Neurotic Definition
Neurotic Meaning
What Does Neurotic Mean?
Neurotic is a term that describes someone who always feels stressed, worried, or emotionally tense. Sometimes it can refer to symptoms from mental health conditions like anxiety.
People with this trait might have frequent mood swings, overthink problems, or struggle with self-confidence.
While being neurotic isn’t a mental illness on its own, it can be a symptom of a mental health issue.
Having neurotic behaviors can also make someone more vulnerable to developing mental conditions later on, since it can be emotionally draining.
In the past, the term was used in psychology as an official diagnosis to describe a wide range of emotional issues, but it no longer refers to a specific condition.
Today, professionals are more likely to use specific terms like “anxiety disorders” or “mood disorders” instead.
What Is a Neurotic Personality?
A neurotic personality is when somebody experiences intense emotional reactions and constant worry, even over small things that would not normally deserve such a strong response.
For example, someone with neurotic tendencies might obsess over a work presentation, imagining every possible way it could go wrong, even if it is a low-stakes situation that they are well prepared for.
This trait makes them more likely to interpret ordinary situations as threatening and minor frustrations as hopelessly difficult.
Since someone with a neurotic personality may feel overwhelmed by small things, having a neurotic personality can make it difficult to handle the responsibilities of everyday life.
Individuals with a neurotic personality type may also struggle with emotional instability.
Their feelings can fluctuate rapidly; they might feel content one moment and overwhelmed by despair or anger the next.
This can be puzzling not only to the individuals themselves but also to those around them, who might find these sudden emotional shifts difficult to understand.
What Is at the Root of Neuroticism?
Root causes of neuroticism can include genetics, family history, relationship dynamics, or trauma. However, there is not one single root cause to explain neuroticism overall.
Things like early attachment issues can also play a role. If a child grows up with neglectful or overly critical caregivers, they might develop a heightened sensitivity to stress.
Sometimes this is called helicopter parenting.
Since they often did not understand why they were harmed as a child, it can make it difficult to accurately determine whether or not they are in a truly dangerous situation.
Negative thought patterns and a lack of healthy coping strategies can reinforce these traits, which makes it even harder to manage emotions as they get older.
What Are Neurotic Disorders?
The term neurotic disorder is used to describe multiple minor psychiatric conditions such as anxiety, depression, and panic disorders.
Unlike trait neuroticism, which is just a way to measure how people respond emotionally to different things, neurotic disorders can make it difficult to have relationships or achieve life goals.
What Is Trait Neuroticism?
Trait neuroticism is simply a part of someone’s personality where they tend to feel negative emotions like stress or worry more often than others. It’s a normal variation and doesn’t necessarily mean there’s a bigger problem.
Neurotic disorders, on the other hand, are serious mental health conditions where feelings of anxiety or sadness are so intense and frequent that they interfere with a person’s everyday life and functioning.
For example, someone with trait neuroticism may be more nervous when they are driving on a road trip, but someone with a neurotic disorder might feel that they cannot make the trip at all without having a panic attack.

What Is a Neurotic Person?
A neurotic person is someone who shows signs of neuroticism, such as emotional instability and reacting strongly to stressful situations.
A person who is neurotic commonly experiences anxiety, depression, irritability, and self-consciousness. It is also common for a neurotic person to interpret common situations as threatening. This can make them feel overwhelmed easily.
They may also suffer from rejection sensitive dysphoria.
Someone with low neuroticism stays calm during a crisis, such as missing a work deadline.
They don’t get too upset and can quickly move past it. Their brain is better at regulating emotional responses, allowing them to remain stable and think clearly under pressure.
On the other hand, someone with high neuroticism feels stress more intensely; missing the same deadline might make them feel very anxious or frustrated.
Their brain tends to amplify these stress signals, making it harder for them to shake off negative feelings, which can linger and make it difficult for them to get other things done.
Sometimes one situation or experience can derail a person with neurotic behaviors for days as they try to recover.
The reactions and feelings of a person who is neurotic are not by choice. They are thought patterns and feelings that are not under their control.
What Is An Example Of A Neurotic Person?
An example of a neurotic person may be a family member who constantly assumes they are being criticized, or that family plans are going to go horribly wrong.
When a person is neurotic, they are emotionally unstable, making them more likely to respond to situations with anger or irritation.
They are likely to experience and express negative emotions and appear anxious or depressed.
Self-consciousness is also common for people who are neurotic. This looks different for each person but can make someone shy, nervous, or reactive emotionally.
Therefore, an example of a neurotic person is someone who struggles to cope with stress and is highly reactive.
What Is Neuroticism in Psychology?
In psychology, the term “neuroticism” comes from the early 20th-century idea of “neurosis,” used by Sigmund Freud to describe mental and emotional disturbances. However, the term now refers to a broader personality trait of being overstressed.
Over the years, as psychology moved away from Freud’s theories, neuroticism became part of the Big Five personality model, which uses it to describe how prone someone is to experiencing negative emotions like anxiety or sadness.
Today, psychologists use neuroticism to help understand differences in how people handle stress and emotions. High levels of neuroticism can indicate a greater risk of mental health issues, and it’s a key factor in psychological assessments and therapeutic approaches.

Neurotic Behavior
What Is Neurotic Behavior?
