Do I Have ADHD? (Quiz) – See If You Have Symptoms


A person with Attention Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), formerly known as attention deficit disorder (ADD), experiences patterns of symptoms that involve inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
ADHD is a developmental disorder that can impact a person’s relationships and daily life.
If a person suspects they have ADHD, some self-screening questionnaires can help them identify some of the signs and symptoms.
However, if you believe you may have ADHD, you should see a medical professional, like your healthcare provider, to get a proper diagnosis and rule out any other possibilities.
Getting tested and getting a proper diagnosis is essential in getting help.
When ADHD goes undiagnosed, symptoms can worsen over time, and it can not only harm a person’s physical and mental health but their relationships, life, and overall well-being as well.
To get tested for ADHD, you can go to your healthcare provider to get a referral for a professional who can evaluate you for ADHD and give a diagnosis.
The guidelines in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), are used to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment of ADHD.

In an ADHD evaluation, the doctor may ask you questions such as your family history, symptoms you’ve experienced in the past and currently, and about your daily life and habits.
One part of getting a diagnosis of ADHD is getting a medical exam and doing hearing and vision tests to rule out any other possibilities.
If there is a test being done for a child or teens, they may also talk to teachers, parents, or other family members about symptoms they may have witnessed too.
They will also review any documentation you may have and rule out other conditions based on different tests.

If you think you have ADHD, talk to someone and reach out to your healthcare provider.
The symptoms you are experiencing may be ADHD or can be caused by another underlying condition. ADHD can be mistaken for other conditions, such as depression or anxiety.
To get help, it is crucial to understand what is causing your symptoms.
Yes, ADHD testing is worth it.
Testing can get a person the help they need and improve their health and overall well-being.
Even if ADHD testing comes back with results that say you don’t have ADHD, they can tell you if you may have another condition that is causing your symptoms and help lead you to treatment.
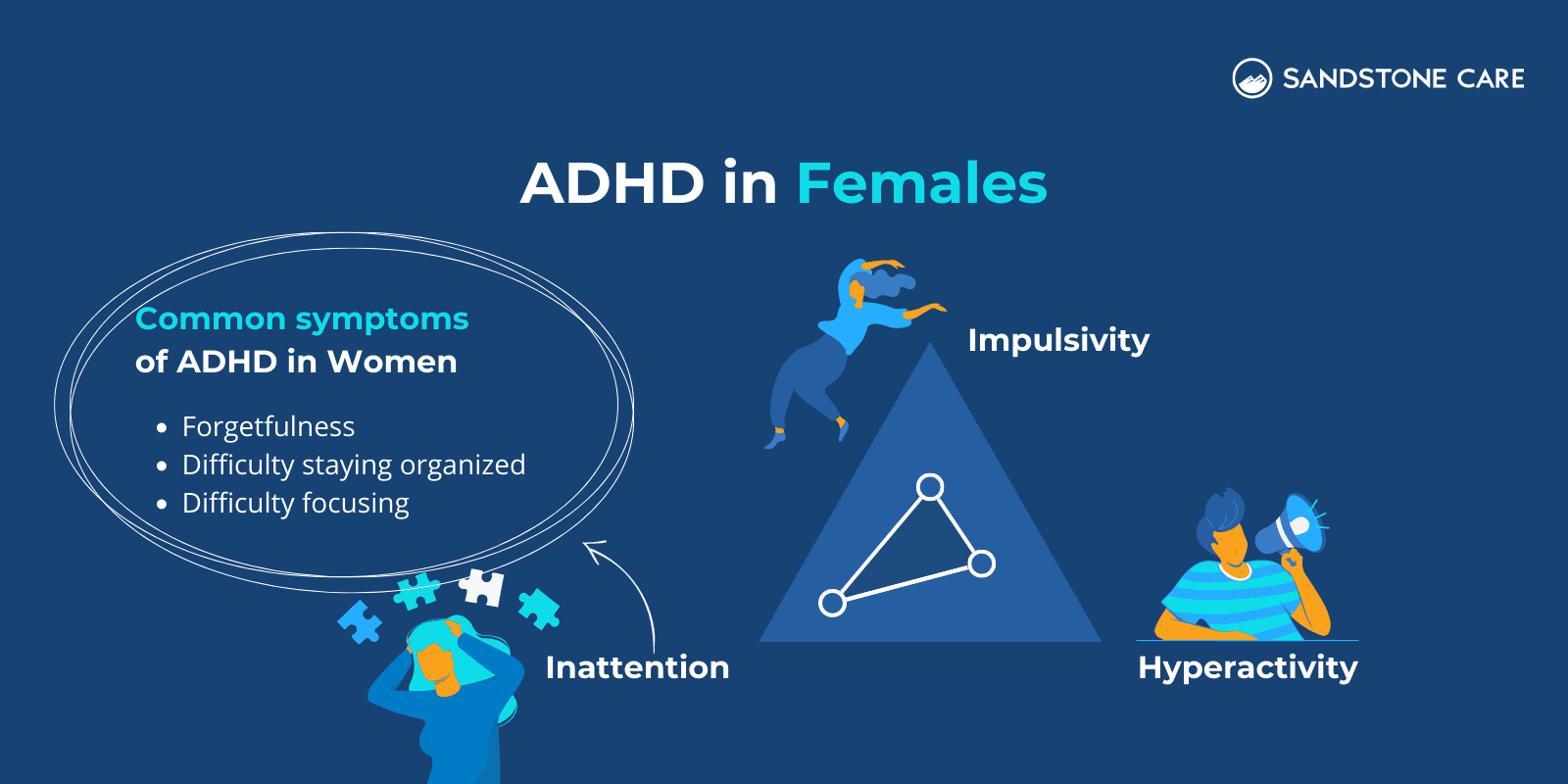
ADHD affects both women and men.
However, it is more common for ADHD to go undiagnosed in women than in men.
One of the main reasons is that women often present symptoms of inattention, which are usually more internal than symptoms of hyperactivity.
ADHD in females may present in symptoms such as difficulty:
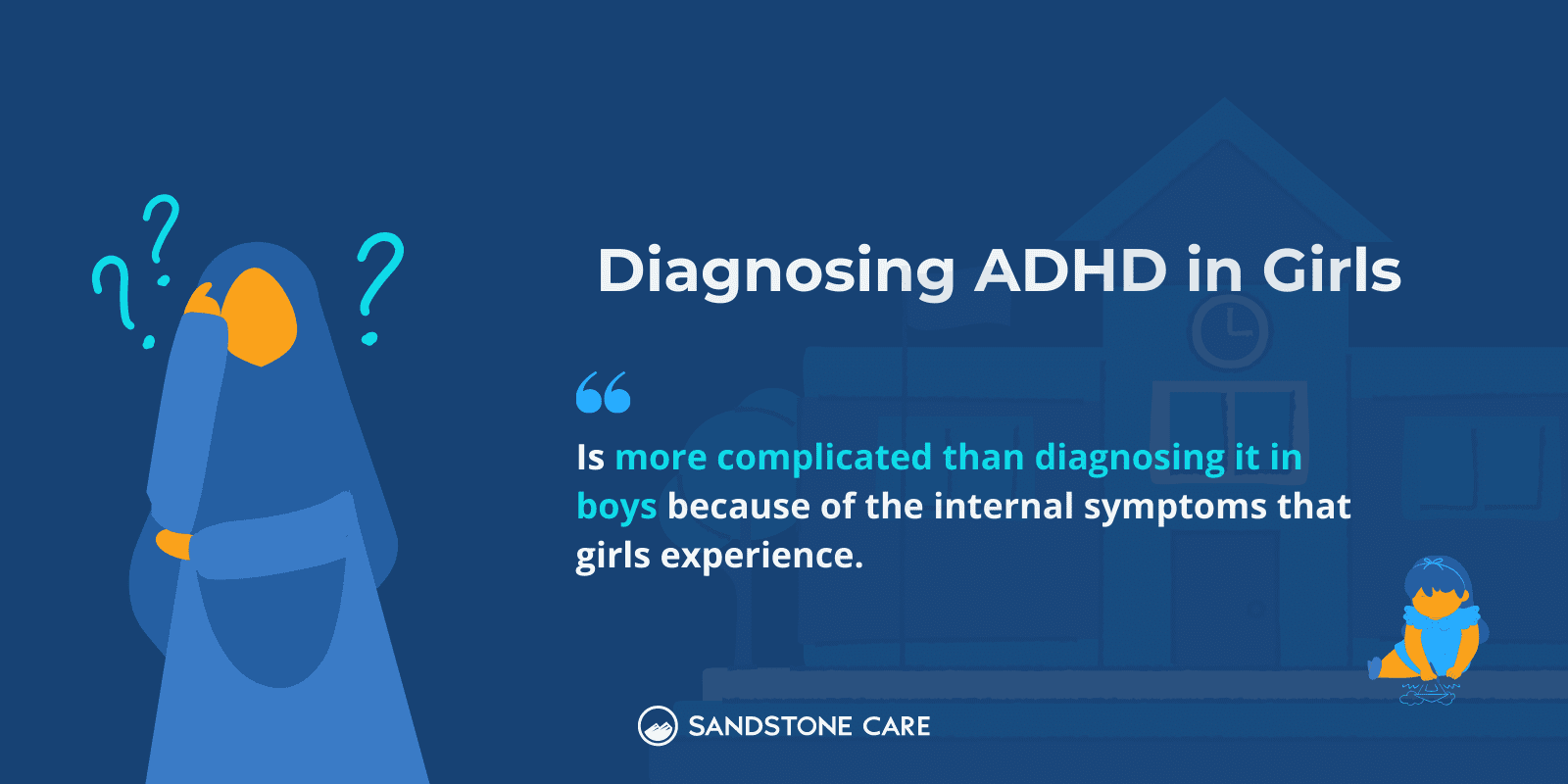
A doctor will do a variety of tests and interviews to diagnose ADHD in girls.
Some of the most common signs a doctor may look out for to indicate possible ADHD in girls can include:
ADHD develops in childhood and is most commonly diagnosed around 12 years old.
However, it tends to be diagnosed later in females because their symptoms are typically not obvious and misdiagnosed for other mental health conditions.
Diagnosing ADHD in girls can be more complicated than diagnosing it in boys because of the internal symptoms that girls experience.
ADHD is also often misdiagnosed as depression or anxiety in girls.
Because it is harder to get diagnosed with ADHD as a girl, they often go undiagnosed for years and experience symptoms that can be hard to manage without proper treatment.
While ADHD most commonly develops in childhood, there can be a possibility of late-onset ADHD.
There are a variety of different tests that can be used to test for ADHD in adults.
The World Health Organization has a self-screening test called the adult-self report scale (ASRS) that can help a person identify signs of adult ADHD.
The length of time it takes for ADHD testing to be done can be different for each individual.
It is important to have a thorough evaluation done by your healthcare provider or mental health professional to ensure that you are getting the right diagnosis and care.
