According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, trauma is an event or circumstance that results in physical, emotional, or life-threatening harm.
Individuals with trauma may experience challenges that impact their mental health, physical health, emotional health, and overall well-being.
Trauma can affect a person of any age, whether they are a child or an adult.
Type 1 trauma refers to an unexpected, single-incident trauma.
Also referred to as “Big T” or acute trauma, it is commonly related to Post-traumatic stress disorder.
Examples of Type 1 traumatic events can include:
Type 2 trauma, also known as complex trauma, refers to trauma that may involve childhood experiences or traumatic experiences during early development.
Repetitive trauma is also a type 2 trauma where trauma is repeated. Complex trauma often becomes part of a relationship in which a person becomes stuck. This occurs in situations such as child abuse from caregivers.
Common examples of type 2 traumatic events can include:
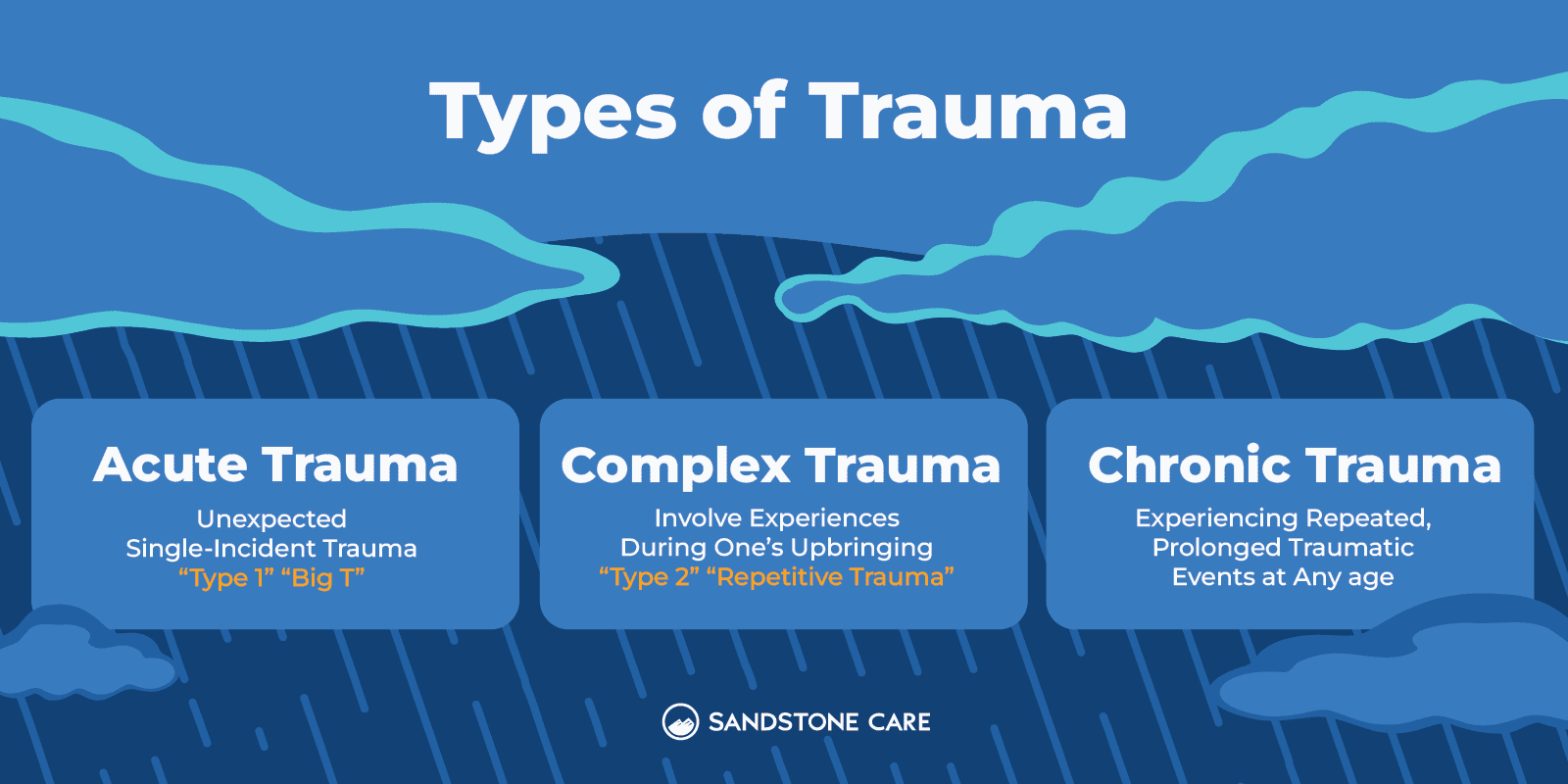
The main types of trauma include acute, chronic, and complex trauma.
