Addiction to Social Media
What Is A Social Media Addiction?
Social media addiction is a behavioral addiction that involves an excessive concern about social media to the point where its use begins to impact your health and everyday life.
It is no secret that social media use is popular among young people in the United States, and many people who use social media don’t see any problems related to their use.
However, with a social media addiction, individuals have an uncontrollable urge to check and use social media.
Overuse of social media has been linked with numerous mental health problems and can lead to social media addiction.
What Is Considered Excessive Social Media Use?
Excessive social media use is typically more than 2 hours a day.
However, it is often recommended to spend a maximum amount of 30 minutes on social media daily.
Why Is Social Media Addictive?
Social media use can trigger the brain’s reward system, boosting the “feel-good” hormone, dopamine.
Because of this, the brain continues to seek out this pleasurable feeling, which can result in an unhealthy cycle.
What Are Examples Of Social Media Addiction?
A common example of social media addiction can be a teenager who constantly needs to check in on Instagram or Tiktok. If they don’t check their social media accounts, they can’t stop thinking about it.

In this scenario, they may become upset or irritated if they don’t have access to social media. These withdrawal symptoms can make it hard for them to focus on other things since all they can think about is getting on social media.
The addiction to social media is highlighted by its negative impact on a person’s life. Socially, personally, emotionally, and as a whole.
How Many Hours Of Social Media Is Considered Addictive?
No set amount of hours defines a social media addiction.
Social media addiction is usually gauged by how much of a negative impact it has on the person and the uncontrollable urge to check or use it.
A person may not necessarily spend four consecutive hours every day on social media, but they may constantly be checking it and finding themselves quickly distracted. They are often pulled into using it again despite the negative consequences.
Why Is Social Media Dangerously Addictive?
Social media use triggers the brain’s reward system and causes a release of dopamine.
Dopamine is known as the “feel-good” brain chemical, and it plays a major role in feelings of pleasure, motivation, and satisfaction.
So, when a person uses social media and gets a surge of dopamine, they begin to crave more rewards and seek them out from social media. Social media algorithms are also programmed to show a constant stream of content that you enjoy the most, which can make it more addictive. Many online video games also use these same strategies to encourage addictive relationships with technology.
