense of purpose and independence. Often, addiction can relate to feelings of hopelessness, and getting support can help people feel more powerful and create a happier life.

What Are The Benefits Of Treatment?
Opioid misuse and addiction can be very dangerous and deadly.
When gone without treatment, symptoms can worsen or lead to opioid overdose.
According to the CDC, treatment for opioid addiction can help normalize brain chemistry, ease cravings, and prevent some withdrawal symptoms.
Getting treatment for opioid addiction can help young adults live a healthier life without using substances.
Different Treatment Modalities for Opioid Addiction
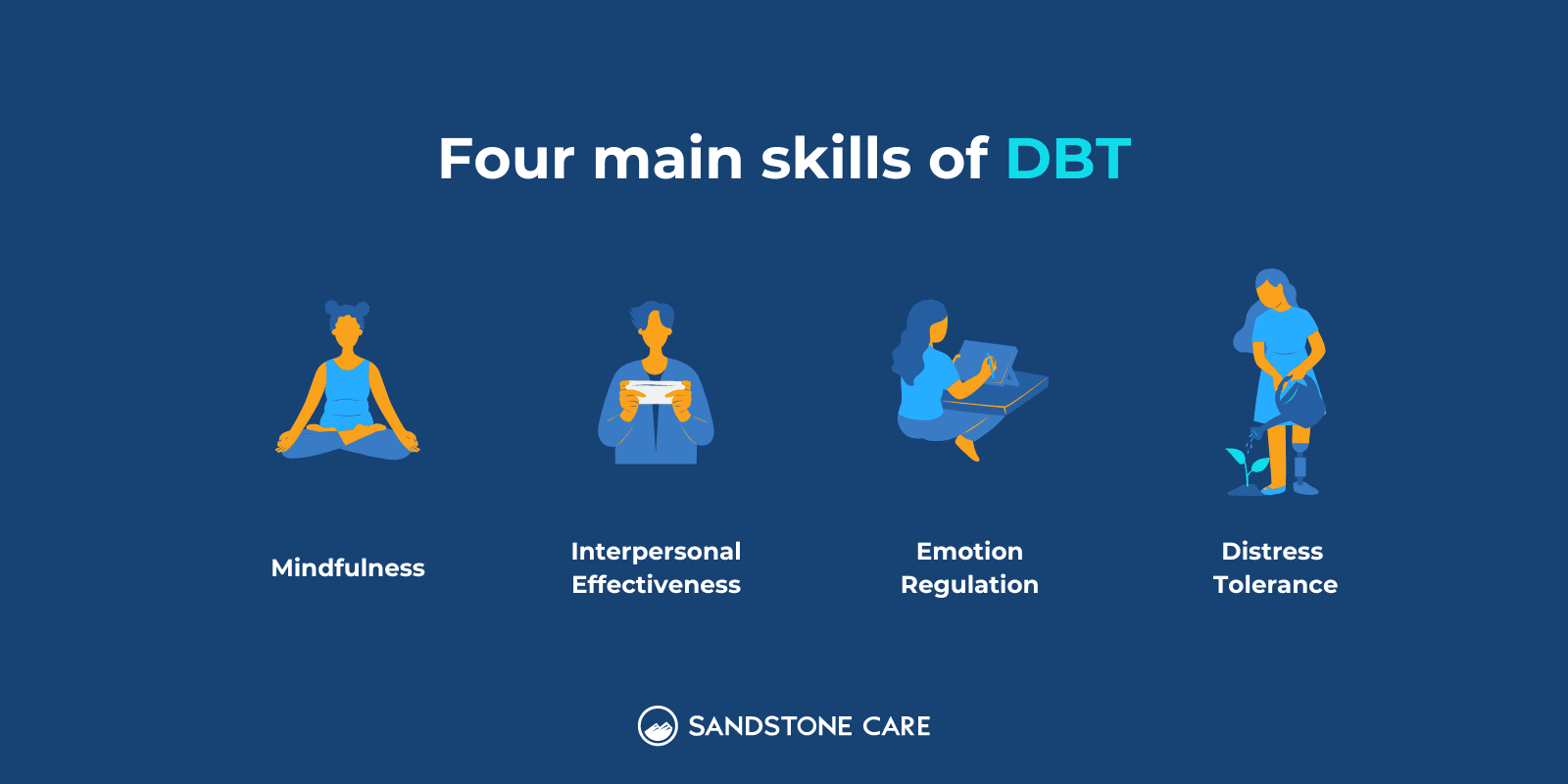
DBT
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) can be helpful for young adults who have co-occurring disorders, meaning they experience both substance abuse and mental health disorders.
DBT focuses on four main skills; mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, emotion regulation, and distress tolerance.
DBT can help young adults because it targets thoughts and behaviors that contribute to risky behavior and destructive choices.
Group Therapy
Group therapy is a form of talk therapy, or psychotherapy, that involves one or more psychiatrists leading a group of young adults to discuss their problems and experiences.
Group therapy can be helpful in the treatment process for young adults because it allows individuals to come together in a safe space and learn and teach each other.
Opioid addiction can feel isolating, and the treatment process can feel difficult at times. Through group therapy, young people can create a support network and meet others they relate to.