Anyone can be affected by trauma.
People of any age, gender, background, or status can experience psychological trauma.
Additionally, marginalized groups sometimes experience generational trauma that is perpetuated by discriminatory systems, such as racial profiling. Survivors in communities that have strong stigmas against mental health issues can also experience extra barriers to seeking treatment for trauma.

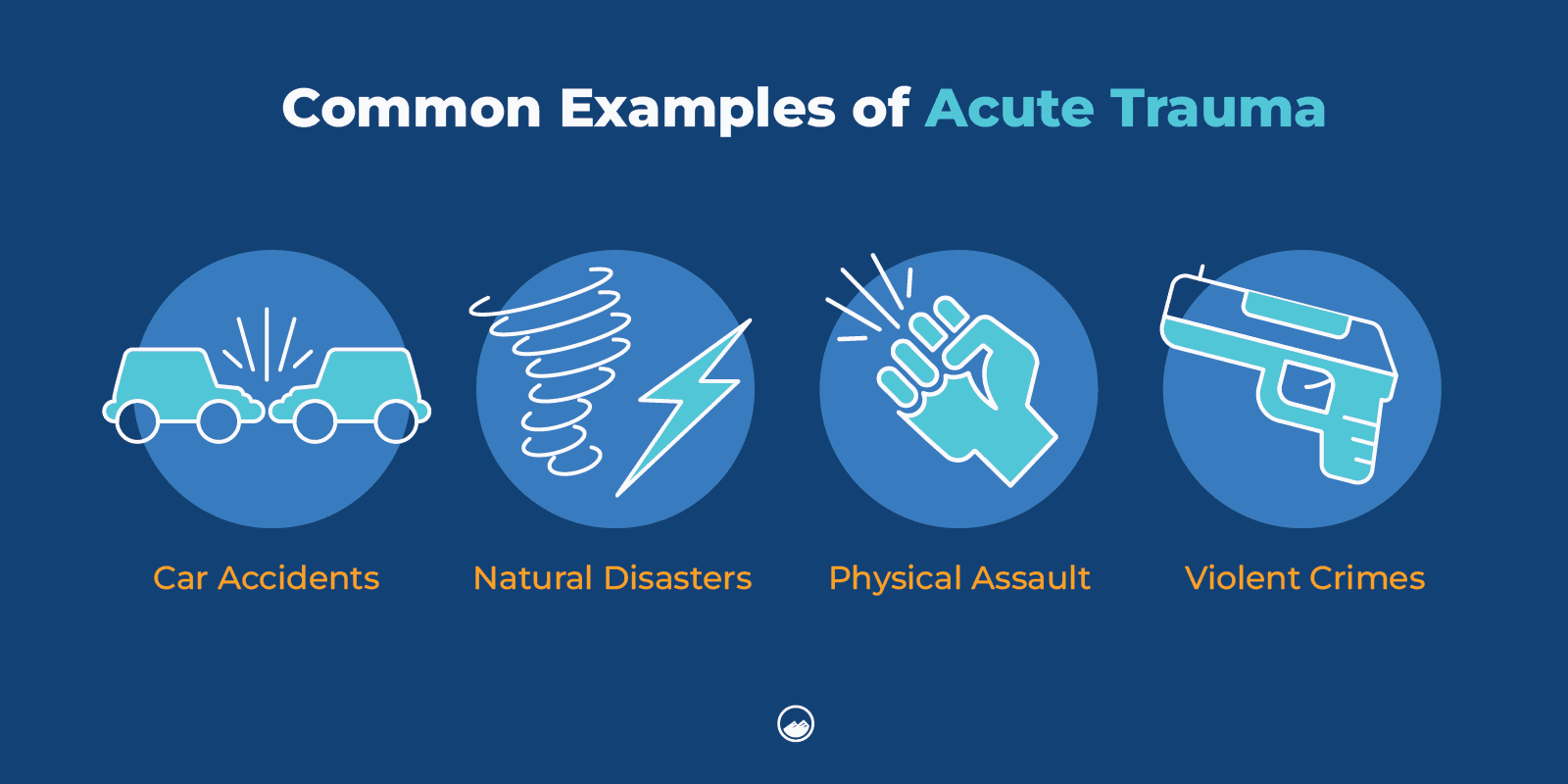
Acute trauma comes from one single incident.
With acute trauma, even if it was just one event, the experience was so overwhelming that it left the nervous system stuck in a threat response. Being in a constant state of alarm can cause several health problems such as anxiety and high blood pressure.
Some of the most common examples of acute trauma include:
Acute trauma can be different for every person.
Some may experience effects of trauma that last for months, while others may still experience effects of trauma for years.
