What Is Dual Diagnosis And How Is It Treated?
A dual diagnosis, also known as co-occurring disorders, is when someone has both a mental disorder and a substance use disorder.
According to MedlinePlus, half of the people with a mental disorder will have a substance use disorder at some point in their life.

Even though the disorders occur together, it does not mean that one caused the other. Both can also be worsened by the other.
It can be difficult to understand what causes both a substance use disorder and mental disorder to occur together, but researchers believe there are a few different possibilities.
One may be the common risk factors that both SUDs and mental disorders share, such as; genetics, trauma, and stress.
Another could be that sometimes, SUDs develop as an unhealthy coping mechanism. People who may be struggling with a mental disorder may use drugs to cope with difficult feelings or symptoms they may be facing.
An individual with a mental illness may try to self-medicate with substances, which will only harm them in the long run.
Substance abuse can also alter the brain, making it more susceptible to developing a mental disorder and vice versa.
Someone with a dual diagnosis has to receive treatment for both disorders.
There are also many different ways dual diagnosis can occur, making treatment plans completely different for each individual.
To treat a dual diagnosis, a person does not need to become sober first. Both mental health and substance use can be treated simultaneously.

It is important to find a dual diagnosis treatment center and providers specializing in both mental health and substance abuse treatment. Good dual diagnosis treatment programs are made for the individual’s needs.
Many addiction treatment centers can help those struggling with mental health issues. However, some drug rehab centers are not equipped to treat a dual diagnosis.
Detoxification is one of the first parts of the treatment process where an individual goes through the process of clearing drugs and alcohol from their system.
Detox allows for the safe management of withdrawal symptoms.
Another part of treatment is therapy, which can help a person learn healthy coping mechanisms. One of the most common is behavioral therapy.
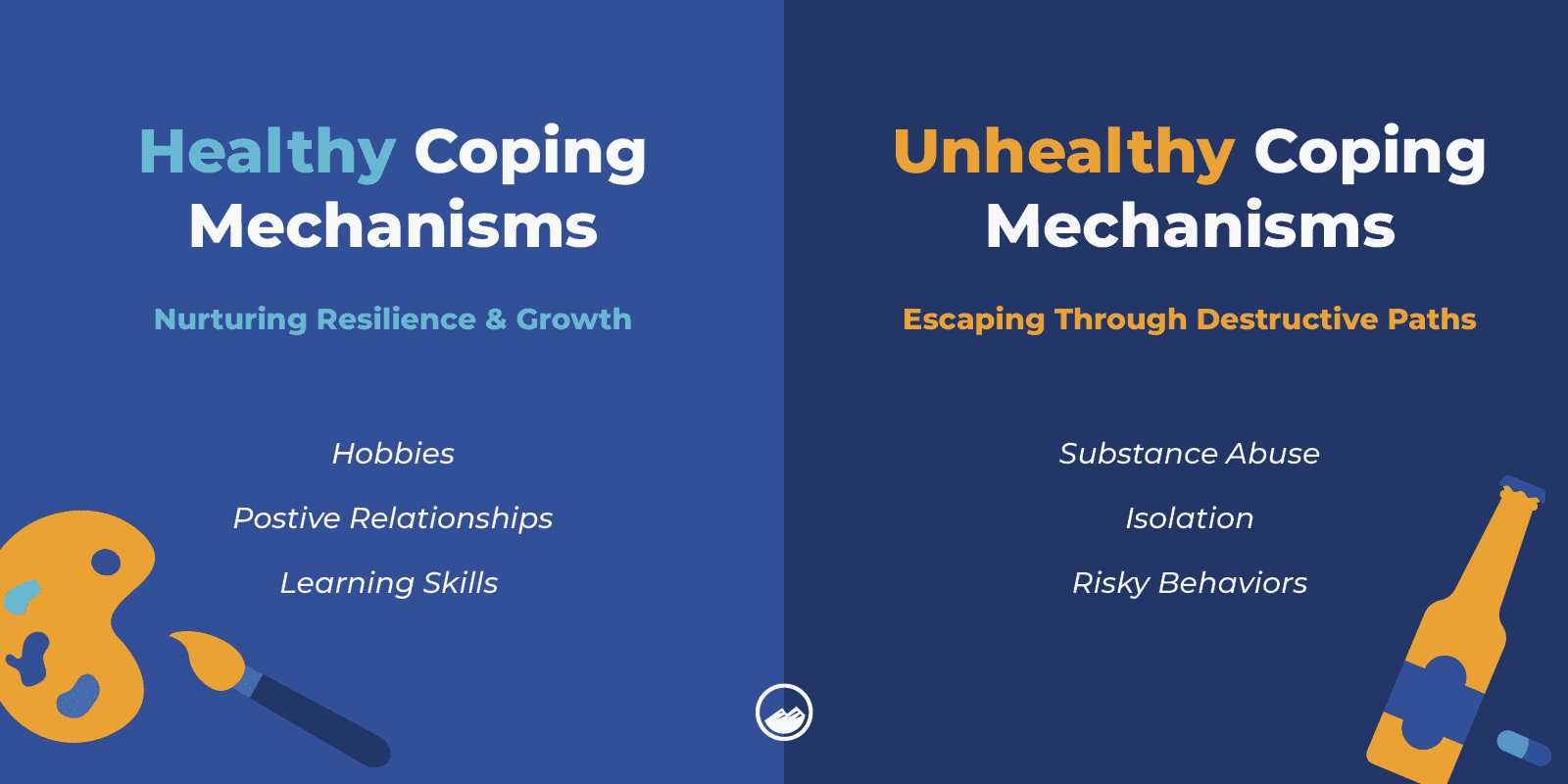
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on how people act, feel, and think. It can help a person with a dual diagnosis change their thinking patterns to benefit them and create healthy habits.
Medications can also be useful for treating both mental disorders and SUDs.
They can also help those with SUDs ease withdrawal symptoms. Medicine can be used to help patients with feelings such as anxiety, mood swings, and the recurrence of traumatic events.
Because dual diagnosis treatment can be complex, it may feel difficult, overwhelming, or isolating.
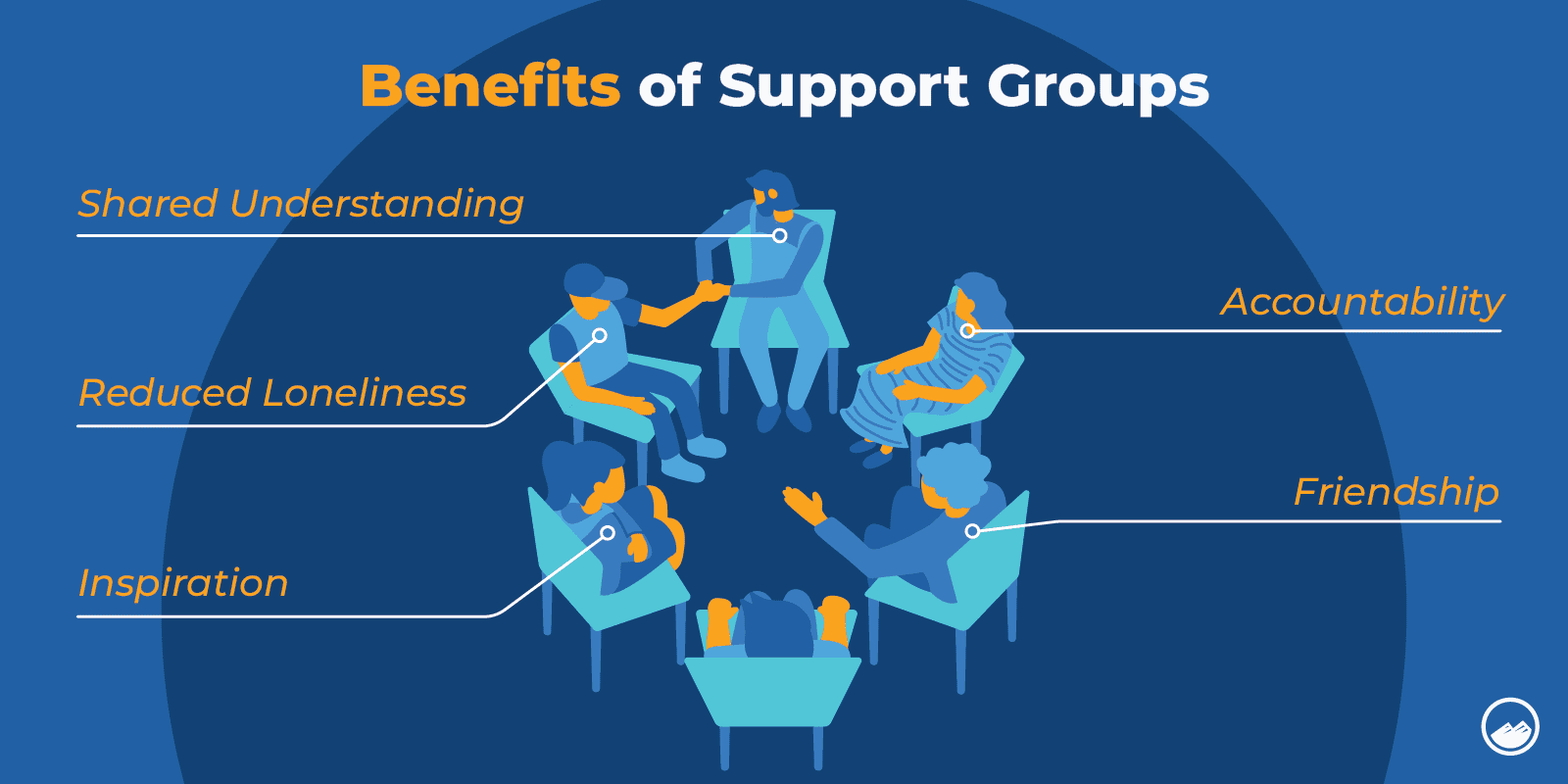
Support groups can be a helpful part of the treatment process.
