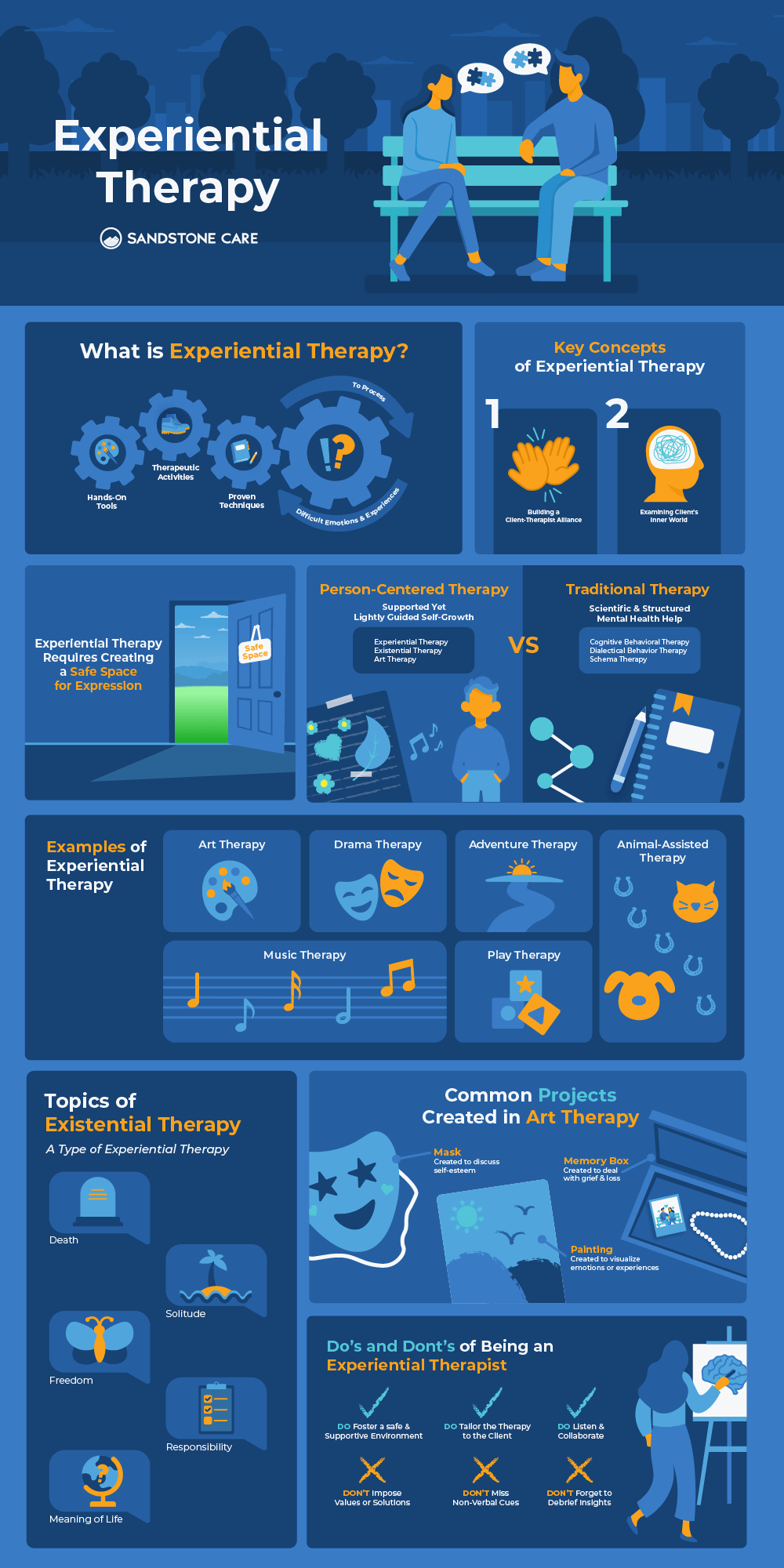
What Is Experiential Therapy?
Experiential therapy uses hands-on tools, activities, and techniques to help a person navigate and process difficult experiences and emotions.
This form of therapy can include role-playing, music, art, acting, animal care, and other recreational activities to process certain emotions.
Experiential therapy can be used to help treat a wide range of mental health conditions and challenges that can include trauma, eating disorders, behavioral disorders, grief, and much more.
What Are the Key Concepts of Experiential Therapy?
