Hangxiety
What Is Hangxiety?
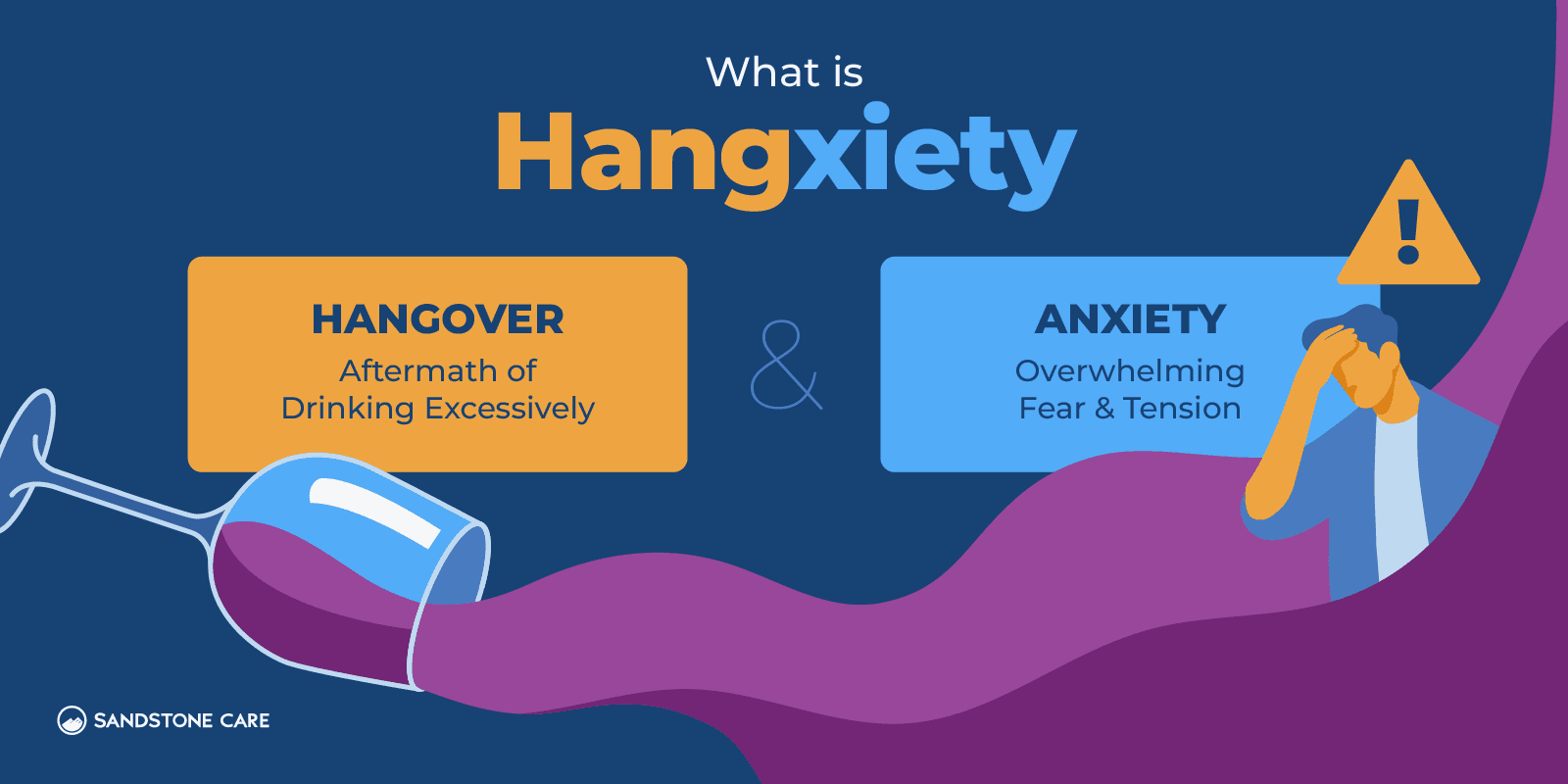
The term hangxiety describes feelings of anxiety, uneasiness, and irritability after excessive drinking.
After a night of drinking, people often experience hangovers, but hangxiety mixes both hangover symptoms and symptoms of anxiety.
Why Do I Get Hangxiety?
Sometimes referred to as post-drinking anxiety, hangxiety can occur when a person drinks too much alcohol.