Acute stress disorder occurs when a person experiences a traumatic event or witnessed one. Witnessing a traumatic event can cause vicarious trauma, which can significantly impact a person’s life.
Symptoms of acute stress disorder typically last a month.
The best way to know if you have acute trauma is to reach out to someone you trust and seek professional support.
A healthcare provider, therapist, clinician, or another mental health professional can help trauma survivors work through emotional responses, diagnose mental illnesses such as PTSD, learn healthy coping mechanisms, and begin to heal.

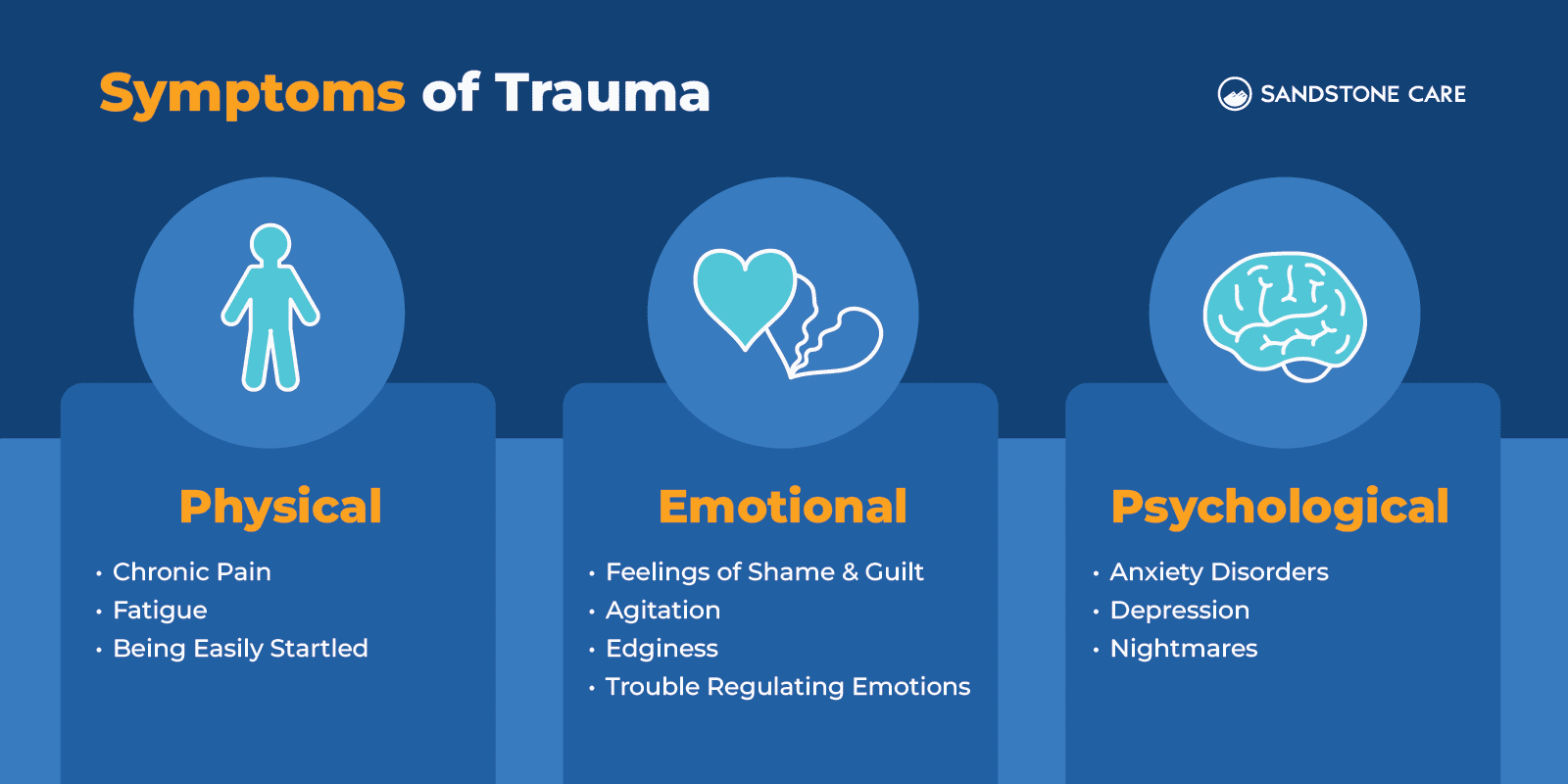
Common symptoms of acute trauma can include:
Psychotherapy is the most common treatment approach for acute trauma therapy.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that can help individuals understand the connection between their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
Trauma-focused CBT is a unique form of therapy that addresses the needs of each unique individual.
Finding a trauma therapist who has the experience and understands, acknowledges, and responds to your life experiences can be helpful.