Neurotic behavior stems from deeply rooted conscious or unconscious anxiety. They may include angry outbursts, perfectionism, or anxiety attacks.
These behaviors, first studied in the 1700s, are difficult to control and often seem irrational or dramatic to others, but they automatically arise when an individual is presented with a real or perceived situation that triggers a personal fear.
What Are Neurotic Behavior Examples?
A person who is neurotic will experience anxiety or panic in ordinary and safe situations. For example, neurotic behavior includes panicking or intense anxiety when grocery shopping or at a family dinner.
While these are ordinary events for many, they often feel stressful and threatening for a person who is neurotic.
Other examples or neurotic behavior include:
- Excessive Worrying
Someone with a neurotic personality might repeatedly check the weather forecast and pack multiple outfits for every possible condition before a simple day trip, constantly worried about being unprepared. - Mood Swings
A person might start their morning feeling cheerful and optimistic, but after a brief, mild critique from a coworker, they become irritable for the rest of the day. - Emotional Outbursts
During a routine discussion about household chores, someone might suddenly burst into tears or become extremely angry when the topic of who has what responsibility is brought up. - Perfectionism
While preparing a meal for friends, a person might become fixated on the presentation of the dishes, adjusting the garnishes obsessively and becoming frustrated if everything isn’t aligned perfectly. - Avoidance of Social Situations
A person might decline an invitation to a movie night with friends out of a preoccupying fear that they’ll have to sit in the middle and bother others if they need to leave the row during the show.
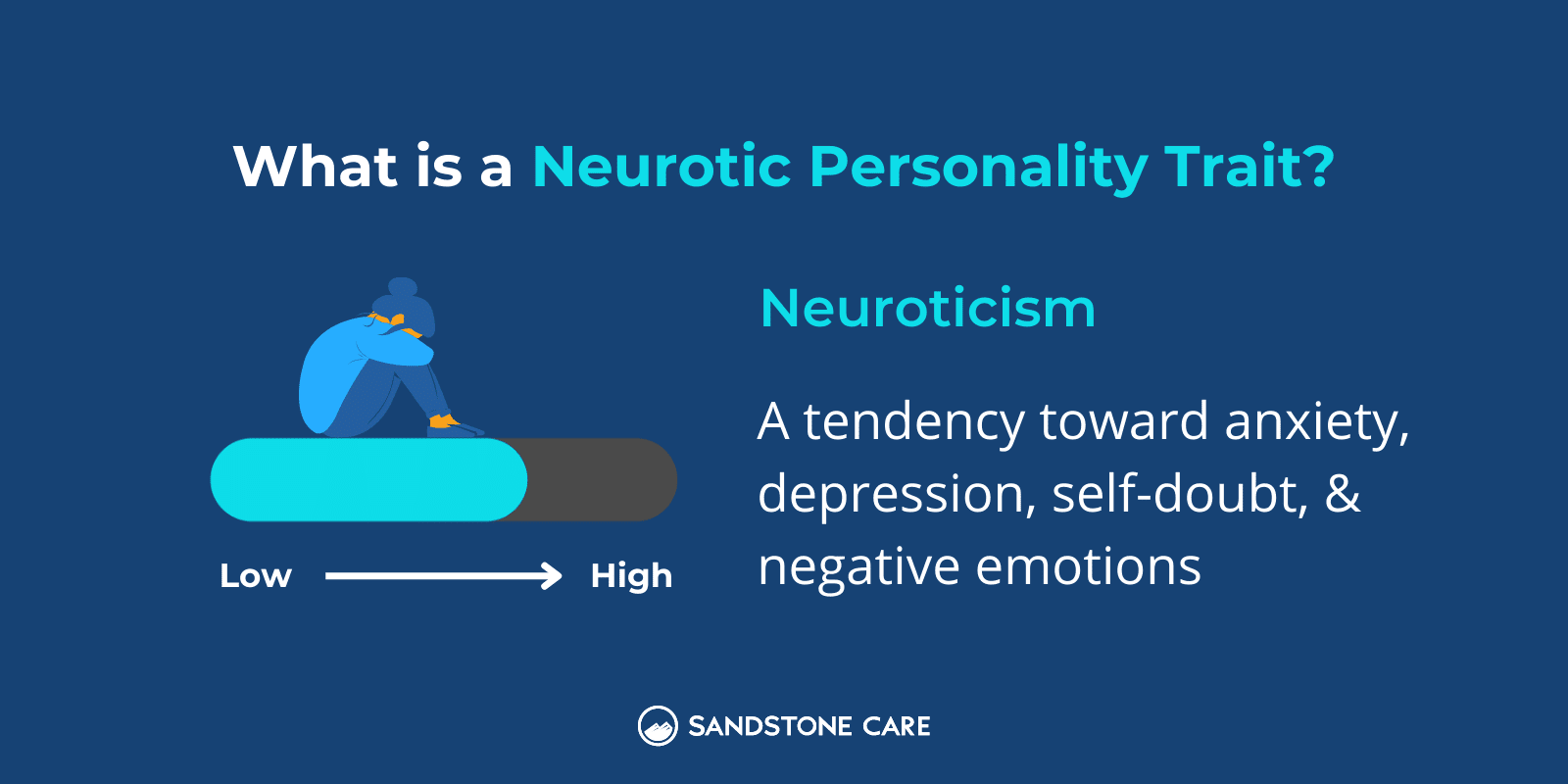
What Causes a Person to Be Neurotic?