Additionally, social media sites often involve very short videos, which some refer to as “hits” of dopamine. These short bursts of chemicals in the brain can increase addictive behaviors.
Social Media Addiction Statistics
What Percentage Of The Population Is Addicted To Social Media?
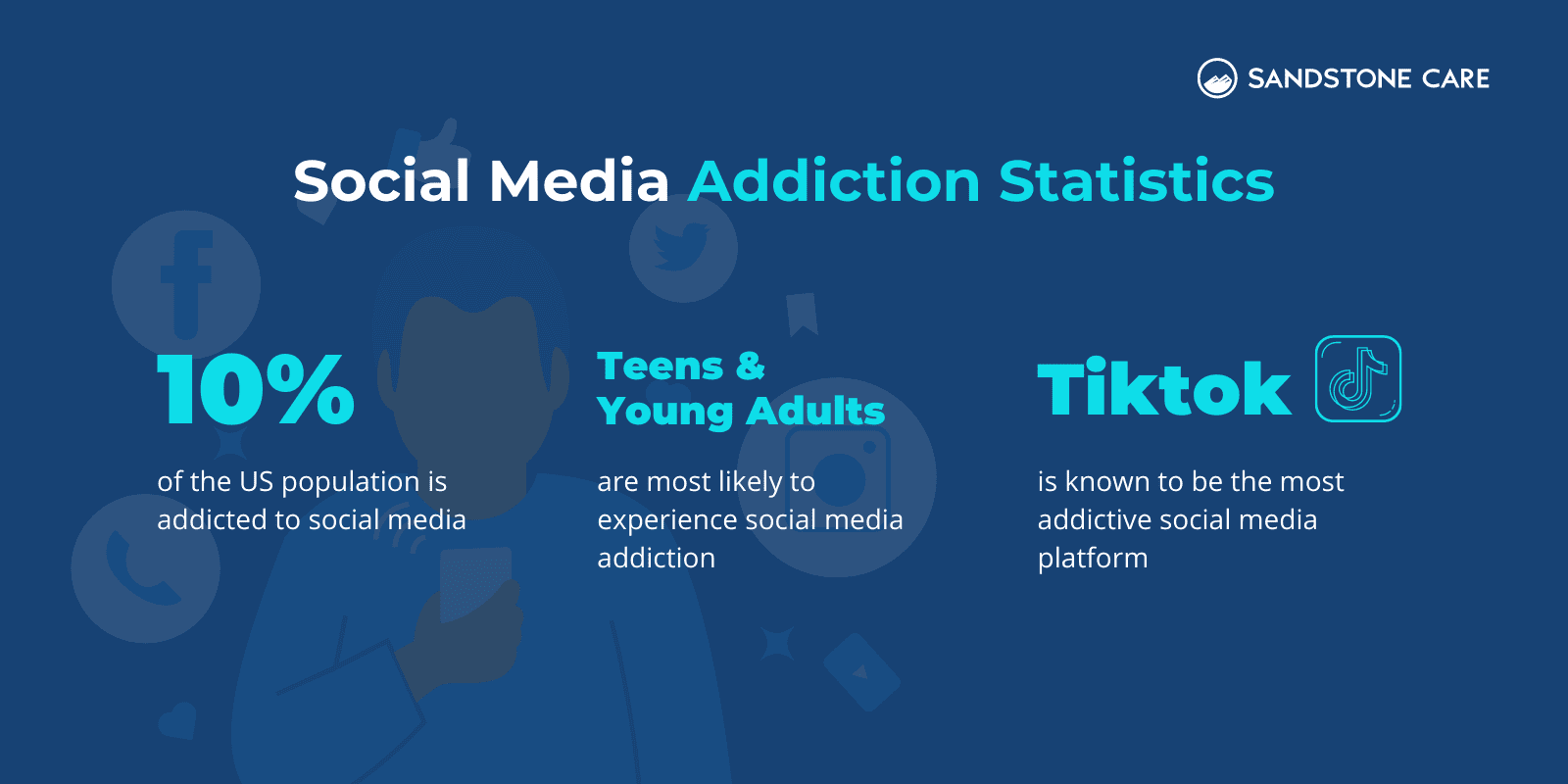
Nearly 10% of the U.S. population is addicted to social media.
However, the exact number is hard to gauge as there is no set guideline for diagnosing social media addiction.
Who Is Most Likely To Experience Social Media Addiction?
Teens and young adults are most likely to experience addictive use of social media.
During the adolescent years, the brain is still undergoing major development. Those developments put teenagers at a higher risk of addictive behavior, including social media addiction. Technology use is often a prevalent factor in the lives of young people, which can make them more susceptible to all kinds of internet addiction.
What Generation Is Most Addicted To Social Media?
Millennials, or those born between 1981 and 1996, are considered to be the age group most at risk for social media addiction.
What Social Media Is Most Addictive?
In recent years, TikTok has gotten a reputation as the most addictive social media platform.
However, Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat are also among the most popular social media platforms used by young people.
What Is A Statistic On Social Media Use?
According to Frontiers in Psychiatry, “an increasing number of studies have linked social media use to negative mental health consequences, such as suicidality, loneliness, and anxiety.”
Causes of Social Media Addiction

What Are The Causes Of Social Media Addiction?
Social media addiction may be caused by a variety of different risk factors, which may include:
- Low self-esteem
- Low self-worth
- Mental health problems, like anxiety or depression
- Stress
What Is The Main Cause Of Social Media Addiction?
There is no single cause linked to social media addiction.
However, excessive social media use and addiction are most commonly linked to stress, depression, and low self-esteem.
Many people start to use social media casually, simply as a way to connect with others or participate in online social networking.
But, sometimes, social media turns out to be an escape from problems or challenges they are facing in their life. Because of this, they may start to use social media as a way to feel good temporarily or as a way to distract themselves.
Some people may also have a “fear of missing out,” also known as FOMO, that keeps them feeling the need to constantly check on what others are doing.