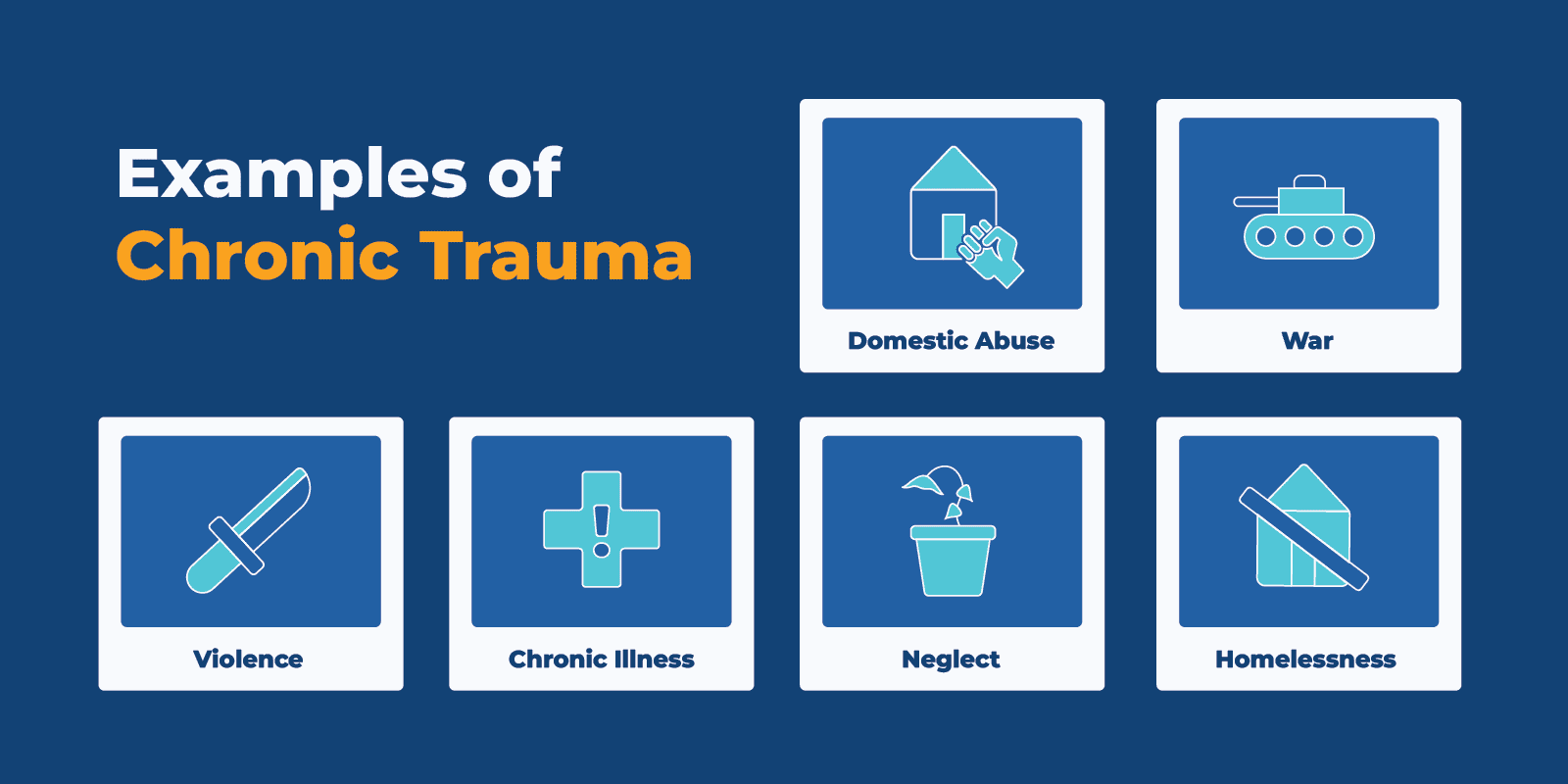
Chronic trauma is when a person experiences repeated, prolonged traumatic events.
Common examples of chronic trauma can include:
Chronic trauma can impact a person’s mental health, make it hard to get through everyday life, and affect how a person views themselves and others.
The impact of trauma can last for months or years. In severe cases, it can lead to self-harm and suicidal ideation.