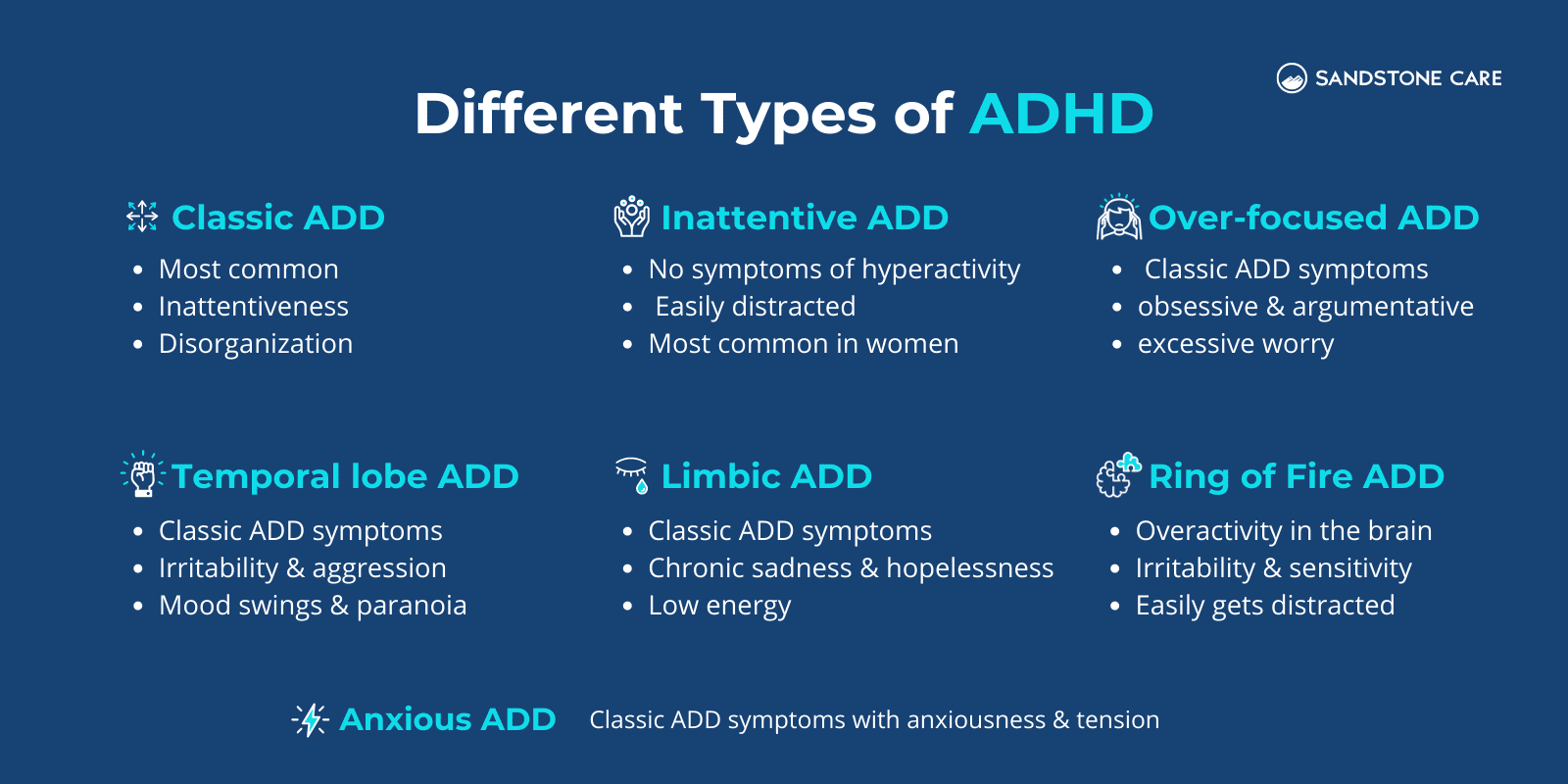
7 different types of ADHD include:
It is believed that each type of ADHD has distinct features and requires specifically different treatment.