Support groups allow people to relate to each other. They can share their experiences, challenges, and successes and learn through each other.
Inpatient rehabilitation can be helpful for someone struggling with severe mental illness or substance abuse. There, an individual can receive 24/7 care and support.
Residential treatment programs can be a good option for those with a severe mental illness or very heavy use of drugs or alcohol.
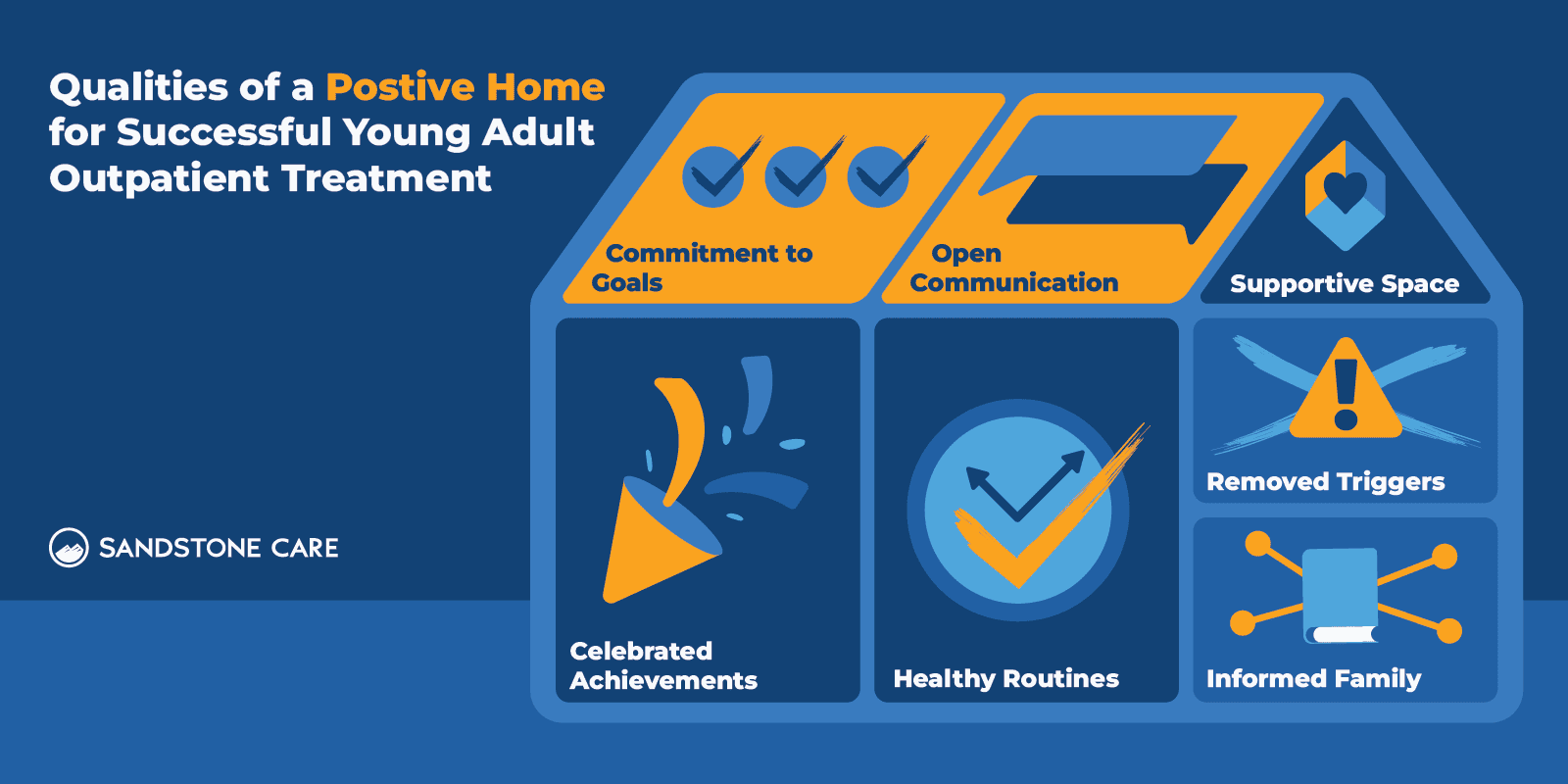
Outpatient treatment programs may be helpful for young adults who may want to still attend school or keep up with their daily responsibilities at home.