Experiential therapy focuses on two key concepts: the relationship between the therapist and the client, and the examination of the client’s inner world.
The first key concept emphasizes the relationship between the experiential therapist and the individual. Also known as the therapeutic alliance, the relationship between the therapist and the individual can significantly impact the success and outcome of therapy.
The second main concept of experiential therapy is the examination of the client’s beliefs, values, feelings, and perceptions.
Experiential therapy treatment plans should help the individual have experiences that allow them to look within themselves and begin problem solving.
What Type of Therapy Is Experiential Therapy?
Experiential therapy is a hands-on form of therapy.
It is an approach to psychotherapy, or talk therapy, that uses immersive tools to help with emotional processing. Different types of experiential therapy may focus on different therapy methods, such as creative expression or animal relationships.
Is Experiential Therapy Evidence-Based?
Experiential therapy refers to a wide variety of different types of therapy.
Some interventions that fall under experiential therapy are more studied than others.
For example, research shows that music therapy can be beneficial both physically and mentally. Studies done with individuals with mental health disorders show improvements in mental health using music therapy.
Experiential Therapy Benefits
What Are the Benefits of Experiential Therapy?
Some of the benefits that can come with experiential therapy include:
- Helping a person process difficult or painful memories and experiences
- Improving interpersonal relationships
- Cope with difficult or negative emotions
- Let go of guilt and shame
- Stress relief
- Treating substance abuse
Who Can Benefit From Experiential Therapy?
Experiential therapy can be beneficial for individuals who have:
- Trauma or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Experienced loss or are grieving
- Eating disorders
- Substance use disorders
- Behavioral disorders
- Anger
- Compulsive behaviors
- Low self-esteem
Is Experiential Therapy Person-Centered?
Person-centered experiential therapy focuses on the individual and their unique experiences and perspectives.
With person-centered experiential therapy, the individual leads their own experiences with the help of the therapist.
Many experiential therapies are considered person-centered because they encourage the individual to reflect and facilitate change for themselves rather than being “fixed” by someone else.
What Are the Cons of Experiential Therapy?
Some of the cons that can be associated with experiential therapy include:
- Cost
Experiential therapy is considered a holistic approach to treatment and may not be covered by insurance. Additionally, experiential therapy can be expensive, especially when paying out of pocket.
- Research
Since various forms of therapy fall under experiential therapy, some of them might not be as studied and backed by evidence as others. If you are looking into experiential therapy, look for information that focuses on the specific form of therapy you are interested in.
One important way to address the cons of experiential therapy is by talking to your insurance provider, healthcare provider, and the treatment center you are considering to see what is covered and what options are available for you.
Experiential Therapy Techniques
What Are the Three Phases of Existential Therapy?
Existential therapy is a form of experiential psychotherapy that addresses anxieties and internal conflict caused by the human experience regarding solitude, death, freedom, responsibility, and the meaning of life.
The three phases of existential therapy include:
- Identification and clarification
- Self-exploration and examination
- Application
Is EMDR Experiential Therapy?
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a form of experiential therapy that is most commonly used to help individuals with trauma process past experiences and manage difficult emotions and stress.
EMDR is a validated form of psychotherapy used to help individuals with trauma or difficult life experiences.
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing involve side-to-side stimulation, typically eye movements, while focusing and recalling traumatic memories. This stimulation can help a person process and uncover certain details and feelings associated with their trauma to help them understand and heal from their experiences.
Is EFT an Experiential Therapy?
Emotion-focused therapy (EFT) focuses on the role of emotion in changes through psychotherapy.
EFT is considered an experiential therapy approach by the American Psychological Association.
In EFT, emphasis is placed on becoming aware of one’s emotions, understanding them, and accepting them to help a person find change.