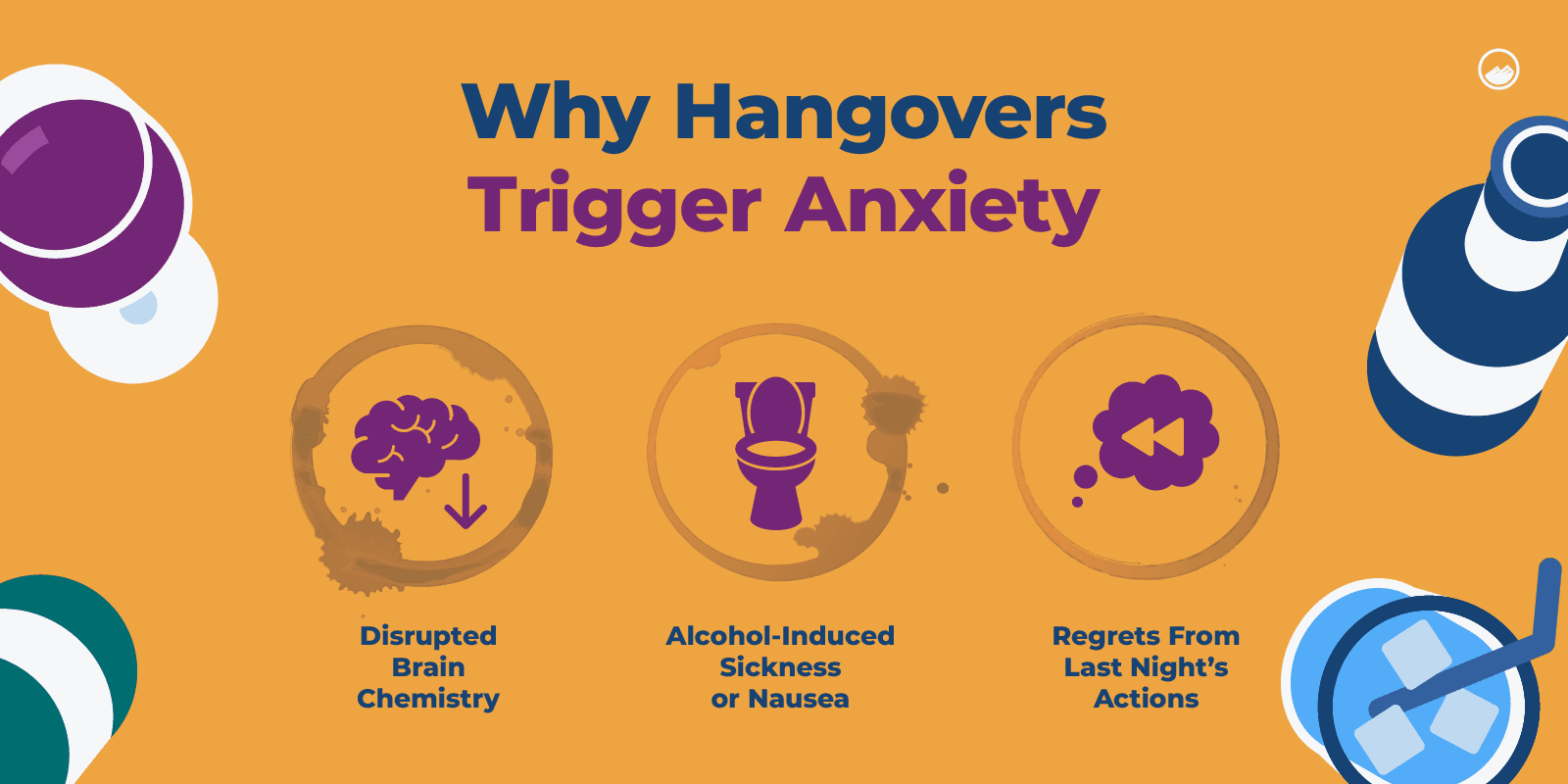
When a person drinks alcohol, it acts on the brain’s gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor. GABA slows down brain activity by blocking certain signals in the central nervous system.
It is known for producing a calming effect and plays a significant role in controlling nerve hyperactivity, which is connected with anxiety, stress, and fear.
When levels of GABA become imbalanced, it can cause feelings of anxiety.
Also, alcohol use is associated with the release of dopamine into the brain, which can cause feelings of withdrawal as alcohol is leaving the system.
How Does Alcohol Boost Anxiety Levels?
Alcohol can affect essential neurotransmitters in the brain.
It can also impact levels of serotonin, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and dopamine in the brain. These are known as “feel-good” chemical.