Social Media Addiction Symptoms
What Are The Symptoms Of Social Media Addiction?
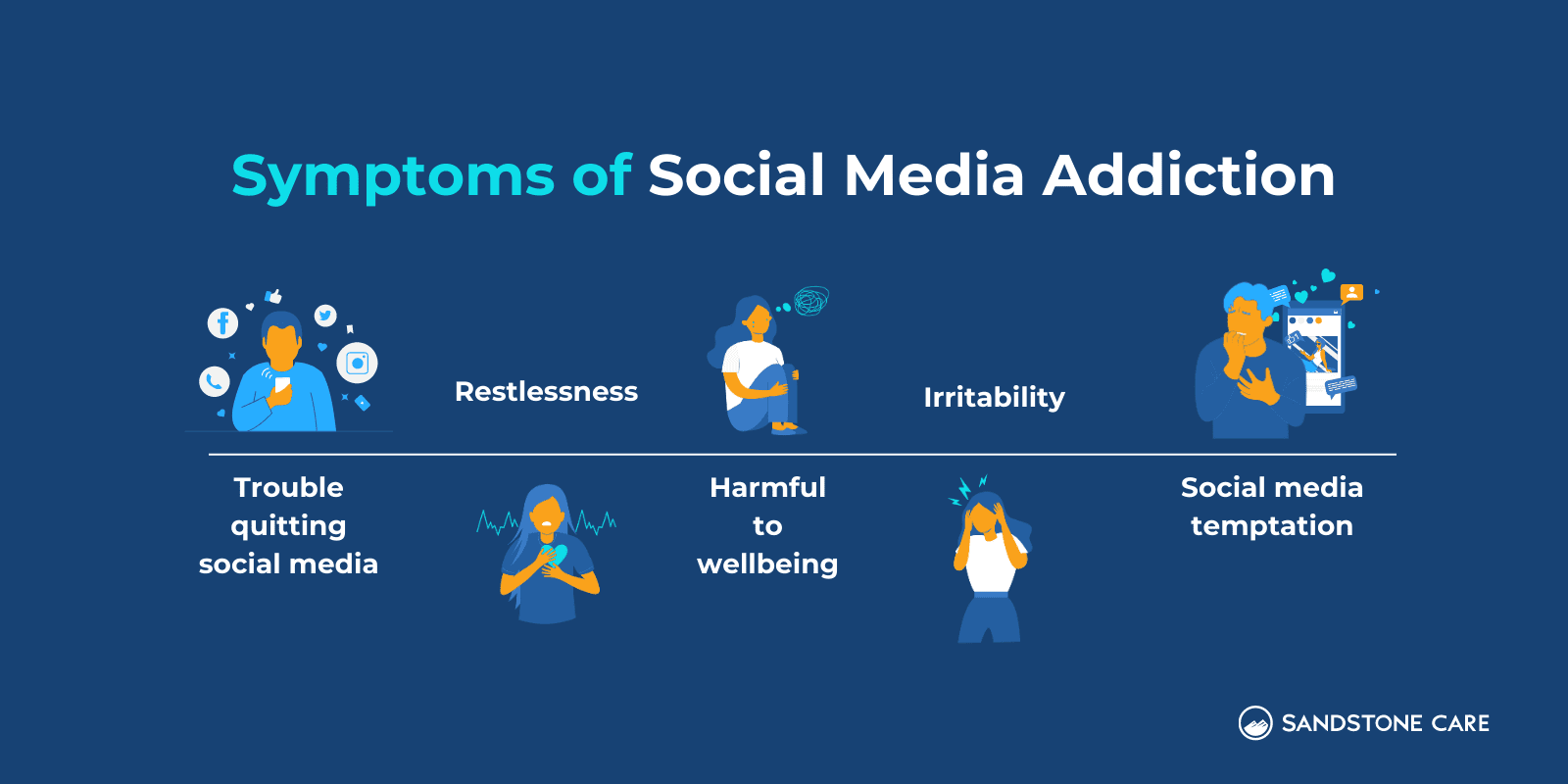
Common symptoms of social media addiction can include:
- Trying to decrease or quit using social media but failing
- Restlessness
- Irritability
- Struggling with delayed gratification
- Urge to check or use social media
- Negative impact on life and health
How Do You Know If You Have A Social Media Addiction?