Experiential Therapy Activities
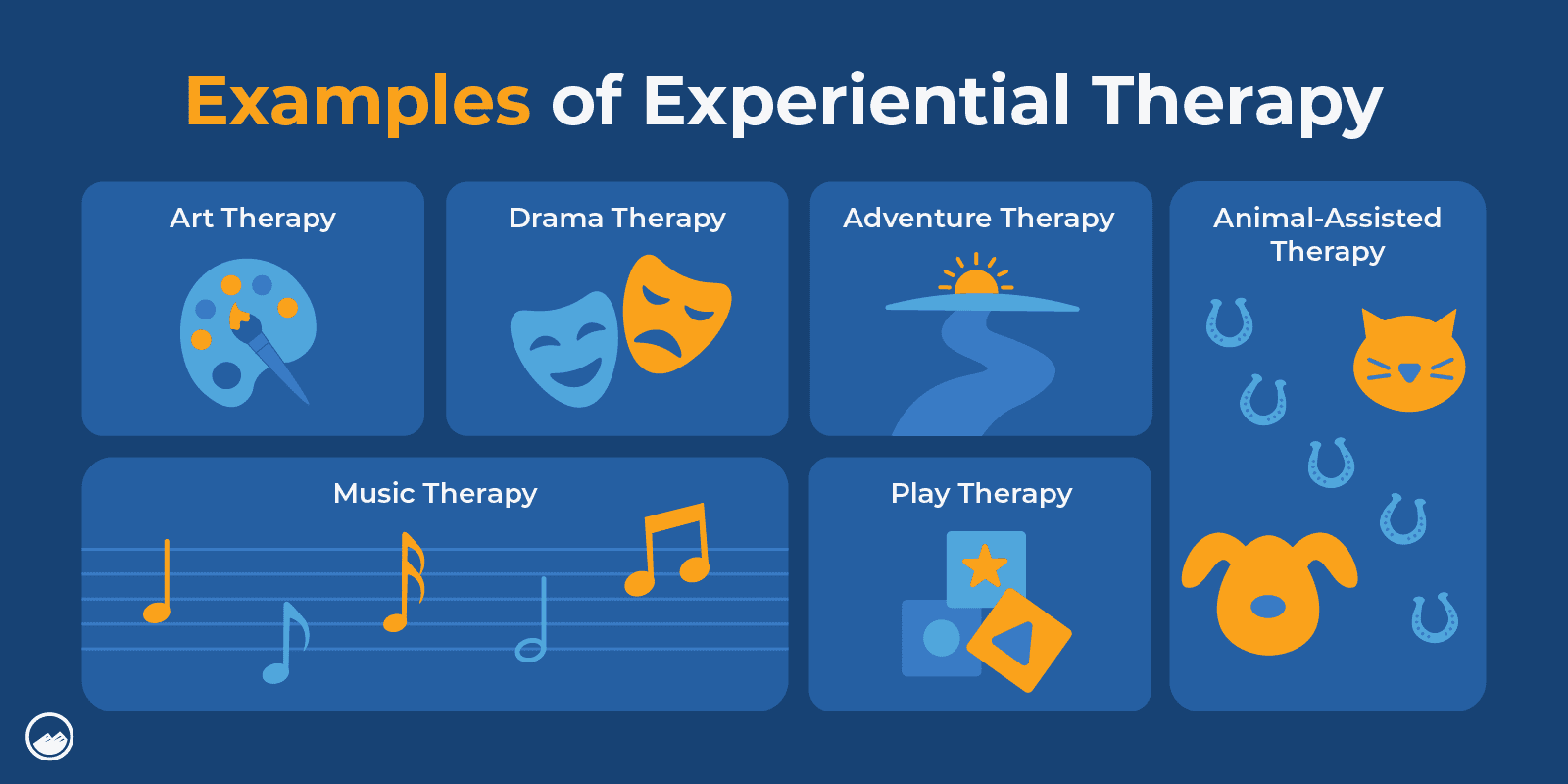
What Are Examples of Experiential Therapy?