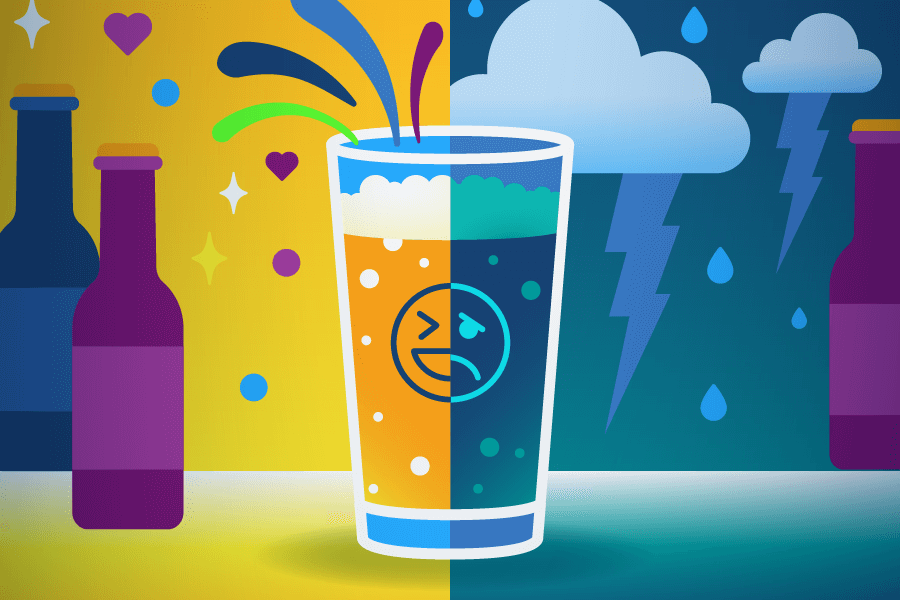
While this feels great at the beginning of drinking, it can lead to feelings of “crashing,” stress and anxiety as the body tries to get rid of the alcohol in its system.
This is why anxiety often appears at the same time as a hangover.
Also, drinking too much alcohol can lead to a loss of inhibition and even memory loss, which can be very disorienting as the brain starts to recover.
People who experience hangovers may also have fears about what they did, if they embarrassed themselves, or if they encountered any dangerous situations while drinking.
These fears, feeling physically ill, and the sudden crash of “feel-good” chemicals create the perfect environment for anxiety to take over.
How Long Does Hangxiety Last?
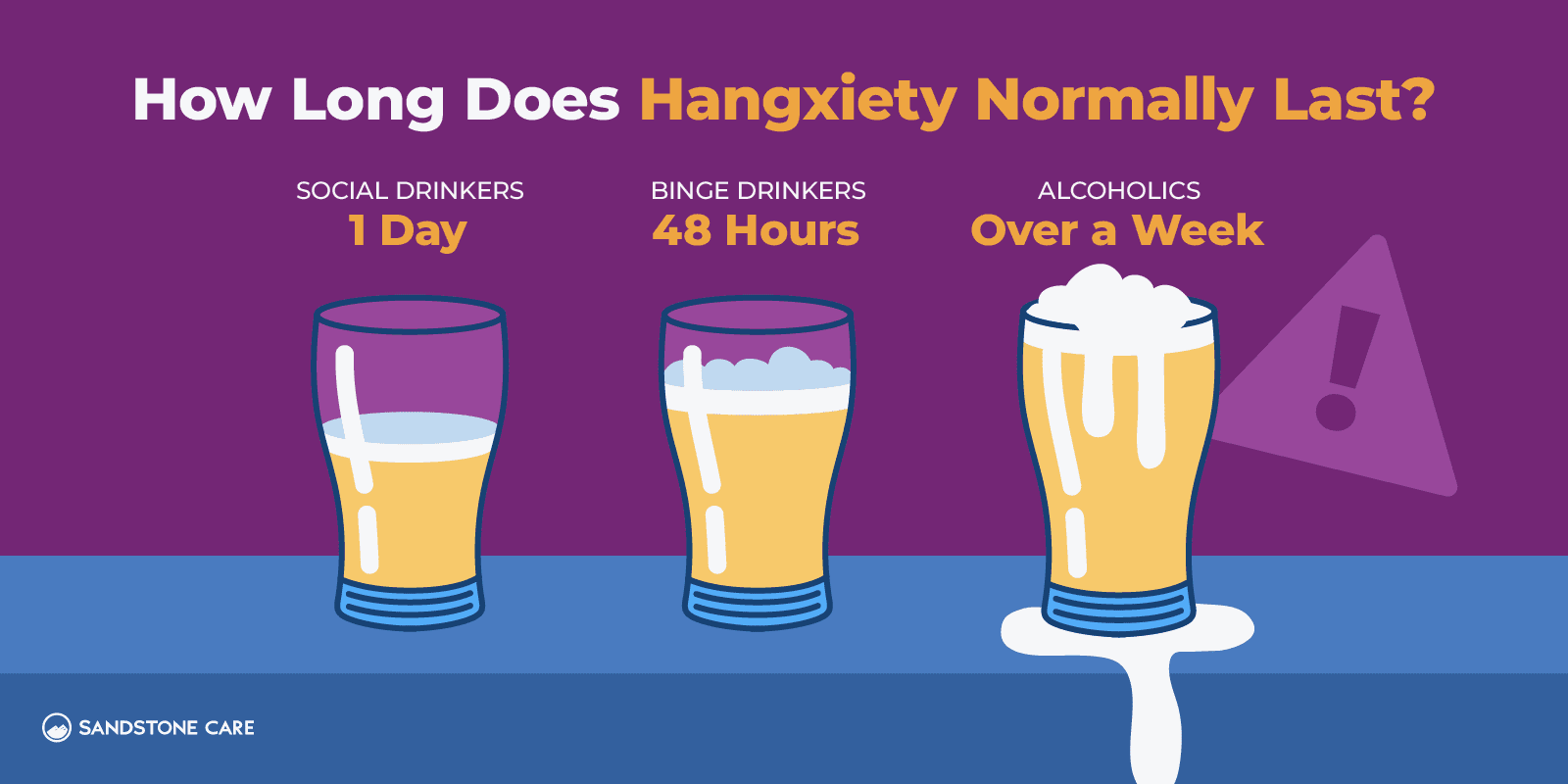
Hangxiety, or anxiety after drinking, can last anywhere from a few hours to up to 48 hours, depending on the amount of alcohol consumed and how your body processes it.
For social drinkers, hangxiety often peaks the morning after drinking and typically fades within a day as the alcohol leaves the system.
However, for individuals who struggle with alcohol use disorder, binge drinking, or alcoholism, hangxiety can last longer and be more intense.
Chronic drinking can disrupt brain chemistry, leading to extended periods of anxiety that may last several days, even after the alcohol is gone.