Common signs of a social media addiction can include:
- Spending a significant amount of time using or checking social media
- Spending a lot of time using social media instead of other activities, hobbies, or responsibilities
- Feeling an uncontrollable urge to check social media
- Becoming upset or irritated if you cannot use social media
Side Effects of Social Media Addiction
What Are 5 Effects Of Social Media Addiction?
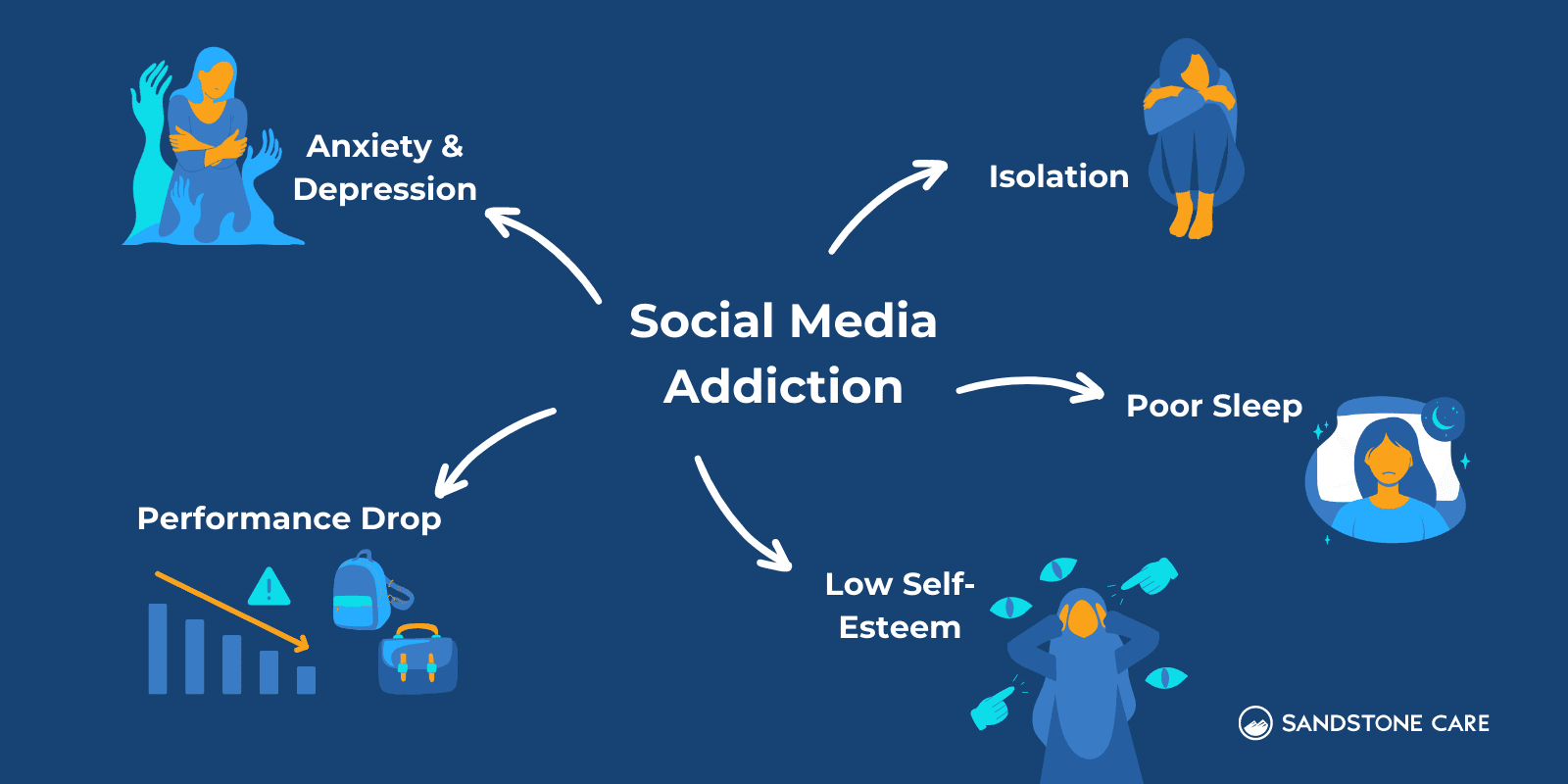
5 effects of social media addiction can include:
- Poor performance at school or work
- Isolation
- Low self-esteem
- Anxiety and/or depression
- Poor sleep
What Are The Long-term Effects Of Social Media Addiction?