Common examples of experiential therapy can include:
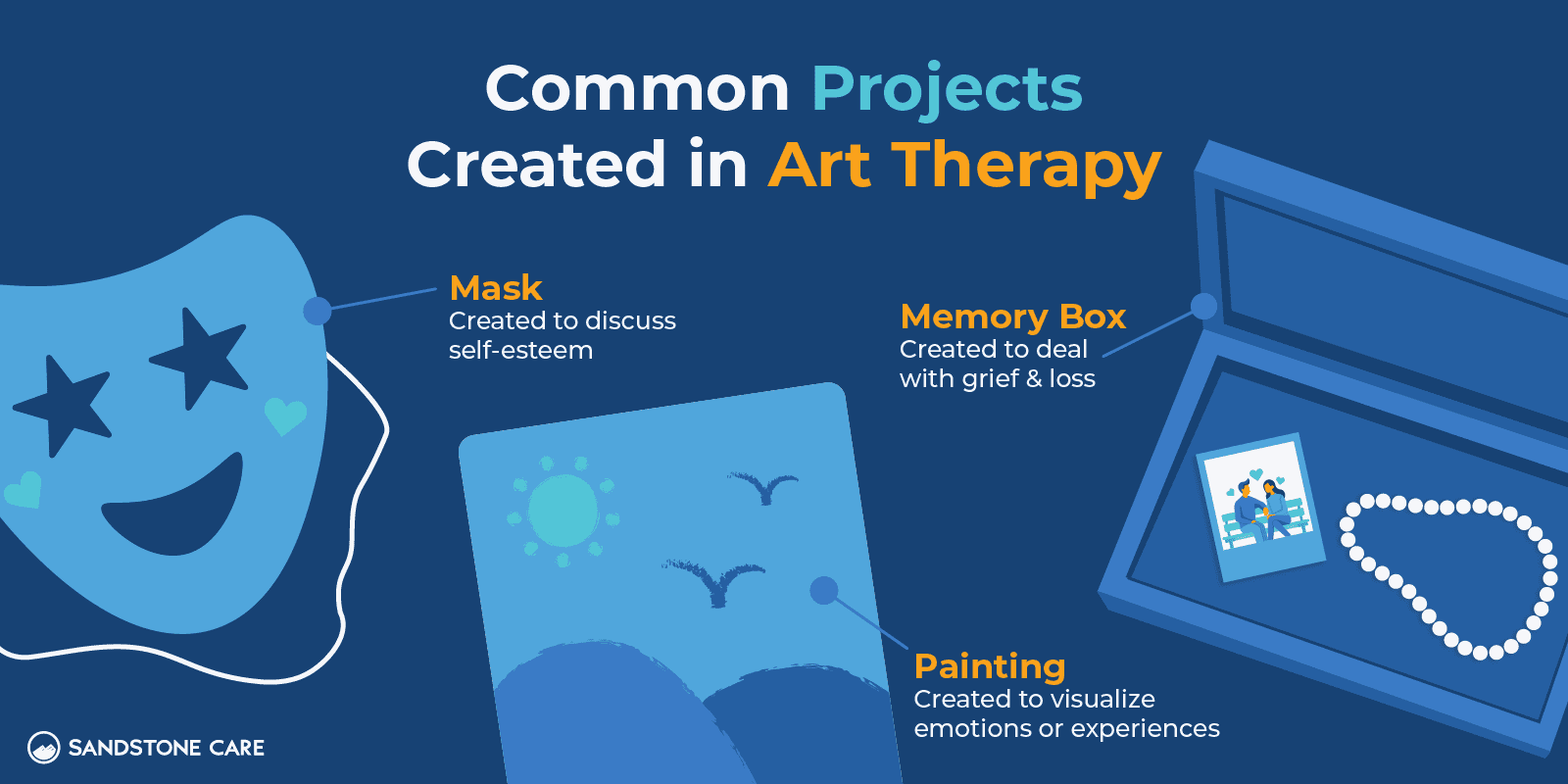
- Art therapy
In this form of therapy, creative processes are used to help increase awareness of the present moment and to also process and understand difficult feelings and experiences. Common examples of art therapy can include drawing, painting, or sculpting.
- Music therapy
Music can help with stress relief and improve one’s mental and physical health.
- Animal-assisted therapy
Spending intentional time with animals, commonly dogs and horses, can promote healing and give a person a sense of companionship, responsibility, and comfort.
- Equine-assisted therapy
Equine-assisted therapy is a common form of animal-assisted therapy where individuals can spend time caring for horses and doing other activities with them.
- Adventure therapy
Outdoor therapy can include wilderness therapy and adventure therapy, where individuals go on excursions and do outdoor activities or therapy sessions.
- Play therapy
Most commonly done with children and adolescents, play therapy can help people work through challenges through engaging activities.
- Drama therapy
Also referred to as psychodrama, drama therapy involves reenacting difficult situations in a safe setting to help a person process it and better understand the feelings that come along with it.
What Are Experiential Exercises?
Experiential exercises can involve activities, role-playing, or simulation to get a person involved and allow them to have their own experiences.
They also include tools and techniques to help a person find the best way to change for the better.
Examples of experiential exercises and activities can include games, role-playing, trips, expeditions, writing, or other hands-on and immersive activities.
Experiential Group Therapy
What Is Experiential Group Therapy?