Some signs and symptoms of chronic trauma can include:
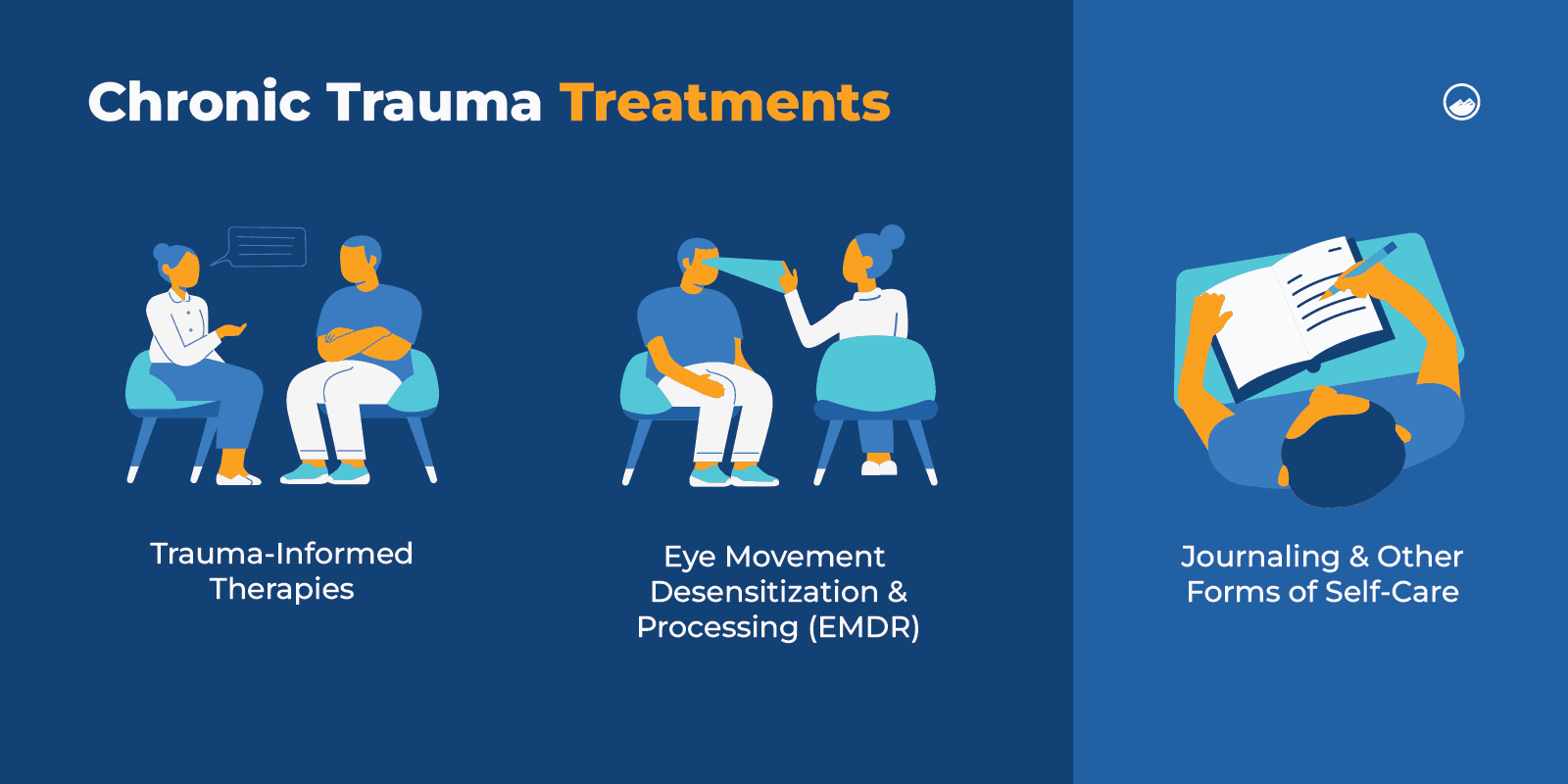
Psychotherapy is a common and effective approach for acute and chronic trauma since there is a wide range of therapies.
Trauma-informed care and trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy can help a person learn to identify, understand, and work through their experiences with the help of a therapist. They can also link trauma survivors to support groups, where they can find people who relate to them and their challenges.