Social media addiction can have serious and long-term effects.
One of the most harmful effects social media can cause is damage to your mental health.
Social media addiction can put you at a higher risk of mental health conditions like anxiety or depression and even self-harming behaviors or suicidal thoughts.
If you or someone you know are experiencing suicidal thoughts, know that you are not alone. Call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 988 or call 911 if you are in danger.
What Are The Impacts Of Social Media Addiction?
Social media addiction can impact your health and, quite frankly, every aspect of your life.
It can impact your daily life at school, work, or at home. Often, the time spent on social media takes the place of activities such as exercise, going outdoors, and spendings time with friends and family in “real life.”
It can cause conflict and problems in relationships and also lead to isolation and feelings of loneliness.
Social media can take a toll on the way you perceive yourself and the world. It can make you feel negative about yourself as you see these “picture-perfect” lives everywhere you scroll.

What Are The Negative Impacts Of Social Media?
Social media can harm your physical and mental health, as well as your overall well-being and daily life.
Social media gives people a platform to share what they want about their lives, whether it is realistic or not.
These unrealistic standards can lead to a negative self-image, low self-esteem, and low self-worth.
Seeing what seems like “picture perfect” faces, bodies, jobs, families, and lives can make people view themselves and their own lives negatively and have them chasing an unrealistic standard that leaves them unhappy.
While social media was created to connect and keep people in touch, it has also proved to make people feel more isolated and harm their mental health and overall well-being.
Social Media Addiction in Teens

How Social Media Affects Teenagers?
Teens are highly impacted by the effects of social media for many different reasons.
Research shows that one is because they are in a time of their lives when figuring out who they are, finding independence, and trying to find acceptance.
Teenagers may see these unrealistic standards on social media and feel they are not good enough or have to look a certain way to be liked or accepted.
Social media usage also takes away from many healthy activities in a teen’s life.
It can distract them from responsibilities, take the place of outdoor time and exercise, affect their sleep, and take time away from being with friends and loved ones.
Social media can isolate teens and worsen mental health issues. They may use social media as a coping mechanism for difficult feelings and experiences going on in their lives, using it as an escape from reality.
Cyberbullying is another major problem when it comes to online platforms, and it is easy to find a lot of hate and negativity on social media.
Why Are Youth Addicted To Social Media?
Social media is designed to make people, especially youth and teens, feel a sense of pleasure.
The brain recognizes this and continues to seek out the behavior, leading to a cycle that can be very hard to get out of.
The youth brain is still going through significant development, making it more susceptible to the negative effects of social media.