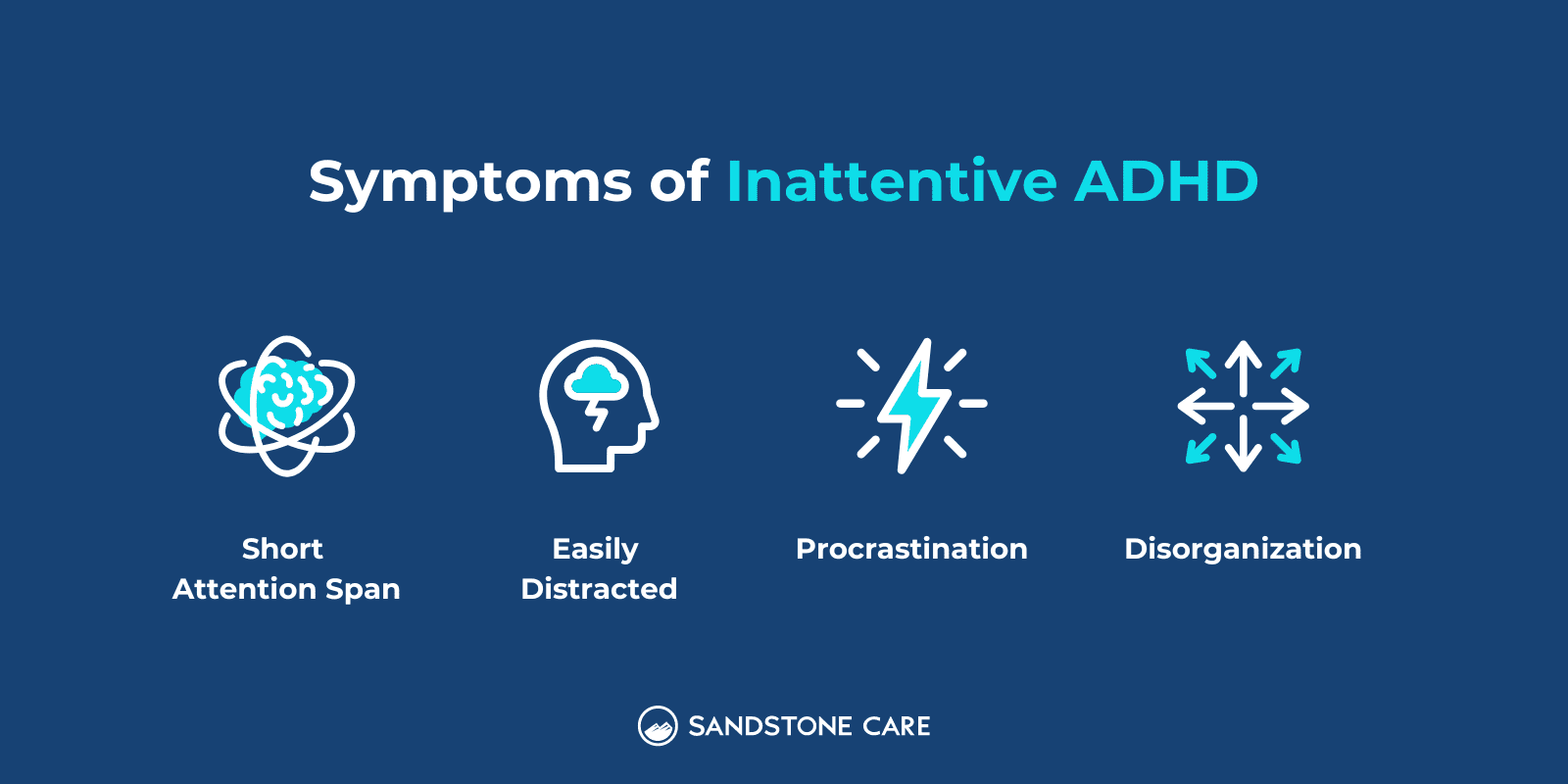
Symptoms of inattentive ADHD can include:
A person with inattentive ADHD may seem introverted and may find themselves “daydreaming” often.
The rarest type of ADHD diagnosed is the hyperactive/impulsive type, without inattention and distractibility.