Some causes that can drive a person to be neurotic include:
- Family history
- Traumatic experiences
- Mental health conditions like anxiety
- Social experiences like bullying or child abuse
Mental disorders, mental illnesses, or mood disorders can also cause neurotic behaviors.
If a person is displaying neurotic behavior, it can also be a combination of multiple factors listed above.
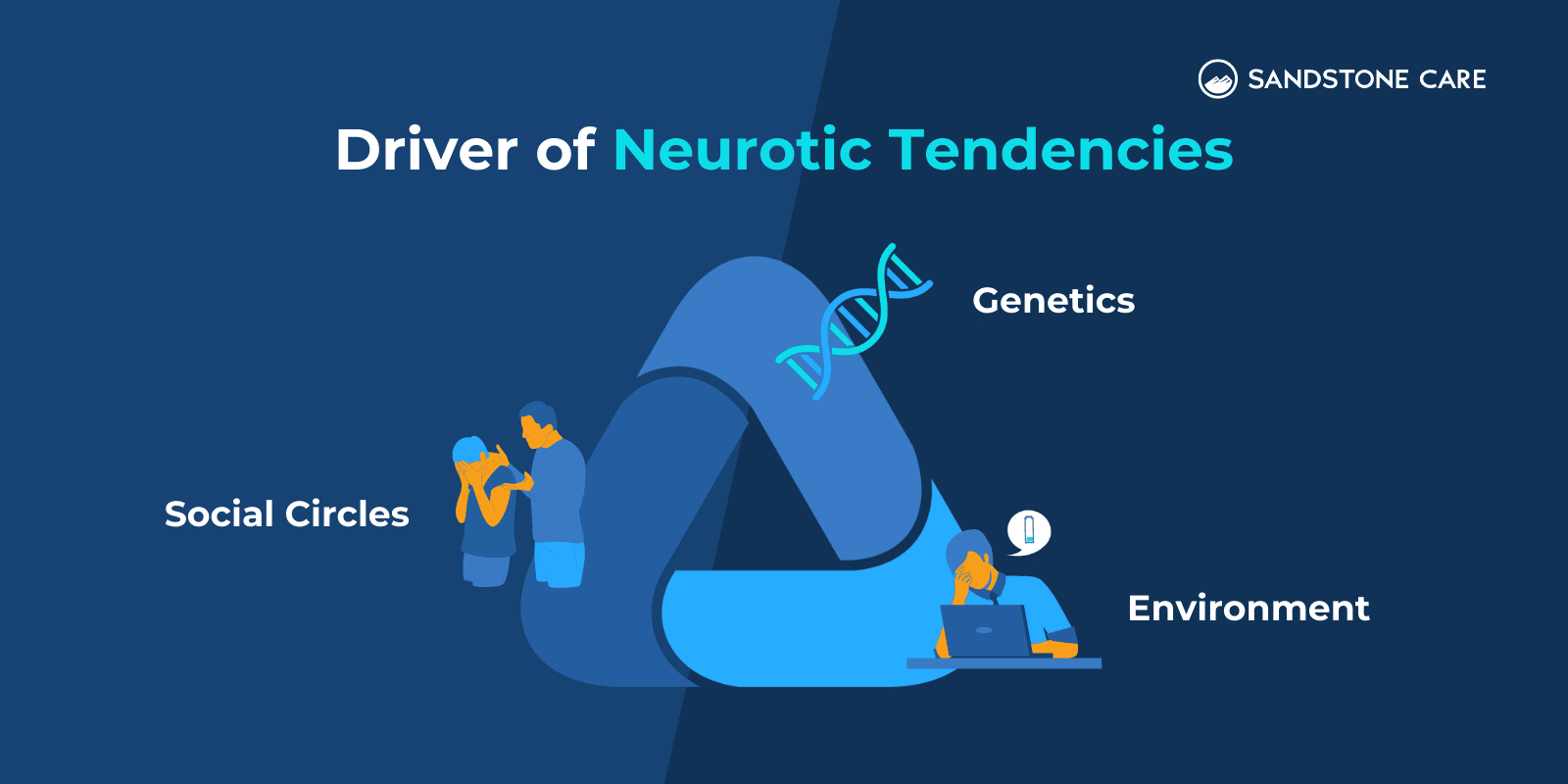
What Drives Neurotic Tendencies?
There are multiple drivers of neurotic tendencies. Each person who tends towards neurotic behaviors is influenced by their environment, social circles, and genetics.
However, a person’s mental health influences their personality, including neurosis. Research shows it is a common comorbidity with many mental health disorders and physical illnesses. Therefore, their mental health or physical health can be a primary driver for neurotic tendencies.
A person who tends towards being neurotic might also be influenced by stress or be overworked. These both increase a person’s anxiety and can lead to neurosis. Therefore, lifestyle changes can help decrease neurosis for some people.
Neurotic Personality Symptoms
What Are the Signs and Characteristics of a Neurotic Person?