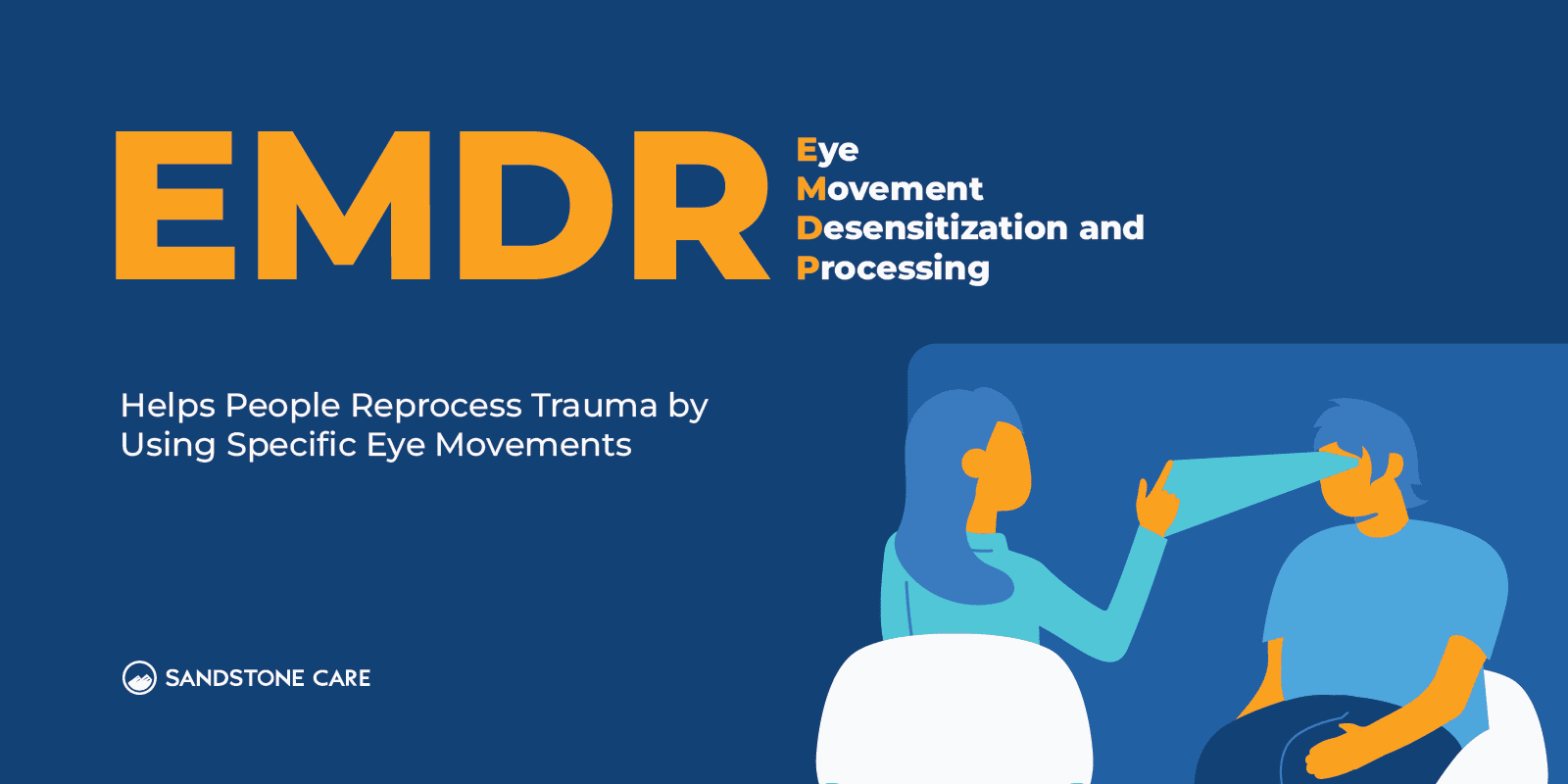
Another treatment option is eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), which can help a person find relief from the distress that comes from their traumatic memories.
It is also important to use self-care methods in addition to seeking professional treatment. Activities such as journaling can help survivors to process feelings and navigate responses to triggers.
Complex trauma typically occurs when a child or young person experiences repeated trauma.
Compared to acute trauma, complex trauma refers to a series of traumatic events experienced over a long period, like months or even years.
The most common examples of complex trauma include:
Complex trauma can have a significant impact on the nervous system.
The brain and body become so overwhelmed that they get stuck in “fight, flight, or freeze” mode.
This impact and the distress that comes with trauma can take a toll on a person’s mental and physical health.

Trauma often refers to a single incident, whereas complex trauma refers to a series of traumatic events.
Complex trauma can affect all people differently.
For many, it can make a person feel very anxious, it can be hard to regulate their emotions, or they may think disconnected from themselves or have a distorted sense of self.
Some of the most common symptoms of complex trauma include:
Some of the most common and effective therapies for complex trauma include:
Early experiences in childhood have a significant impact on your life.
Childhood trauma could involve abuse, witnessing domestic violence, bullying, neglect, refugee or war experiences, natural disasters, losing a loved one, accidents, or serious illness.
According to SAMHSA, more than two-thirds of children reported at least 1 traumatic event by the age of 16.