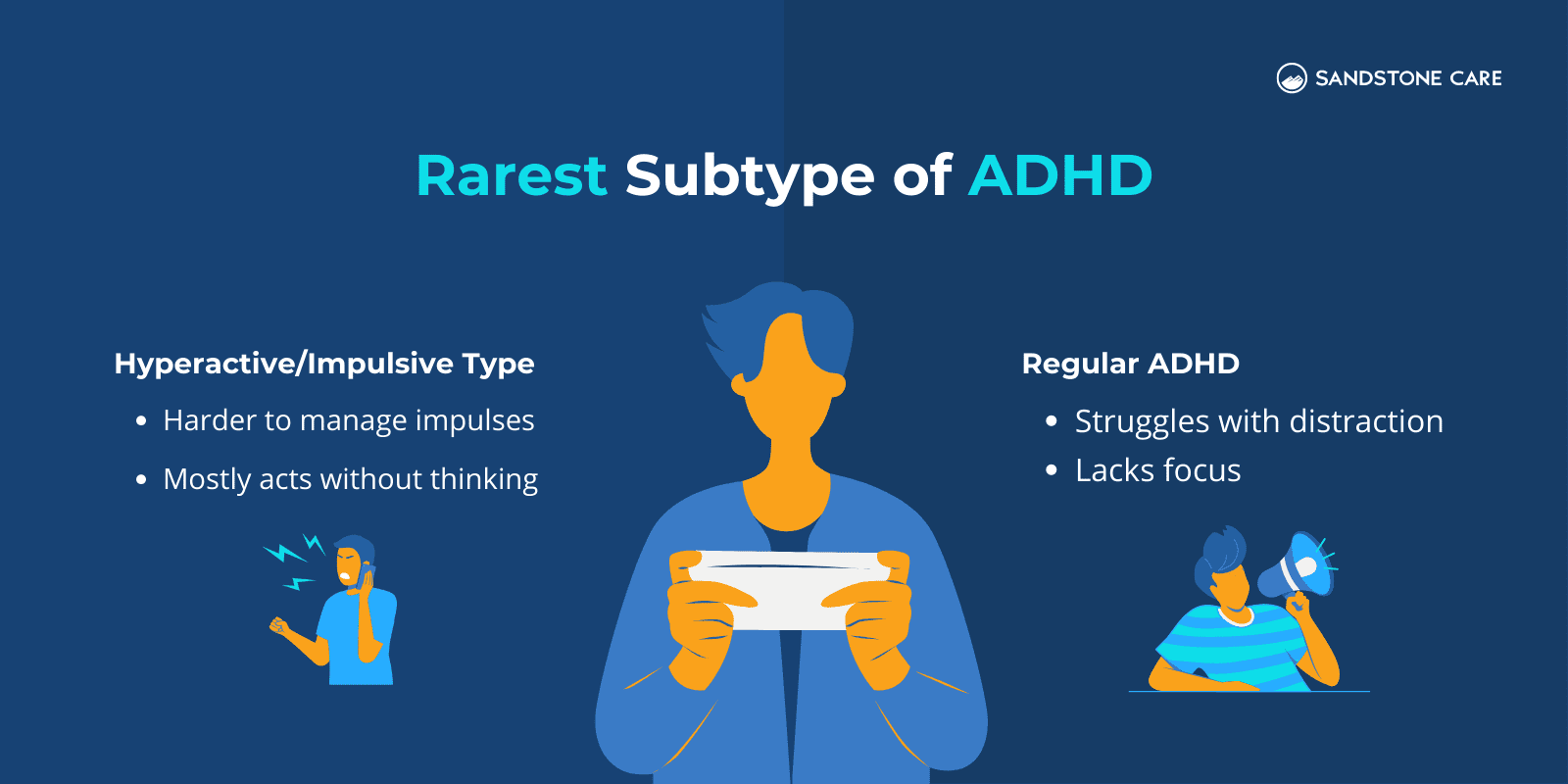
ADHD can look very different from person to person, depending on the way they are presented.
However, common symptoms of inattention in ADHD include:
Common symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity in ADHD include:
When ADHD goes undiagnosed, it can cause problems in almost every aspect of a person’s life.
They may experience problems in their relationships and social life, have trouble performing at work or school, and experience mood swings, anxiety, and depression.
Each individual’s experience is different and unique.
But, for many with ADHD, it can be hard to focus and get things done. It can also be very frustrating because as much as a person may try to finish things or pay attention, they are unable to.
On the other hand, a person with ADHD may feel very energetic, and it can be hard to control impulses.
Some people with ADHD may experience “meltdowns,” which are outbursts that happen when emotions get built up.
ADHD can involve:
Emotional meltdowns may cause a person to cry, get angry, yell, or laugh.
Meltdowns can be a way for a person to self-regulate their emotions, and a person may find relief afterward.
Individuals with ADHD may also experience a “shutdown” where they have so many emotions that they “space out.” They may have a hard time speaking and explaining what they are feeling.

Stimulants are the most common medication used to treat ADHD.
Two different stimulant medications include methylphenidate and amphetamine.
ADHD is not curable.
However, with treatment, a person with ADHD can manage their symptoms and live balanced, sustainable lives.