Signs of a neurotic person may include:
- Having large mood swings
- Reacting strongly to everyday situations
- Feeling paranoid over upcoming events
- Having low self esteem
- Getting caught in a “loop” of arguments and thoughts
A person who is neurotic will often experience and express negative emotions like anger or irritation. They are likely to react negatively to stress and overreact in situations with little to no stress. Therefore, they can come across as moody or unstable.
Another key sign of a neurotic person is low self-esteem. Depending on the person, this might be expressed as self-doubt or acting self-consciously.
A neurotic person commonly experiences obsessive thought patterns. While these might be expressed or internalized depending on the individual, it often looks like making the same statement or argument multiple times.
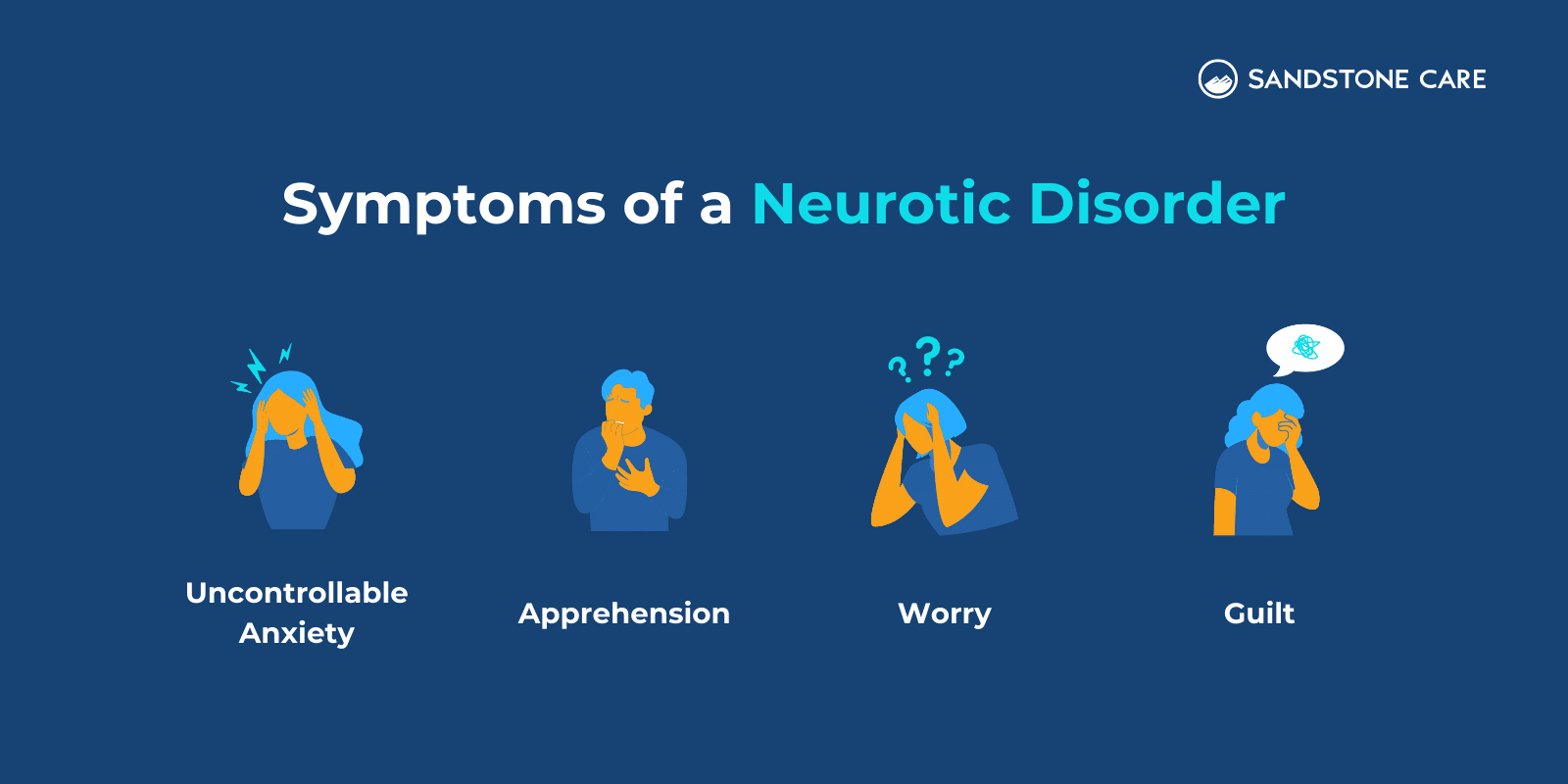
What Are the Symptoms of a Neurotic Disorder?
Symptoms of a neurotic disorder include uncontrollable anxiety, apprehension, worry, and guilt.
They may also include:
- Poor Stress Reactions
They might react more strongly to stress, feeling quickly overwhelmed or upset by small problems. - Emotional Instability
Their emotions can change rapidly, going from happy to sad or angry with little or no cause. - Obsessive Thoughts
They often have unwanted thoughts that they can’t shake, which might lead them to repeat certain actions, like washing hands or checking if the door is locked, to ease their anxiety.
For example, someone with neurotic anxiety might feel a disproportionate level of fear about being late for an appointment, leading to panic attacks or extreme distress that disrupts their ability to function normally in that moment.