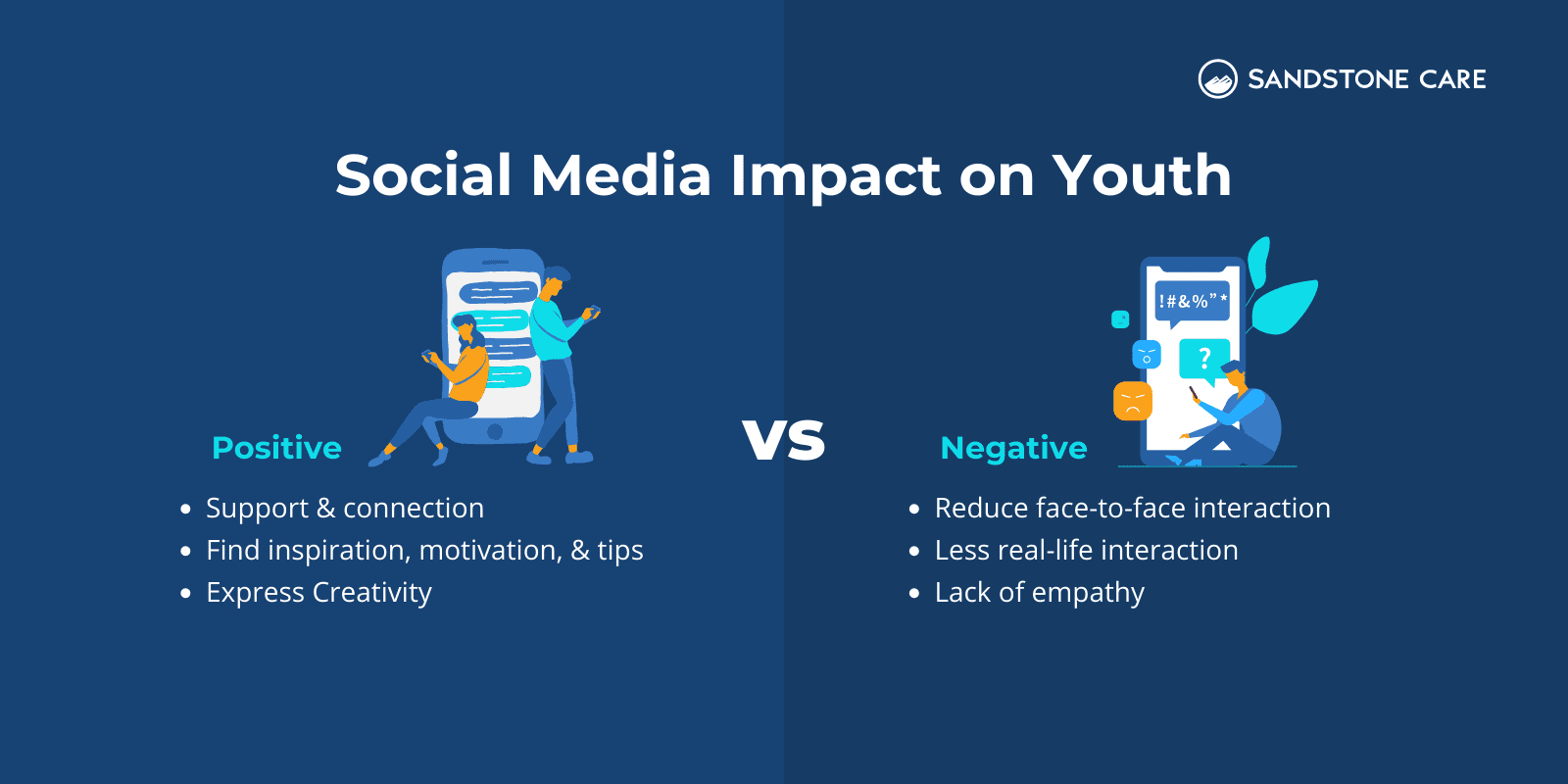
What Are The Positive And Negative Effects Of Social Media On Youth?
Now, there can be some positive sides to social media when it comes to young people.
One of the biggest is connection.
Many young people find social media as a place to find support and connection with their friends, peers, and loved ones.
Social media is where people can find inspiration, motivation, and tips and express creativity.
However, it can be easy to fall into a habit of mindlessly scrolling and consuming too much social media.
What Are The Negative Effects Of Social Media On Social Skills?
It is no surprise that social media reduces face-to-face interaction.
As people spend more time on a screen, they spend less time interacting in “real life.”
Social media and excessive internet use have created a barrier when it comes to communication and social skills. Often, on these platforms, you can see a lack of empathy and cruelty that is heightened by anonymity; people say whatever they want, even if it is harmful.
While social media can create great opportunities to connect, in-person and offline social interaction is crucial to the development and well-being of each individual, especially young people.
With social media, people are less engaged, stuck in their own bubbles, and often forget that there is a large, connected, and real world outside their electronic devices.
What Impact Does Social Media Have On A Child’s Body Image?