Rest, hydration, and cutting back on alcohol can help reduce hangxiety in both cases.
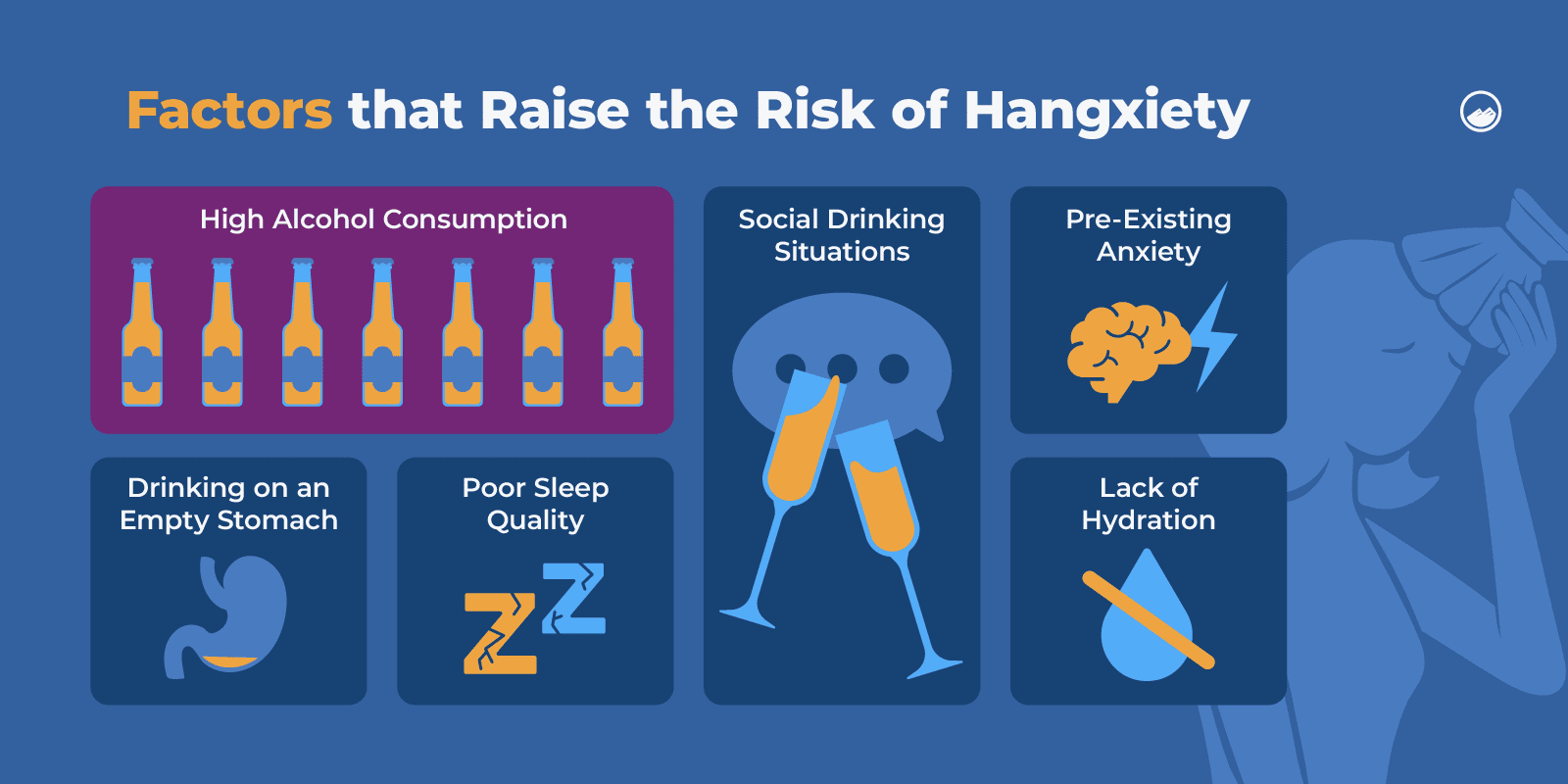
Who Is at Risk for Hangxiety?
Individuals at a higher risk of experiencing symptoms of hangxiety can include people who:
- Already experience anxiety or have an anxiety disorder
- Are diagnosed with depression
- Don’t frequently drink or drink too frequently
- Are highly shy
- Struggle with memory loss from drinking
Causes of Hangover Anxiety
What Causes Hangxiety?
Hangxiety happens when the sedative effects of alcohol wear off, then you can experience symptoms that are similar to withdrawal symptoms from alcohol.
When a person drinks alcohol, it disrupts brain activity and brain chemical levels.
Consuming alcohol can cause an excess of “feel-good” chemicals. These “feel-good” chemicals impact a person’s mood and may cause them to feel more relaxed while they are consuming the alcohol.
However, the next day, as the alcohol leaves the system, these chemical levels go down, causing a declining and anxious mood.
Additionally, the stress hormone cortisol is triggered after drinking alcohol, which can make a person feel more on edge and anxious.
The chemical imbalances that occur when a person drinks alcohol can trigger the body to go into a “fight or flight” mode.
What Is the Connection Between Alcohol and Anxiety the Next Day?
Anxiety can occur from alcohol the next day because the brain is trying to rebalance its chemical levels.
Can Dehydration Contribute to Hangxiety?
The dehydration caused by alcohol use can have a negative impact on emotions and contribute to symptoms of hangxiety.
Alcohol is a diuretic, meaning it can cause people to urinate more and become dehydrated more quickly.
When a person is dehydrated, it can lead to physiological responses that trigger anxiety symptoms, such as increased heart rate, confusion, and headaches.
Do Hangovers Cause Anxiety?
Yes, hangovers can lead to symptoms of anxiety, depression, and irritability.
Why Do Hangovers Cause Anxiety?
When a person consumes alcohol, it impacts a number of different brain chemicals.
As the effects of alcohol wears off, these brain chemicals fluctuate as well.
GABA is a neurotransmitter that slows down activity in the central nervous system, resulting in a calming effect.
However, changes in GABA levels can lead to feelings of anxiety, especially when coupled with an increase in glutamate.
High levels of glutamate caused by alcohol use can lead to mood changes and increased feelings of anxiety.
Why Did I Start Getting Hangxiety?
If you have drunk alcohol before and never experienced symptoms of hangxiety until recently, it might be because your stress levels are higher.