What Are Common Neurotic Traits?
Some common neurotic traits include moodiness and constant worry.
They are also likely to struggle with perfectionism, wanting to make everything a certain way to reduce stress. This is a result of having very little ability to manage stressful situations.
Another common neurotic trait is rumination, where a person repeatedly thinks or talks about something. An example is a person who goes over their packing list multiple times to make sure they have everything.
How Do Neurotic People React To Stress?
People who are neurotic tend to struggle with stressful situations and have a low tolerance for stress.
Their reactions are often over the top and do not fit the circumstance at hand. They are likely to be quick to anger, irritable, and unstable emotionally with small stressors.
Neurotic Anxiety

What Is Neurotic Anxiety?
Neurotic anxiety is a specific type of anxiety that’s more intense and persistent than the everyday anxiety people commonly experience.
It’s important to distinguish from regular anxiety because it can severely disrupt someone’s daily life. While regular anxiety might arise from obvious stressors and usually fades away, neurotic anxiety can linger and feel overwhelming without a clear reason.
For example, someone with neurotic anxiety might worry excessively about something minor, like a casual meeting with friends, imagining disastrous outcomes that are very unlikely to happen.
They might feel physical symptoms too, such as stomach aches or a pounding heart, which are more severe than what you’d expect from just nerves.
Understanding the difference between neurotic anxiety and regular anxiety is crucial because neurotic anxiety may require specific treatment approaches, such as therapy or medication, to manage its symptoms and prevent it from taking over a person’s life.
What Is The Difference Between Anxiety And Neurotic Anxiety?
Anxiety is a healthy and normal reaction for people when worried about an important meeting or conversation that is coming up.
However, neurotic anxiety is the opposite of healthy anxiety. It is an overreaction to the situation that is often persistent after the cause of anxiety has passed. This is because a person with neurotic anxiety has a low tolerance for stress and frustration due to overestimating threats or problems that occur.
What Is A Neurotic Anxiety Example?
An example of a person with neurotic anxiety is a perfectionist.
A person with perfectionist tendencies is never satisfied, constantly feeling the need to achieve, and always thriving for something they should or could do. Healthy anxiety can help a person to make improvements. However, a person with neurotic anxiety is compulsive about making continual changes and achievements.
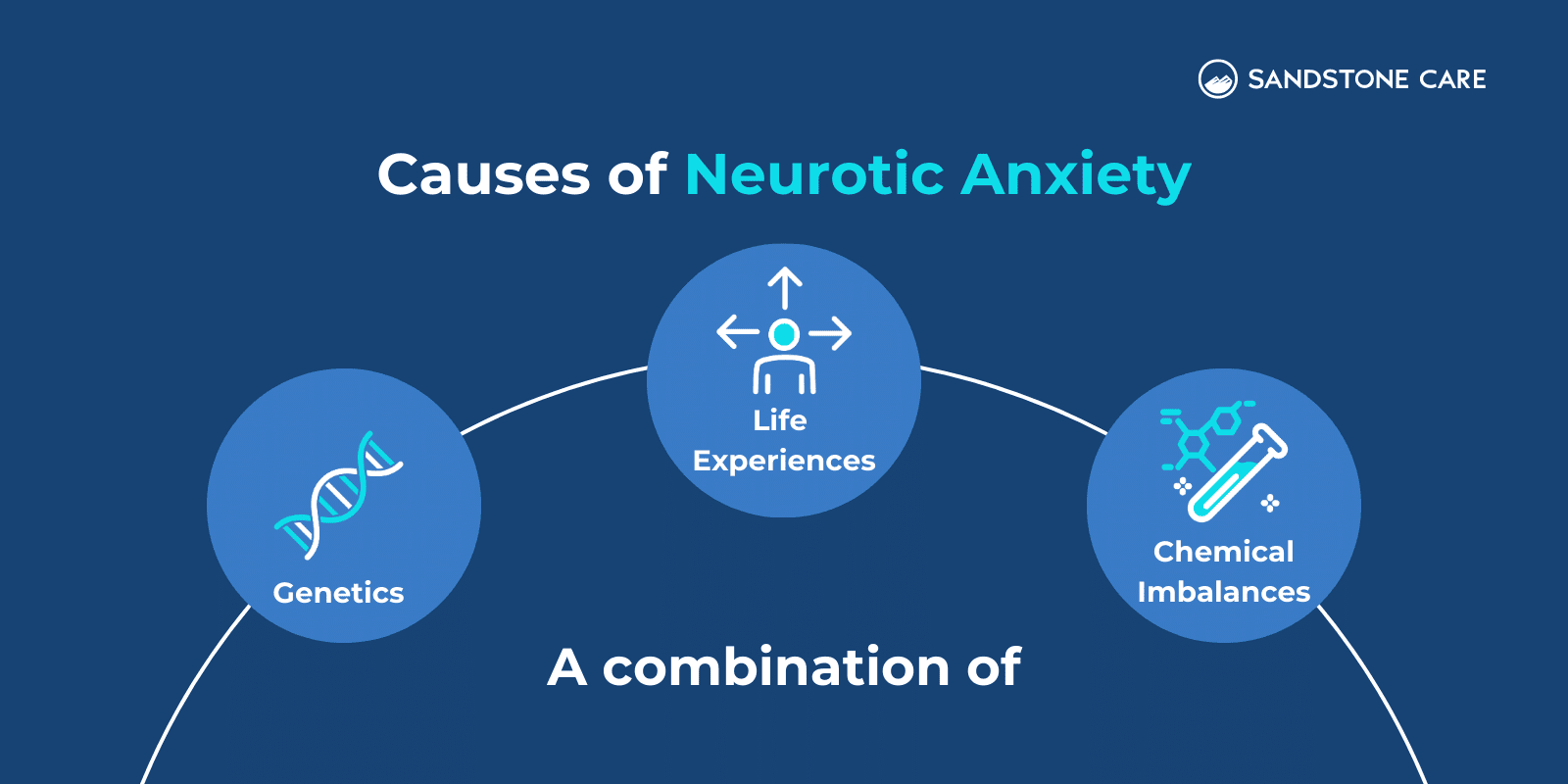
What Is The Basic Cause Of Neurotic Anxiety?