If someone is receiving outpatient treatment, it is most effective when they have a supportive home environment. It can also require a higher level of commitment because the individual is not as closely monitored as they would be in inpatient treatment.
If a loved one is struggling with a dual diagnosis, it is extremely important to learn about mental health, substance abuse, and addiction.
Sometimes what the person may need is not to be fixed right away but to be understood.
The more you know, the better you will be able to provide help and support that your loved one may need.
What Are Three 3 Common Mental Health Issues In Young People?
According to the CDC, the most commonly diagnosed mental disorders in children ages 3 to 17 in 2016-2019 were ADHD, anxiety, behavior problems, and depression.
Approximately 6 million children were diagnosed with ADHD, 5.8 million with anxiety, 5.5 million with behavior problems, and 2.7 million with depression.
It is also reported that depression and anxiety have increased over time.
Additionally, about 4.1% of adolescents ages 12 to 17 from 2018 to 2019 were diagnosed with a substance use disorder.
What Is The Most Common Mental Illness In Young Adults?
Anxiety disorders and depression are two of the most common mental health issues in young adults.
According to the Journal of Psychiatric Research, anxiety appears to be the most common among young adults ages 18 to 25 and has increased more rapidly in this age group than in everyone else.

Anxiety is characterized by feelings of worry or fear that affect someone’s ability to complete daily activities.
Common symptoms of anxiety include:
- Feelings of nervousness or restlessness
- A sense of panic
- Increased heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sleeping problems
- Having headaches or unexplained pains
People struggling with anxiety or depression may look for ways to escape or numb difficult situations or feelings.
They may turn to drugs or alcohol as a way to cope.
Over time they may use substances to self-medicate, which can result in more problems and a dependence on the drug.
Dependence happens when someone repeatedly uses a drug over time and cannot stop without experiencing withdrawal symptoms. Dependence often occurs with addiction but is not the same thing.
Is Dual Diagnosis Common?
According to the National Alliance on Mental Illness, about one-third of people who struggle with severe mental illness also struggle with substance abuse.
Dual diagnoses are very common and are treatable.
What Is An Example Of Dual Diagnosis?
Common mental disorders that can also be associated with substance use include depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, ADHD, schizophrenia, and more.