It could also be because you might have been drinking excessive amounts of alcohol, and your body is becoming dependent on it, resulting in withdrawal symptoms when you stop drinking.
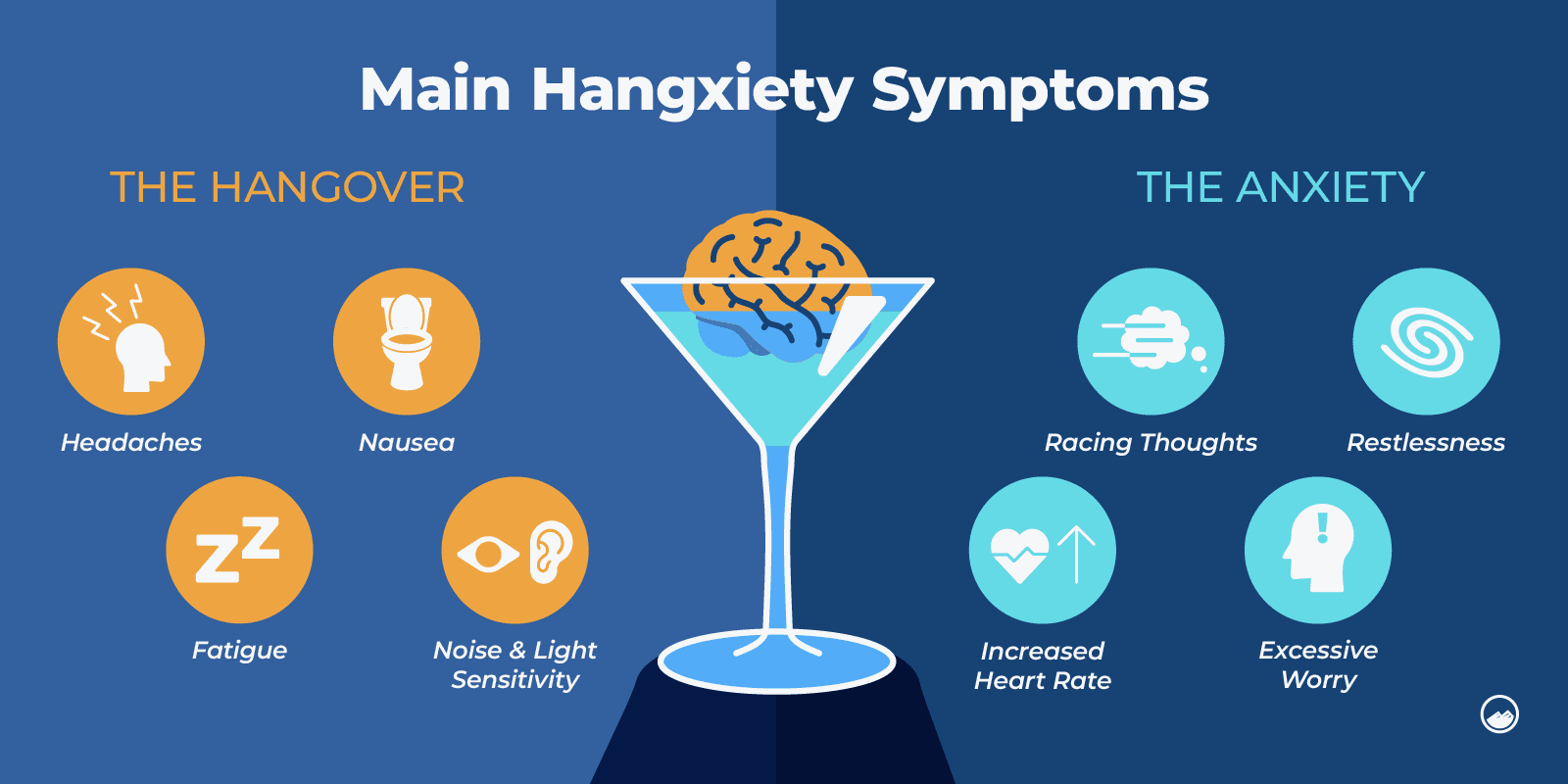
Hangxiety Symptoms
What Are the Symptoms of Hangxiety?
Common emotional and physical symptoms of hangxiety can include:
- Irritability
- Increased heart rate
- Paranoia
- Feelings of guilt or shame
- Sweating
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sense of dread
- Difficulty focusing
When a person is hungover, they can experience symptoms including headaches, dizziness, nausea, dehydration, and low blood sugar.