The basic cause of neurotic anxiety is a combination of genetics, life experiences, and chemical imbalances.
However, the cause of neurotic anxiety will vary for each person.
How Do You Overcome Neurotic Anxiety?
People with neurotic anxiety can overcome it. Like other types of anxiety, it is highly treatable through a trusted mental health treatment facility.
Overcoming neurotic anxiety often includes treatments like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and lifestyle changes that benefit a person’s overall well-being. Through these changes, a person can build a life that helps them to overcome neurotic anxiety.
However, treatment has many individual differences. Working with a healthcare professional helps people to discover the most effective steps to overcome neurotic anxiety.
How Long Does Anxiety Neurosis Last?
The length of anxiety neurosis will vary for each person, depending on the cause.
When a person has untreated mental health disorders, anxiety neurosis will last longer.
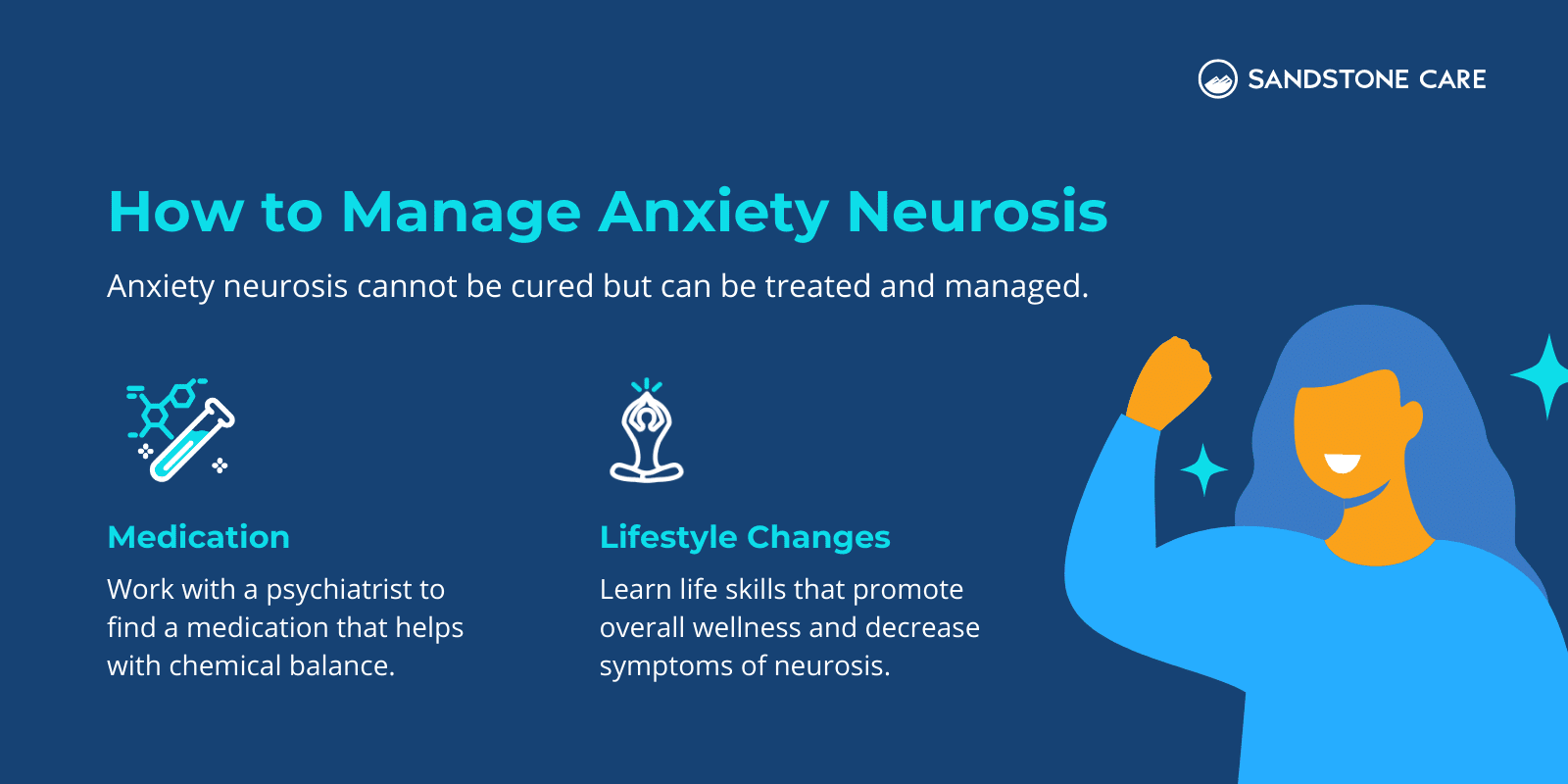
Can Anxiety Neurosis Be Cured?