Family Therapy
Addiction affects the whole family.
Family involvement is an essential part of the treatment process for opioid addiction and any mental illness for young adults.
Family therapy allows family members to come together in a safe space and talk about their feelings and experiences.
Through family therapy, members can learn how to solve problems effectively, become more aware of each other’s needs and feelings, and connect in ways they may not have before.

Academic Support
One major part of the treatment process is helping young adults become the person they want to be.
By providing academic and vocational support, young people can receive guidance and help in their goals and working towards a new life.
Often, it can be difficult to see a life without substances, especially if they have been a part of your life for a long time. People can sometimes create a sense of self-centeredness around drugs or alcohol, making it hard to feel that they have an identity outside of substances.
By focusing on academic, vocational, and social skills, young adults can better envision a new, happier, healthier life for themselves and move forward.
Young adult opioid addiction can be treated through individualized, age-specific care. MAT has proven to be effective in treating OUDs. Sandstone Care is here to support teens and young adults with mental health and substance use disorders. Call (888) 850-1890.
Opioid FAQs
You have questions. We have answers.
Our goal is to provide the most helpful information. Please reach out to us if you have any additional questions. We are here to help in any way we can.
You can first start by finding a good time to talk about an opioid misuse problem. If they appear to have been using opioids prior to talking, it is probably not a good time to talk.
Without being judgemental or accusing them, you can talk to them about the concerns you have, and the negative effects opioids are having or can have on their lives and the people in it.
Hearing that you need help with opioid addiction can be a hard conversation.
Everyone reacts differently, and it is completely normal for someone to have a strong reaction. It is helpful to stay calm and not engage in any arguing. Rather, ensure them that you care and will be there for them.
It is also important to get professional help. You can reach out to counselors, therapists, family doctors, or health care providers and see if they can provide you with any additional resources.
Educating yourself and your loved ones about opioid addiction and treatment makes all the difference and helps young people see how important it is to do something about it now.
The standard for care for OUD in young adults includes medication, commonly combined with a form of psychotherapy.
Common medications used to treat opioid use disorders include buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone.
Naloxone is used to prevent opioid overdose and works by reversing the toxic effects of the overdose.
MAT is the use of medications in combination with other counseling and behavioral therapies.
According to SAMHSA, of the 2 million people who have an opioid use disorder, MAT proved to be clinically effective and reduced the need for inpatient detoxification services.
Common medications used in MAT for opioid addiction may include methadone, suboxone, and naltrexone.
MAT for young adults can help in recovery and living an independent life.
Benefits of MAT can include:
- Improved survival
- Increase treatment retention
- Decrease illicit opiate use
- Decrease criminal activity among those with SUDs
- Help gain and maintain employment
Opioid abuse and overdose have become a public health crisis in the United States.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the National Institute of Health have focused on five major efforts to improve opioid problems.
These efforts include:
- Improved access to treatment and recovery resources
- Promoting the use of overdose-reversing drugs
- Gaining a better understanding of the opioid epidemic
- Providing support for research on pain and addiction
Utilizing better practices for pain management
The beginning to solving opioid problems is educating yourselves and your loved ones on the dangers and severity of opioid abuse and addiction.
By knowing the risks, young people can better understand how opioid abuse can harm their physical, mental, and psychological health.