Scrolling on social media is constantly feeding unrealistic expectations into the minds of young people.
These artificial standards can cause a child or teen to have a negative body image, low self-esteem, and low self-worth. Having a negative body image can have drastic impacts on a teenager’s health, including increasing their risk of developing eating disorders.
Social Media, Mental Health, and Your Brain
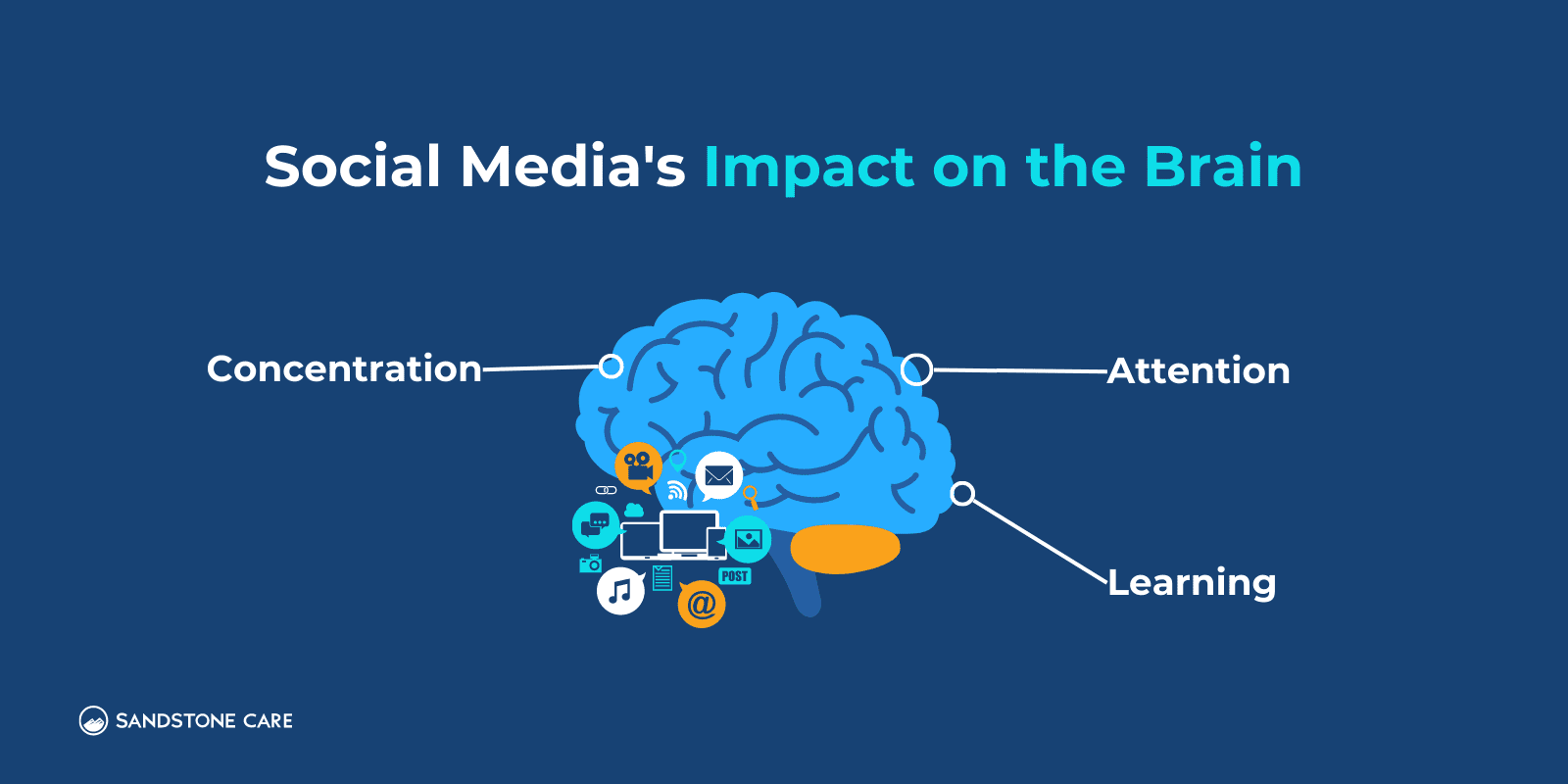
What Does Social Media Do To Your Brain?