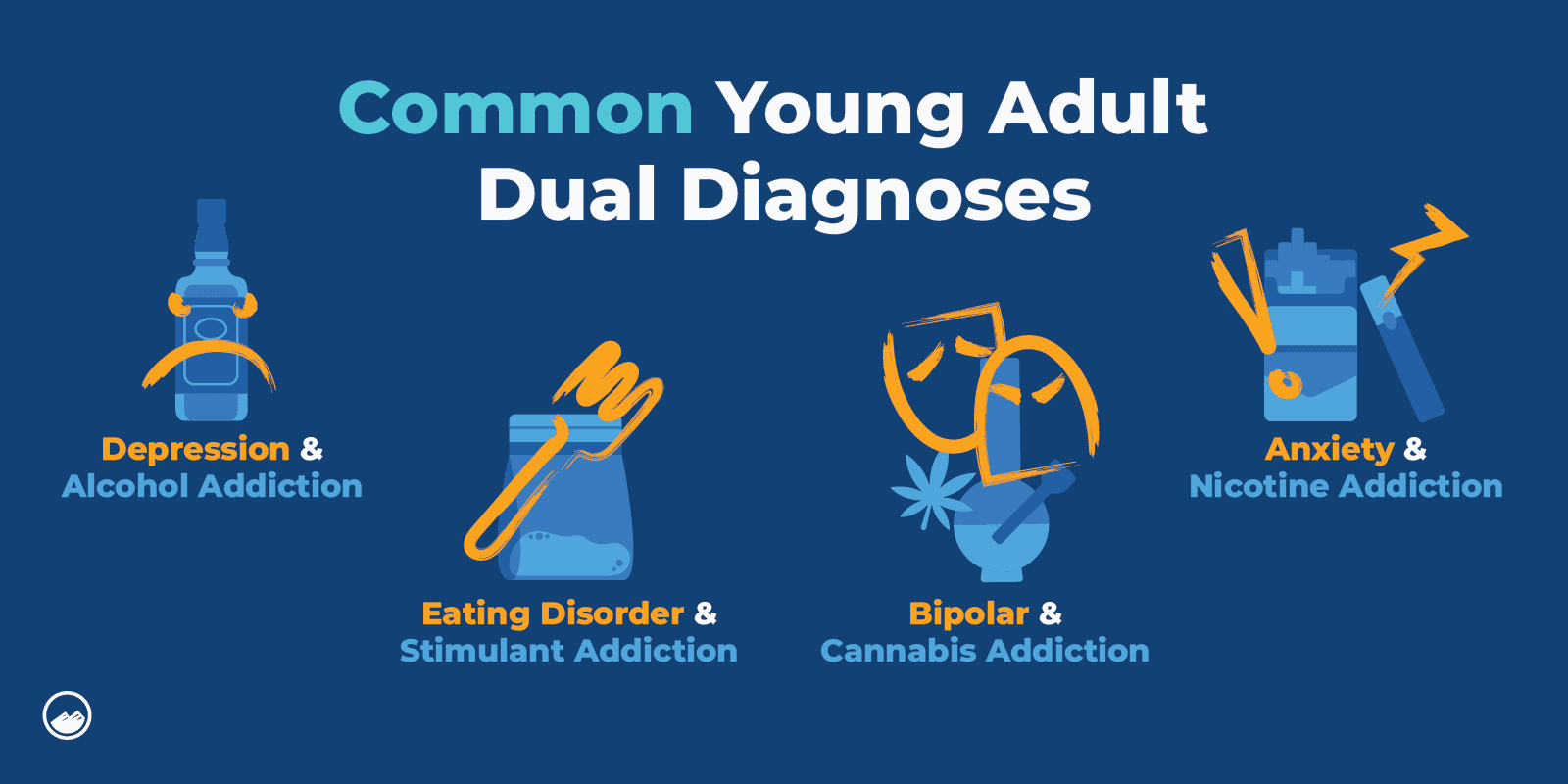
One example could be someone with depression who abuses alcohol, marijuana, or stimulants.
Depression can cause feelings of extreme sadness, unworthiness, and loneliness. A person may look for relief and turn to substances to self-medicate.
Additionally, people with anxiety disorders commonly have extreme feelings of worry. They may abuse depressants as a way to relax like alcohol, marijuana, and prescription drugs.
People with bipolar disorder may experience extreme highs and lows. Because of this, they may try to use a variety of different drugs to self-medicate.
Personality disorders like narcissistic or borderline personality disorders can make it difficult for someone to understand or relate to other people. They may use drugs to try and numb their feelings, like prescription drugs or alcohol.
Self-medicating may offer short-term relief because of its impact on the brain. However, in reality, self-medication results in worsened or increased symptoms and only make matters worse.
What Are The Signs Of Dual Diagnosis?
The signs of dual diagnosis can differ because of all the different ways it can occur.
Some signs of dual diagnosis may include:
- Sudden changes in friend groups and close relationships
- Difficulty performing well in school
- Use of drugs to escape emotional distress
- Have a previous history of mental illness
- Having to take drugs to feel normal
- Repeatedly trying to quit using drugs but relapsing each time
- Extreme emotional highs and lows
- Irregular sleeping patterns, for example, staying up all night and sleeping all-day
- Constantly lying or stealing
- Engaging in self-harming behaviors
Do Young Adults Experience More Mental Illness Than Older Adults?
According to the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health, adults ages 18 to 25 were the highest percentage of people who suffered from any mental illness.
Young adulthood can be a stressful time, filled with many changes and transitions. Throughout the mid-twenties, the brains of young adults are going through major development.