Anxiety neurosis cannot be cured, but it can be treated through medication, therapy, and more.
Through treatment, people work with a psychiatrist to find a medication that helps to find chemical balance. Additionally, people can learn how to make lifestyle changes that provide overall wellness and decrease symptoms of neurosis.
How To Deal With A Neurotic Person
How Do You Deal With Neurotic People?
When dealing with a neurotic person, it is helpful to understand that high neuroticism is based on anxiety.
Therefore, if a person’s friend is neurotic, they can be gentle and supportive of them. This might look like helping them to feel comfortable in a situation by reassuring them they are safe. Reassurances can be verbal or physical to help a person feel comfortable and safe.
However, people who are neurotic are responsible for themselves. Therefore, a person can give a neurotic person space if they are reacting with anger or hostility, which will protect them from these reactions.
Are Neurotic People Toxic?
Neurotic people are often seen as toxic, but they are not inherently toxic.
Neuroticism is a personality trait that can have many benefits. A neurotic person who is healthy is likely to be cautious, plan for the future, and be a conservative decision-maker. This can be very effective and helpful in many personal and professional relationships.
However, a neurotic person who is not healthy might be toxic. This will depend on the level of neuroticism and how that person manages their mental health.

Is It Mean To Call Someone Neurotic?
Calling a person neurotic generally refers to their reactions. A neurotic person has dramatic and irrational physical, mental, and emotional reactions.
What Are The Effects Of A Neurotic Person On Society?
Neurosis has many public health implications, as it increases a person’s risk for many co-occurring and chronic mental and physical disorders.
Additionally, neurotic people impact those they spend time with. However, the effect they have will depend on how their mental health and neurosis are managed.
An unhealthy person who is neurotic is often toxic. However, a person who is neurotic and healthy can be a wonderful addition to a home and workplace.
Neurosis Diagnosis
Is Neurotic Disorder In The DSM?
The neurotic disorder is not in the DSM; it was eliminated in 1980. However, neuroticism is listed in the DSM as one of five personality traits.
How do you diagnose neurotic personality disorder?
Neuroticism is a trait that is part of two personality disorders, including borderline personality disorder (BPD) and antisocial personality disorder (ASPD).
As a personality trait, it is characterized by obsessive thinking, anxiety, distress, and dysfunction in daily tasks.
How Do I Know If I’m Neurotic?
Working with a mental health care professional is the best way for a person to learn if they are neurotic.
However, common traits include a tendency towards negative emotions, anxiety, mood swings, and low self-esteem. These traits can be self-identified or identified by a loved one.

What Is The Big 5 Trait Of Neuroticism?
The big five personality traits include extroversion, agreeableness, openness, consciousness, and neuroticism.
Neuroticism is defined as a tendency to experience anxiety, depression, self-doubt, and other negative feelings. As a personality trait, people have neuroticism at different levels, and it can appear differently depending on the combination of other personality traits they have.
What Is Emotionality?
Emotionality is a way to measure how quickly and strongly a person reacts to things emotionally.
It covers how sensitive someone is to emotional situations, how intense their feelings are, and how they show and handle these emotions.
Some people might react very strongly and openly to things that happen to them, while others might keep their feelings more contained or not react as much.
In psychology, this concept helps us understand why people behave differently in the same situation.
People with high emotionality might feel and show joy, sadness, or anger more vividly than others. This trait affects things like how someone makes decisions, manages relationships, and copes with stress, all of which are important for their overall mental health and happiness.
What Is Negative Emotionality?
Negative emotionality is a personality trait that describes a person’s tendency to experience negative emotions more frequently and intensely than others.
This trait is similar to neuroticism in that it encompasses feelings such as sadness, anger, anxiety, and irritability.
People high in negative emotionality react more strongly to stress and are more likely to perceive situations as threatening or hopelessly difficult.
Is Neuroticism Related To IQ?
Neuroticism, like other personality traits, is related to IQ.
Research has people with high neuroticism tend to have lower IQs. However, a person’s IQ is also correlated with other personality traits. Therefore, every person is unique in their IQ and combination of personality traits.