Social media impacts the brain’s reward center, causing users to feel pleasure from checking in, scrolling, or interacting on social networking sites.
After a while, the brain seeks this pleasurable activity over and over again to the point that it can become uncontrollable.
Social media use can impact important brain functions like concentration, learning, and attention. Some research suggests that these impacts can worsen symptoms of other mental health conditions such as ADHD or social anxiety.
How Does Social Media Affect Self-Esteem?
When scrolling on social media, you are consuming the lives of others.
Images of perfect lives and faces show up repeatedly, creating this false image of what a person’s life should be or what they should look like.
The use of social media can make a person feel negative about themselves and their lives. They may start to compare themselves with their peers, feel that they are less than others, or aren’t doing enough.
Social media can take a toll on a person’s self-esteem and break down their confidence.
How Does Social Media Affect Body Image?
In a world of “influencers” and “public figures,” the standard of beauty has changed and led people to fall under the false impression that they may not be good enough because they don’t look like the people they see online.
With filters, photoshop, and the “right angles,” a false illusion of the “perfect body” is portrayed and stamped into the minds of young people.
As they look at themselves, they may question why they don’t look like the others they see all day while they are scrolling. This can hurt their self-esteem, self-worth, and self-image.
At What Point Does Social Media Use Become Problematic?
Problematic social media use happens when it starts to get in the way of your daily life, responsibilities, relationships, and mental health.
When social media use gets to a point where you can’t control it, where you feel the need to be on it, or where it is causing problems in your life, you should reach out for help.
How to Stop Social Media Addiction
Can You Recover From Social Media Addiction?
The good news is that social media addiction is treatable, and recovery is possible.
With support and guidance, you can learn ways to limit your social media use and acknowledge any underlying problems that may be a trigger or result of social media addiction.
How Do You Break A Social Media Addiction?
Different ways can help individuals break a social media addiction and recover.
One is by going through a social media cleanse or detox.
This can include limiting screen time, deleting social media apps, muting notifications, or completely stopping social media use for a set amount of days.
You can also try doing new hobbies and activities to take the place of social media habits. This can not only help distract you from the urge to check social media but also create new healthy habits to incorporate into your daily routine.
Sometimes, excessive social media use and addiction become a way for a person to cope with difficult feelings or emotions. Getting professional help and going to therapy can help a person address these challenges and learn new ways to cope.

How Long Does It Take To Recover From Social Media Addiction?
The length of time it takes for a person to recover from social media addiction is different for everyone.
What Are The Treatment Options For Social Media Addiction?
Even though social media addiction is not a recognized disorder in the DSM-5, there are many different treatment options available.
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, is a common approach to treating a variety of different mental health conditions and substance use disorders.
Interventions like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and support groups can be helpful for individuals with social media addiction.
FAQ
You have questions. We have answers.
Our goal is to provide the most helpful information. Please reach out to us if you have any additional questions. We are here to help in any way we can.
Some of the main reasons people use social media include:
- Staying in touch with friends and family
- Entertainment
- Shopping/researching products
- Staying updated on current events
- Avoid boredom
- Networking
- Date/ meet new people
- Share opinions
- Maintain a business
- Share photos and videos with others
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) does not recognize social media addiction as a mental disorder.
There is no exact amount of hours it takes on social media to be considered addictive.
Excessive social media use is typically considered anything over 2 hours a day.
To gauge how addictive social media has become, you should look more at how negatively it is impacting a person’s life, health, and well-being rather than the amount of time a person is spending on it.
Some people do a 5-day social media detox, while others may even go a year or more without social media.
Commonly, a social media detox is 30 days, when you completely stop social media use and consumption.
There is no set amount of time a social media detox has to be.


Let’s take the next steps together
Excessive social media use can lead to addiction and other harmful effects, especially in young people. Sandstone Care is here to support teens and young adults with mental health and substance use disorders.