Young people are beginning to find a higher sense of self at this time, along with independence. Many young adults want to experience new things, which can also result in experimenting with substances.
Experimentation is one of the factors that can lead young adults into substance abuse and addiction, even if it is only one time.
The same features that allow young people to be extremely absorbent and learn new things also make them more susceptible to things like mental health disorders and substance use disorders.
It is important for a person of any age to receive treatment for mental illness. Failure to address the problem, especially at an early age, can cause symptoms to worsen and can lead to life-threatening problems.
Who Is Most Likely To Be Diagnosed With A Mental Illness In Young Adults?
Some risks factors that can increase the likeliness of a young adult developing a mental disorder may include:
- Female gender
- Genetics/ family history of mental illness
- Negative family environment
- Rejection or discrimination
- Homelessness or unemployment
Often, those with a dual diagnosis have experienced trauma or stressful life events at some point in their life.
What Are The Symptoms Of Depression?
Depression is a mood disorder that causes persistent feelings of sadness.
It can affect someones thinking, feeling, and ability to handle everyday things.
Different forms of depression can cause symptoms and signs to differ depending on the person.
Some common symptoms of depression may include:
- Feelings of sadness, emptiness, guilt, or hopelessness
- Irritability
- Loss of interest in things you once loved
- Fatigue
- Restlessness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Memory problems
- Sleep problems such as sleeping too little or too much
- Eating changes
- Self-harming behaviors
- Thoughts of suicide
Someone with depression may try to find ways to escape their sadness or feel “normal” again.
They also may try to achieve a “high” or feelings of euphoria to numb the pain.
Over time, the brain is altered with substances and needs more and more a drug to achieve this feeling of normalcy. This can eventually lead to addiction and worsened symptoms later on.
What Is CD Disorder?
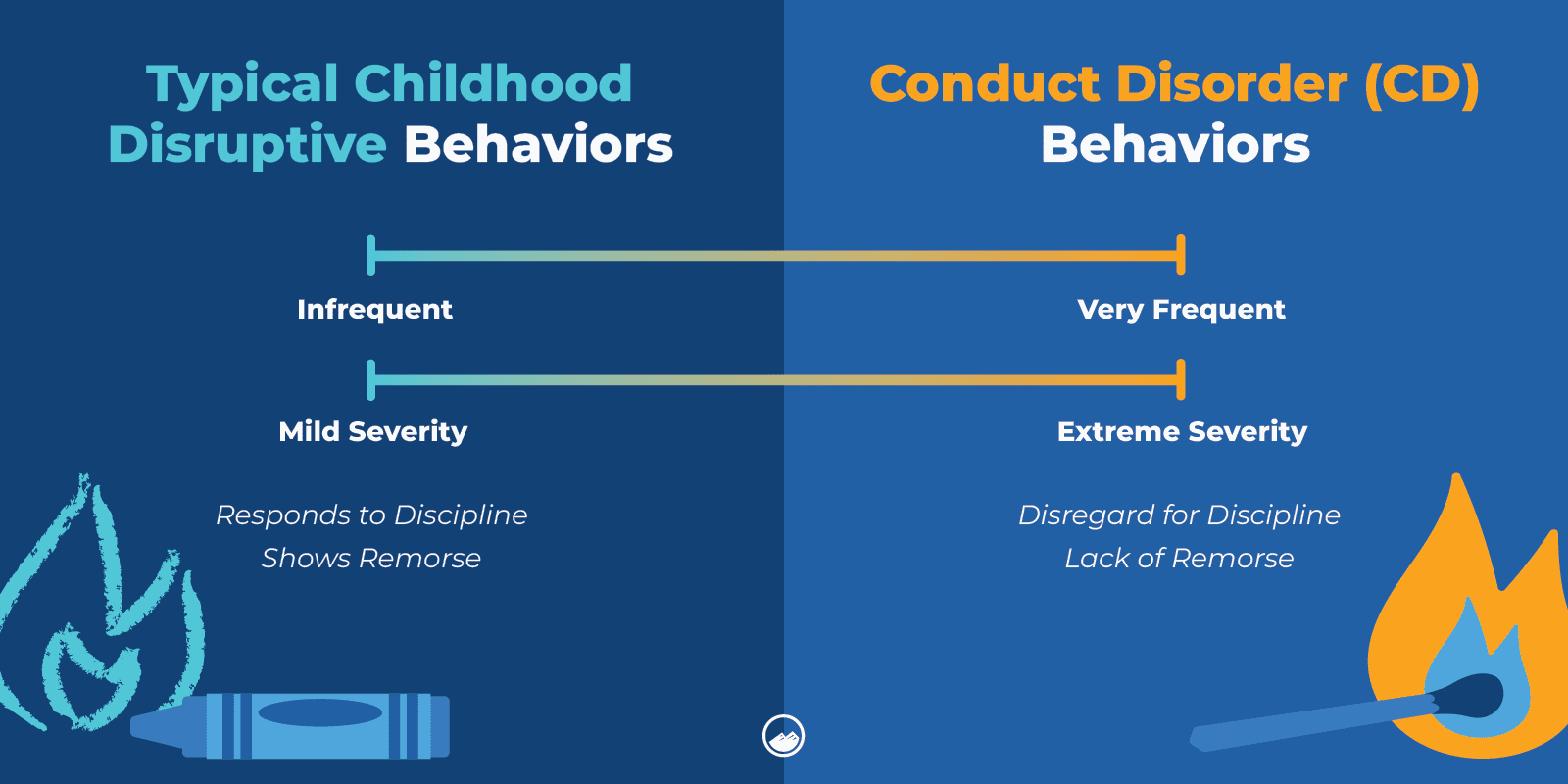
Conduct disorder (CD) is a behavior disorder that typically occurs in children and adolescents.
CD can be diagnosed when children exhibit patterns of aggression, violating rules, or breaking social norms at home or in school.
Behaviors of someone with a CD disorder can include:
- Running away
- Staying out past curfew
- Skipping class
- Bullying or fighting
- Being cruel to animals
- Lying
- Stealing
- Damaging others’ property
CD is on the spectrum of disruptive behavioral disorders and oppositional defiant disorder (ODD).
CD often occurs co-morbidly with other mental health conditions, such as depression, ADHD, and learning disorders.
Comorbidity refers to the presence of two or more disorders or illnesses that occur in the same person.
Comorbidity is sometimes used in the same context as co-occurring.
What Is The Most Common Co-occurring Disorder With Mental Illness?
According to MentalHealth.gov, substance abuse occurs most commonly with:
- Depression
- Anxiety disorders
- Schizophrenia
- Personality disorders
What Are The 5 Signs Of Mental Illness In Young Adults?
Each mental illness has its own warning signs. However, five common signs of mental illness in young adults include:
- Extreme mood changes
- Isolating themselves from friends and family
- Changes in sleeping or eating habits
- Inability to perform daily activities
- Substance abuse
Why Do Young Adults Have Worse Mental Health?
Multiple factors contribute to poor mental health in young adults.
Young adults have a lot on their plate. They are searching for a sense of identity while handling the challenges of everyday things like school, work, and life transitions.
One important factor is that young adults are still experiencing major brain development throughout their mid-twenties.
Specifically, the region of the brain called the prefrontal cortex. This area plays a part in impulse control, emotion regulation, planning, and coordinating behaviors.
This can affect the decisions young adults make and make them more likely to engage in risky behavior.
The developing brain is essentially wired to learn new things and adapt. However, all the new brain changes and physical and emotional changes in young adulthood can also make individuals more susceptible to mental health issues.
Brain development also plays a role in young adults’ stress management. It may be difficult to navigate and respond to stress compared to older adults.
This can lead to patterns of unhealthy coping mechanisms such as substance abuse.
Another reason could be the increased use of social media amongst teens and young adults.
While social media can be used as a great way to network and connect with others, it often portrays unrealistic standards and can have a negative impact on someone’s self-esteem, image, and worth.