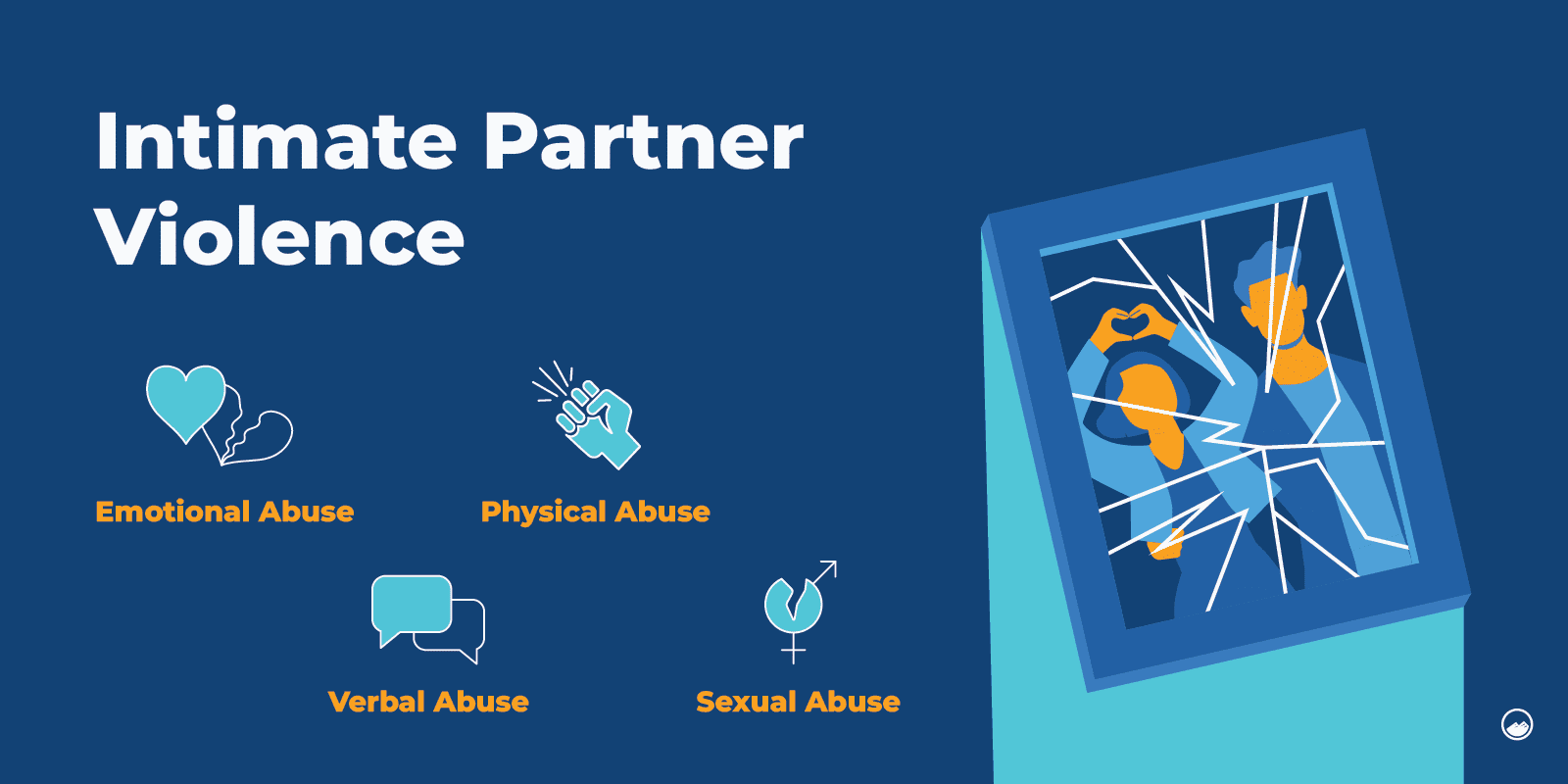
Intimate partner violence is defined by the Centers For Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as “abuse or aggression that occurs in a romantic relationship.”
This may include emotional, verbal, physical, or sexual abuse.
Medical trauma happens when a person has a psychological and physiological response to a negative or traumatic medical experience.
Examples of medical trauma can be during childbirth, when a person experiences an emergency c-section, obstetric violence, or has an infant in the newborn intensive care unit.
Medical trauma can also be associated with cancer, heart attacks, or a stay in the intensive care unit.
One of the most common forms of trauma is physical abuse, whether between a partner, a child, or another person close to you.
Physical abuse is defined by the CDC as “the intentional use of physical force that can result in physical harm.”
Cyberbullying and bullying typically impact children, teens, and young adults and can cause effects that last long after the bullying has stopped.
It can affect a person’s mental health, self-esteem, confidence, and physical health and lead to problems such as anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation.
If you or a loved one are experiencing suicidal thoughts, seek help now. Know that you are not alone and that there is support for you. You can call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 988 or call 911.

Community violence occurs between unrelated individuals, most commonly in settings outside of the home.
Examples of community violence can include assaults, fights, or shootings.
According to the CDC, youth and young adults ages 10-34, specifically in communities of color, are disproportionately impacted by community violence.
Natural disasters happen suddenly and can lead to emotional and physical distress.
With natural disasters, many people lose their homes, are faced with life-threatening situations, or lose a loved one.