These symptoms can also contribute to feelings of anxiety after a night of heavy drinking.
What Does Hangxiety Feel Like?
Hangxiety involves general hangover symptoms coupled with increased anxiety, feelings of irritability, stress, panic, and fear.
A person may feel like they are unable to sleep or relax, and they might also experience feelings of shame and guilt.
Feelings of shame might stem from regrets regarding their alcohol consumption and feelings of embarrassment.
Why Is Anxiety Worse After Drinking?
There are various reasons why a person’s anxiety might worsen after drinking.
One reason is that the person already has anxiety or depression, and they are using alcohol as a way to cope.
Alcohol might make them feel better for a short amount of time, but once the brain chemicals rebalance and the effects of alcohol wear off, the symptoms of anxiety can come back even worse.
Additionally, alcoholic beverage use can be connected with gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors.
This impacts communication with the brain, and if there is too much GABA, it can cause an increase in anxiety symptoms.
How Do I Know If I Have Hangxiety?
Some common signs of hangxiety can include:
- Increased heart rate
- Feeling jittery
- Feelings of depression or anxiety
- sense of shame or guilt about drinking
- Paranoia
- Irritability
- Racing thoughts
How to Prevent Hangxiety
Can Hangxiety Be Prevented?
Chances of experiencing symptoms of hangxiety may be reduced or prevented if you limit the amount of alcohol you consume, stay hydrated, or choose to abstain from alcohol.
How Can You Avoid Hangxiety?
Some ways to avoid hangxiety can include:
- Limiting alcohol intake
- Eating before consuming alcohol/ making sure not to drink on an empty stomach
- Don’t mix different types of alcohol; for example, don’t mix beer and spirits.
- Stay hydrated
What Are Ways to Stop Hangxiety?
If you are experiencing hangxiety and need ways to find some relief, you can do things such as:
- Drinking water
- Getting plenty of rest
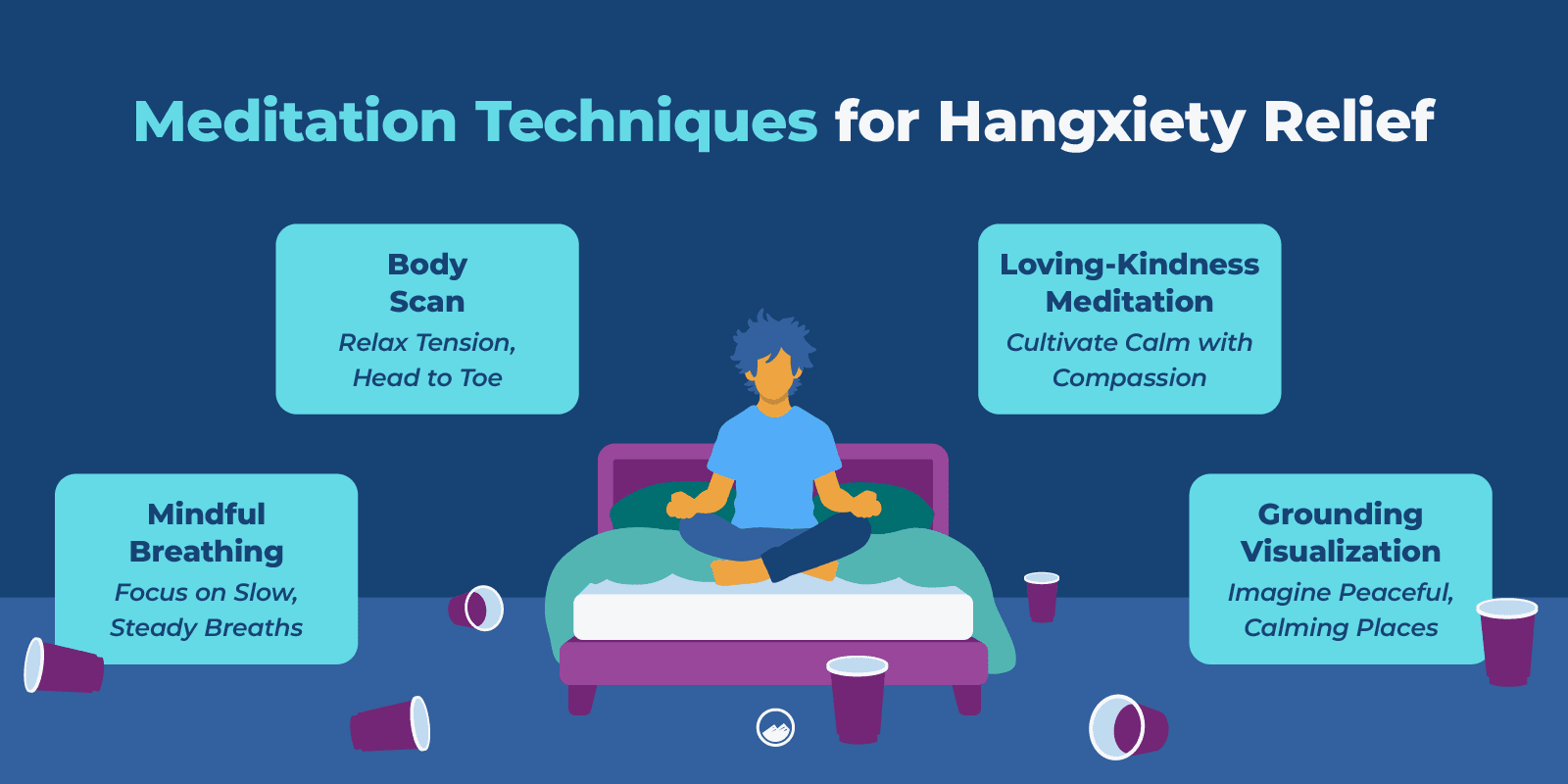
- Practicing mindfulness and meditation techniques
- Eat a nutritious meal as soon as you feel able to keep something down
- Spend time with friends or family
How to Get Rid of Hangxiety
Can You Make Hangxiety Go Away?
Typically, hangxiety will go away after the first 24 hours after drinking. However, some ways to feel better sooner can include rehydrating and sleeping.
How Do You Get Rid of Hangxiety Fast?
The best ways to get rid of hangxiety fast are to get as much rest as possible and to drink plenty of water or something with electrolytes.
Breathing, somatic, and meditation techniques can help to settle your emotions while your physical body recovers.
What Foods Reduce Anxiety?
Eating a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains can help reduce anxiety much more than eating processed foods.