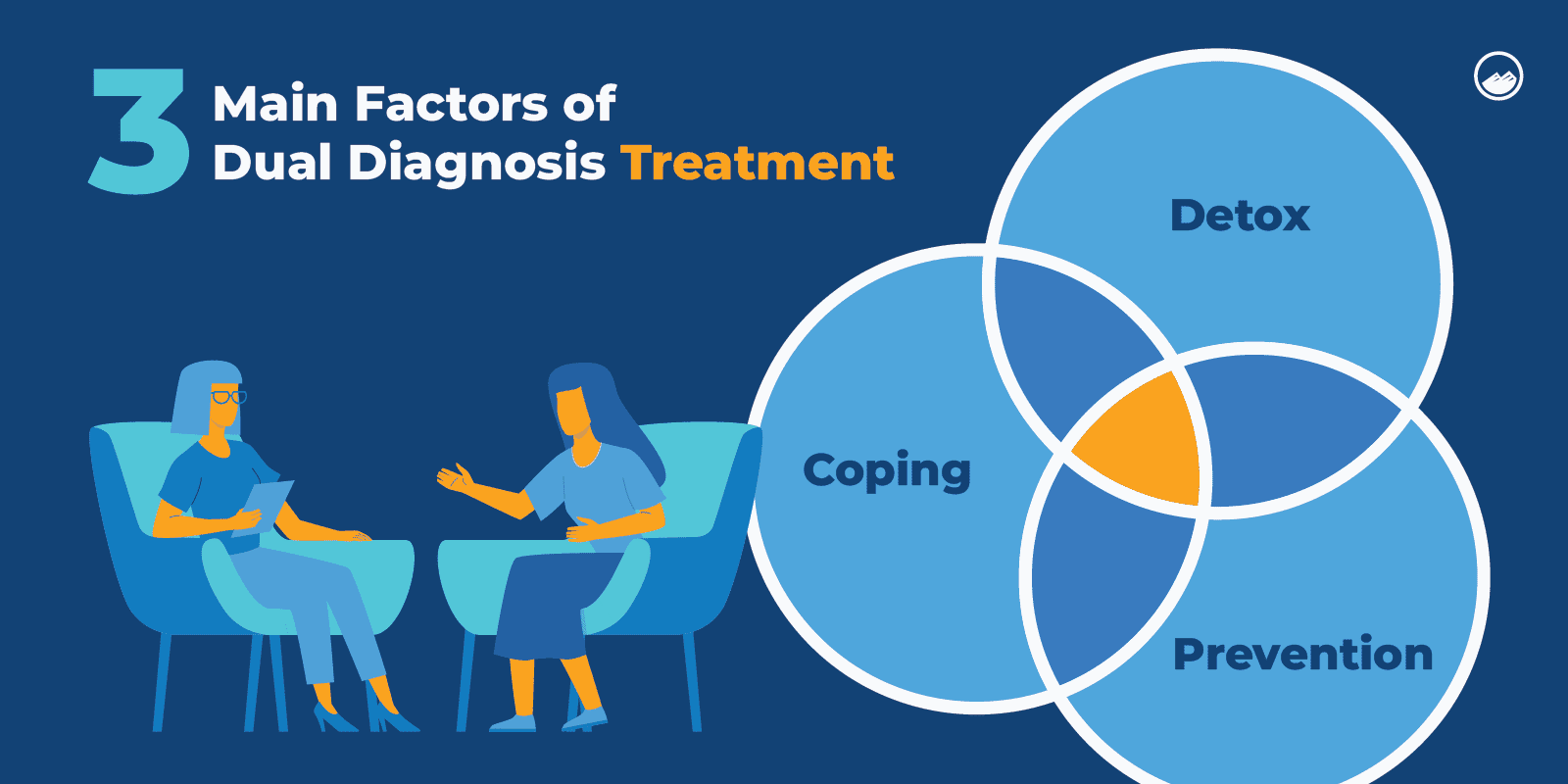
What Is Meant By Dual Diagnosis Treatment?
Dual diagnosis treatment recognizes that an individual is struggling with both a mental illness and substance use disorder and aims to treat both problems.
Dual diagnosis treatment consists of three main things:
- Detox: Getting rid of harmful substances in the body.
- Coping: Finding healthy ways to cope with underlying issues.
- Prevention: Learning how to prevent relapse to remain sober.
For someone struggling with both a mental illness and SUD, it is important to find an effective dual diagnosis treatment program.
Dual diagnosis treatment should involve care providers who specialize in substance abuse and mental health and work together.
Psychotherapy is also a big part of dual diagnosis treatment and, at times, is combined with prescription medication if needed.
Staying sober is one of the most important parts of treatment. If substance abuse continues over the course of treatment, it can only make the situation worse and prevent someone from getting the help they need.
Failing to receive treatment for mental illnesses and substance abuse can result in serious negative effects in every aspect of someone’s life. Over time, it could also cause someone to feel helpless and suicidal.
If you or a loved one is struggling with suicidal thoughts, reach out immediately for professional help or call the National Suicide Prevention Line at 800-273-8255.


Let’s Take the Next Steps Together
Dual-diagnosis is when someone has both a mental disorder and a substance use disorder or addiction. Sandstone Care is here to support teens and young adults with mental health and substance use disorders.