Neurosis Treatment
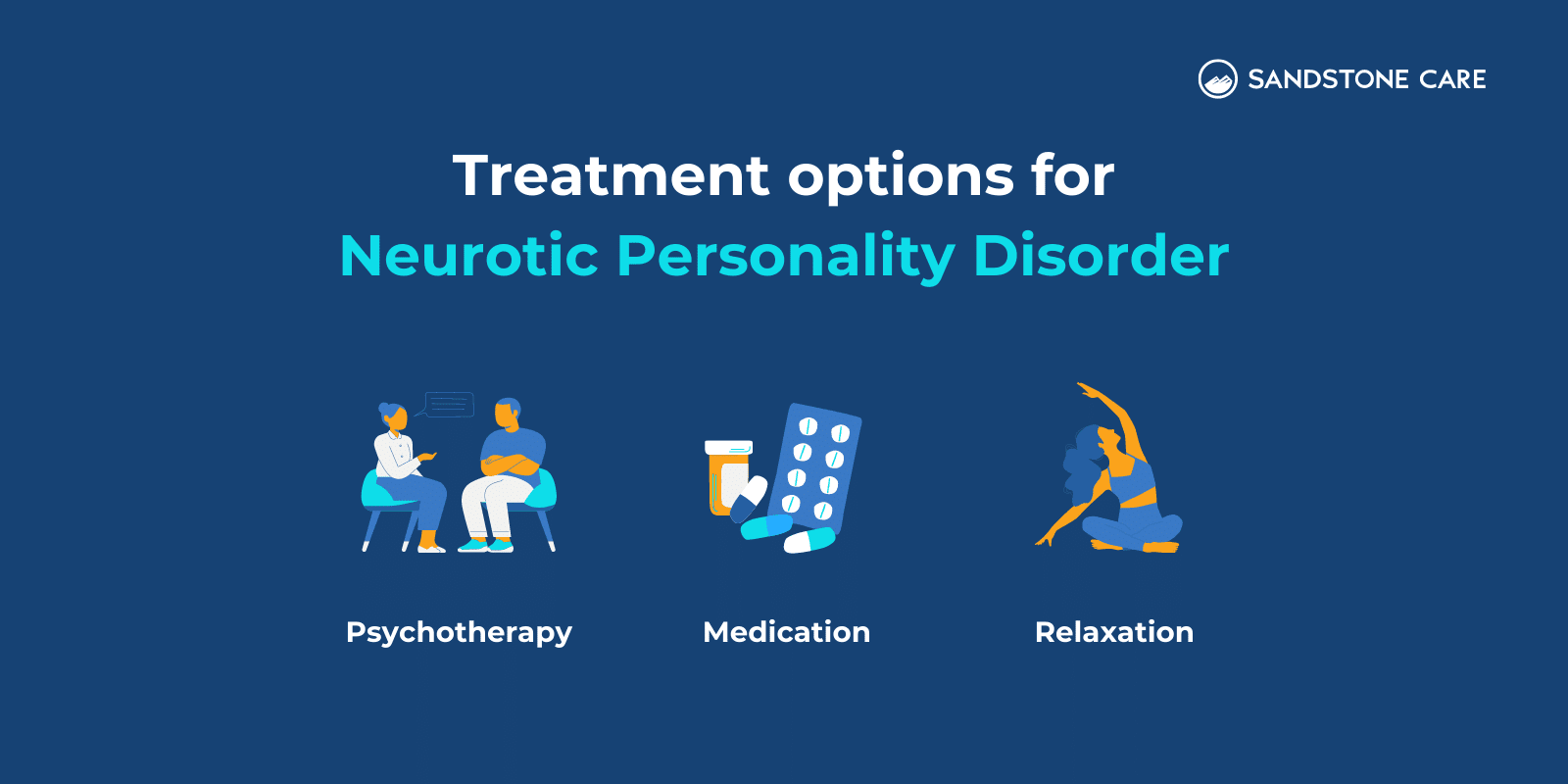
What Is The Best Treatment For A Neurotic Personality Disorder?
The best treatment for neurotic personality disorder often involves psychotherapy, where talking with a therapist can help someone understand and manage their emotions and behaviors more effectively.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy, for example, is widely used because it helps people change negative thoughts and behaviors into more positive ones.
Medication like antidepressants might also be recommended if symptoms are severe, particularly if they include anxiety or depression.
In addition to therapy and medication, learning relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation can help manage stress and anxiety symptoms.
Making changes in daily routines, like adding regular exercise and improving sleep habits, can also make a significant difference in managing the disorder.
Can Someone Stop Being Neurotic?
Many people are neurotic due to a combination of factors, including genetic and environmental.
Therefore, someone can decrease neurotic behavior. However, they may be predisposed to neuroticism but can be healthy and functional.
How Do You Overcome Neuroticism?
Overcoming neuroticism is possible by learning healthy coping skills.
However, a certain level of neuroticism will likely remain part of a person’s personality. A person can adjust their behavior and reactions to stress, building more tolerance to frustration. Healthy coping skills can help a person to benefit from the positives of neuroticism.
How To Be Less Neurotic:
- Improve awareness: A person who is neurotic has neurotic thinking patterns and behaviors. Being mindful of these patterns gives them a better understanding of their feelings which helps them to feel more in control.
- Learn relaxation techniques: When a person is neurotic, they are very sensitive to stress. However, there are many ways to help themselves to relax, including breathing techniques.
- Acceptance: It is only when someone accepts that they have neurotic patterns that they can interrupt them. Therefore, acceptance is key to learning to be less neurotic.
- Exercise: For people who are neurotic, exercise is very important. It is a way to improve overall health, improve chemical balance, and release extra energy.
- Self-care: A person who is neurotic commonly struggles with other mental or physical health issues. Learning to care for themselves can help decrease neurotic behavior. This might include medication, lifestyle changes, and therapy.