These experiences can stay with a person for a very long time and impact how they feel, how they think, and how they act.
Examples of natural disasters can involve earthquakes, landslides, volcanoes, extreme heat, wildfires, floods, tornadoes, hurricanes, and more.
Along with natural disasters, there are also human-caused disasters.
Examples of human-caused disasters can include industrial accidents, shootings, acts of terrorism, and mass violence.

Traumatic experiences from refugee trauma can involve imprisonment, torture, assault, malnourishment, bombs, and exile.
These experiences can affect the mental and physical health of children and adults long after the traumatic events occur.
Sexual abuse is a sexual act or sexual behavior that is forced on another person without their consent.
Abuse and sexual harassment can have short- and long-term effects on a person that can be very difficult to process and cope with.
Human or sex trafficking refers to the use of force, fraud, and coercion to obtain a type of labor or commercial sex act, according to the U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
The trauma that a person endures from sex trafficking can be very difficult to talk about and may cause them to not reach out for help.
Children, adults, and families can be affected by mass violence, acts of terrorism, and community violence.
The trauma that one experiences from these events can have a profound impact on the way a person views themselves, the world, and their physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
These events can lead to anxiety and isolation out of fear of it happening again and concern about the safety of themselves and their loved ones.

When a person loses someone close to them, it is not easy.
Traumatic grief can happen when they lose someone suddenly and unexpectedly.
For example, if a parent loses a child or a family member experienced a violent death.
Traumatic grief is different from when someone loses a person from an expected loss, such as a loved one passing away after a long illness.
Like all grief, the process of recovering is unique to each person.
While both situations can be extremely difficult, traumatic grief more often leads to complicated grief and intense feelings.
Emotional trauma is the impact that is left after a person experiences events that leave them feeling unsafe, scared, or helpless.
It can come from either a single event or can be part of prolonged, repeated stressors.
Emotional trauma can come from things like abuse, bullying, or discrimination.
A person does not have to experience a physical injury to experience emotional trauma.
Some of the most common signs and symptoms of emotional trauma can include:

Emotional trauma can make a person feel unsafe and experience persistent feelings of fear and anxiety.
It can also lead to physical symptoms, such as headaches, chest pain, insomnia, and other physical health issues.
Emotional trauma can impact a person’s daily life and affect their responsibilities, feelings, well-being, and relationships.
Trauma affects all people differently. You may not even know that someone is facing challenges with emotional trauma because they may deal with it behind closed doors and seem perfectly fine on the outside.
Emotional abuse and emotional trauma can lead to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
PTSD depends on each individual and can range in severity. It can last months or years and can happen if a person either experiences or witnesses a traumatic event or events.

Physical trauma involves serious injury to the body.
Three types of physical trauma can include:
Symptoms of physical trauma can include:
Physical trauma most often comes in the form of violence, physical abuse, or sexual abuse.
There is no set length of time for how long physical trauma lasts.
For some, the effects can be felt for weeks; for others, it can be months or even years.
Physical trauma can lead to emotional, mental, and physical challenges.
It can make it hard to get through everyday life; it can impact the way a person feels and can affect a person’s relationships.
FAQ
Our goal is to provide the most helpful information. Please reach out to us if you have any additional questions. We are here to help in any way we can.
One of the most common forms of trauma is considered to be emotional abuse.
This can be for many reasons, one being that individuals who are emotionally abused may be afraid to talk about it or seek help because they feel that others will not believe them.
Emotional abuse can also stem from many different types of traumas, both physical and non-physical.
The 4 F’s of Trauma include:
When a person experiences trauma, the body becomes overwhelmed and can get stuck in survival mode.
It can cause a person to act in certain ways that feel uncontrollable, as the body and brain’s way of protecting itself from what it perceives to be a threatening situation.
Any kind of trauma can be difficult to heal from.
Chronic and complex trauma can be especially difficult to heal from because of prolonged exposure to trauma and experiencing multiple instances of traumatic events.
Trauma is not easy to recover from, but it is more than possible to find support and heal from your experiences.
It can feel even harder to recover from trauma if you are trying to do it alone. It is essential to reach out for help and seek professional support to help you work through trauma and give you the right tools to help manage and cope.
It can be hard to open up about trauma because some people may get the response that they are overreacting or may be told that their feelings are not valid and that they should just “get over it.”
Trauma can make it difficult to regulate your emotions, leading to mood swings, anger, and what seems to other people as “overreacting.”
If you have experienced trauma, whether it be one time or over a long period, your feelings are valid. Seek professional support to help you work through difficult feelings and experiences.


Different types of trauma can affect each individual in unique ways. Seeking support can help you heal and learn to cope. Sandstone Care is here to support teens and young adults with mental health and substance use disorders.