Experiential therapy can be done in both an individual and group setting.
In experiential group therapy, individuals come together and take part in group activities as a whole while still gaining their own unique, individual experiences.
How to Teach Experiential Therapy to a Group?
In experiential group therapy, each individual is unique and has their own experiences.
Teaching experiential therapy to a group means helping facilitate these experiences and understanding that each person is getting something different out of the experience.
When experiential therapy is taught to a group, it can involve activities such as art, adventuring, role-playing, or other hands-on activities.
A leader or therapist for experiential therapy will facilitate these activities and collaborate with the individual while also allowing them to take the lead and have control of their experience.
Experiential Family Therapy
What Is Experiential Family Therapy?
Along with individual and group experiential therapy, there is also experiential family therapy.
Mental health challenges and substance use disorders can impact a family both as individuals and as a whole.
Navigating the worlds of addiction treatment, outpatient mental health programs, and other psychiatry solutions can be overwhelming. Family therapy helps the family heal together in one setting, rather than isolating one individual.
Experiential therapy can help promote growth and change within a family and improve interpersonal relationships.
When Do You Use Experiential Family Therapy?
Experiential family therapy can be helpful when a mental health condition or substance use disorder is present in a family member or multiple family members.
It can also be helpful for family members who have experienced trauma, loss, and grief or who have anger or behavioral concerns.
Experiential family therapy can be helpful when there is conflict within the family or when a family unit has a difficult time expressing themselves and communicating their feelings.
What Is the Primary Goal of Experiential Family Therapy?
One of the primary goals of experiential family therapy is to discover and address conflicts and difficulties within a family through activities and experiences.
However, for each family, the goals are unique and specific to them. Everyone’s goals for therapy can be different.
Common goals of family therapy in general can include:
- Improving communication
- Setting boundaries
- Breaking out of cycles of generational trauma
- Creating a healthier family environment
- Learning healthy coping mechanisms for difficult situations within the family
What Does Experiential Family Therapy Focus More On?
Experiential family therapy focuses more on uncovering underlying problems within a family through activities like role-playing, arts, or guided imagery.
Family therapy focuses on using experiences to help family members express and understand certain feelings and problems to each other in a healthy way.
What Is a Major Limitation of Experiential Family Therapy?
One major limitation of experiential family therapy is that sometimes, members of a family go through experiences in therapy but are unable to connect with them or apply them to their personal lives.