According to research, chronic inflammation is a feature of numerous neurological disorders, including anxiety disorder.
“Inflammatory foods” often include one of two components, one being refined sugars and the other being processed vegetable oils.
Omega-3 fatty acids are known as healthful and anti-inflammatory and have been found in studies to decrease inflammation and balance neurochemistry, or in other words, relieve some symptoms of anxiety.
Other foods associated with eased anxiety symptoms include dark chocolate, leafy greens, broccoli, avocado, and lentils.
Do I Need Professional Help for My Hangover Anxiety?
When a person drinks alcohol from time to time or experiences a night where they just drank too much, it doesn’t always mean that they need professional help with alcohol use or even anxiety.
However, if a person is often experiencing anxiety due to frequent drinking, it can be a sign that they should reach out for professional help.
If alcohol use starts to affect a person’s everyday life, relationships, mental health, or physical help, it is an indicator that they need help.
If you are experiencing hangxiety often, it can be an indicator that you should start decreasing your alcohol consumption and possibly talk to someone about it.
Sometimes, a person attempts to self-medicate with alcohol as a way to cope with underlying mental challenges that they might be going through.
In order to help ease the hangxiety symptoms, a professional needs to help them get to the root cause of the individual’s drinking pattern and address the underlying concerns.
If you are using alcohol to manage symptoms of anxiety, it can become a serious cycle that gets more and more dangerous over time.
What Is Alcohol Dependence?
Alcohol dependence occurs when a person is unable to control their drinking.
They need to drink more and more alcohol to achieve the same desired effects, and if they stop drinking, they will experience withdrawal symptoms.
Alcohol dependence also leads to problems with a person’s mental and physical health, along with issues in one’s personal life, such as in their relationships.
Alcohol use disorder is a medical condition where a person cannot stop or control alcohol use despite the negative consequences it has on their health and life.
Signs of alcohol dependence for people with anxiety can include:
- Needing an alcoholic drink to start the morning
- Drinking heavily for four or more days a week
- Needing to have alcohol to face or engage in social settings
- Binge drinking
If you think you or a loved one might have an alcohol use disorder, consider taking this quiz to see if you need to reach out for professional help.
How Is Hangxiety Treated?
If you frequently experience hangxiety, talk to your healthcare provider.
There are numerous treatments available to treat both anxiety and alcohol use disorder.
Recognizing a problem, seeking professional help, and understanding the root cause are the first steps in getting help for hangxiety.