With family therapy, each individual has to be committed to it, and if one person isn’t feeling the connection, it can impact the whole family structure and the success or results of family therapy.
One way to address this limitation of experiential family therapy is by having each family member go through individual therapy.
Going to both individual and family therapy can help a person get their concerns and needs addressed and experience their own separate healing journey so that when they are ready, they can allow themselves to fully experience family therapy.
If one individual in a family is struggling, then it can be hard for the whole family to move forward.
Humanistic Experiential Therapy
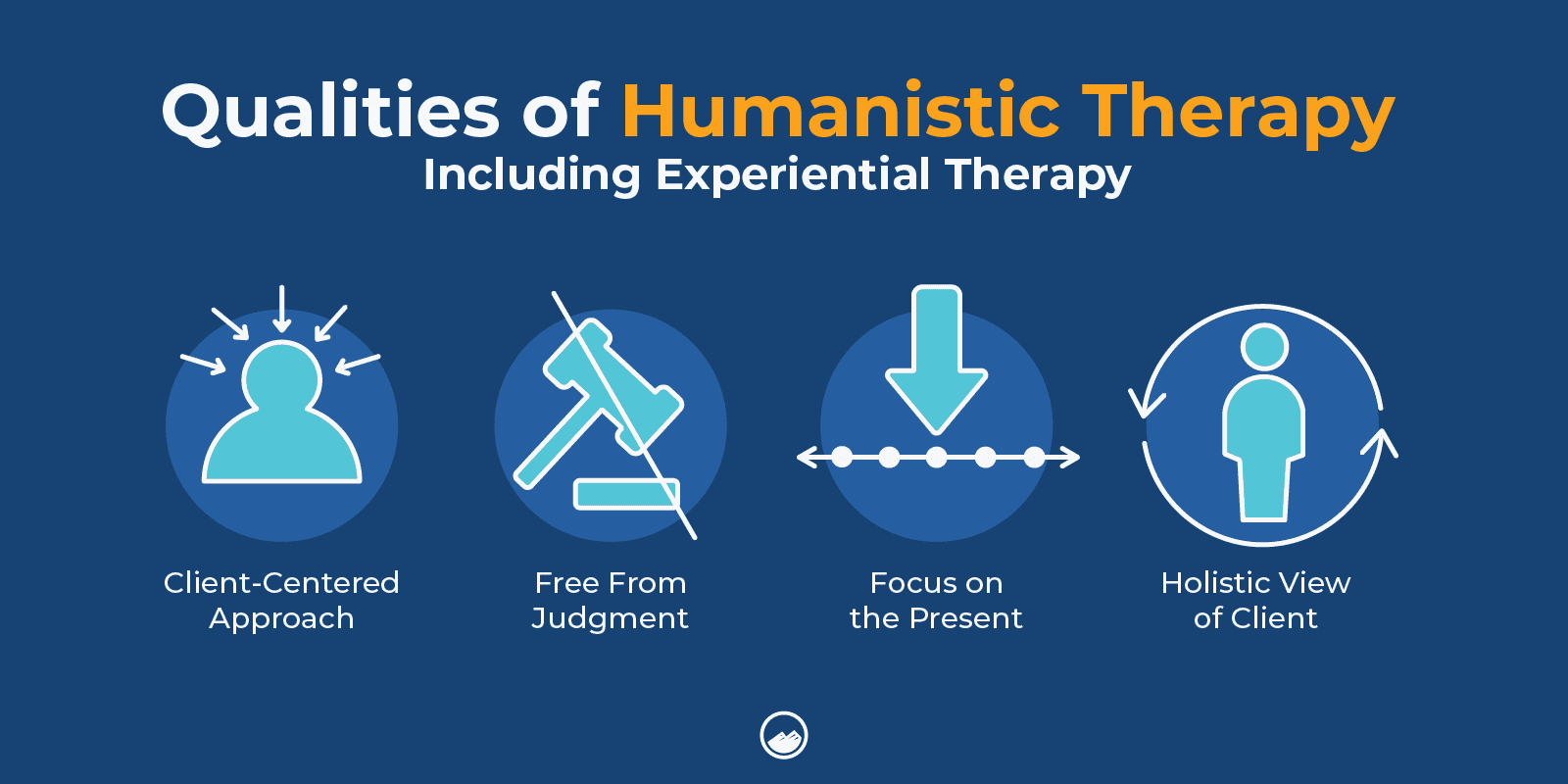
Is Experiential Therapy Humanistic?
Humanistic psychology focuses on the individual.
Humanistic therapy focuses on the person rather than the assumption that a person would have the same concerns as someone with similar characteristics.
Humanistic therapy also emphasizes the positive aspects of a person and focuses on change and growth. It is most commonly used for individuals with depression, anxiety, panic disorders, personality disorders, or addiction.
Humanistic therapy also focuses on the present moment rather than focusing on the past or future, which experiential therapy does as well.
Experiential therapy is humanistic because it focuses on present experiences in helping a person heal. Additionally, the therapist’s role in experiential and humanistic therapy is more equal, rather than having the therapist be an authority figure.
However, humanistic therapy has plenty of different approaches. Humanistic therapy can involve gestalt therapy, narrative therapy, experiential therapy, or existential therapy.
What Is the Focus of Experiential Therapy?
The focus of experiential therapy is to help an individual better process and understand their feelings and experiences through immersive and expressive tools and methods.
Experiential therapy focuses on emotions and experiences and living in the present moment.
Is Humanistic Therapy the Same as Existential Therapy?
Existential therapy is a form of humanistic therapy.
It focuses on acceptance and confronting the fear and anxiety that can come with the human experience.
When taking an existential approach to therapy, the focus is on self-awareness and the constant change that individuals go through, which are humanistic characteristics.
Experiential Therapy Training
What Is the Role of the Therapist in Experiential Therapy?
In experiential therapy, the role of the therapist is to be a collaborator rather than an authority figure.
They aren’t there to provide solutions for the individual, but is there to encourage them and help them on their path to finding their own answers.
What Are the Methods of Experiential Training?
There are a variety of different experiential training methods that can include things like:
- Role-playing
- Reflection
- Art
- Games
- Simulation
- Rock-climbing
- Sculpting
- Animal-assisted therapy
- Drama therapy
Experiential training can be done with individuals or in group settings as well.