Often, ADHD is treated with behavioral therapies and medication. It is important to find the treatment center and treatment team that works best for you and your needs.
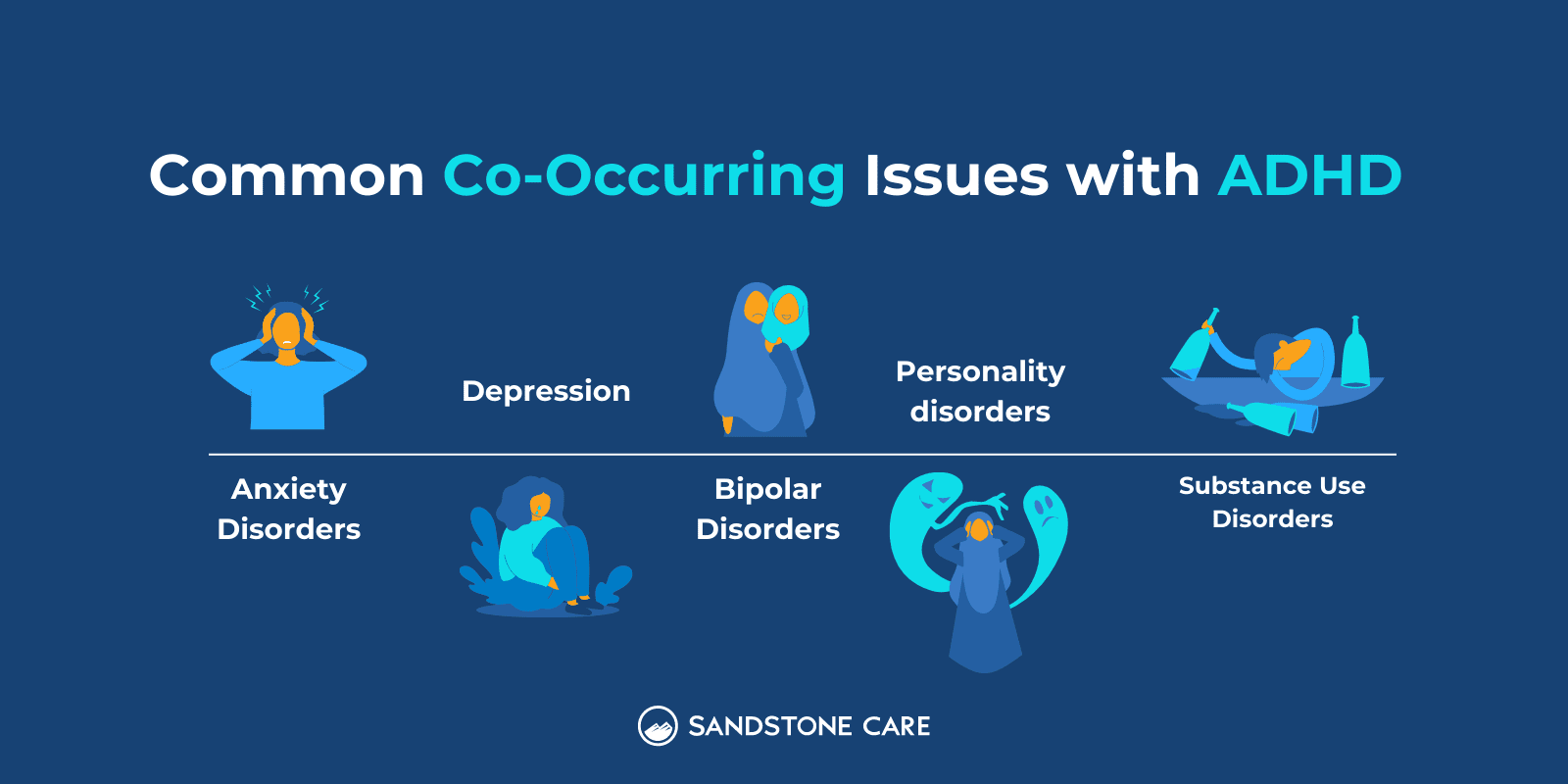
According to BMC Psychiatry, the most common comorbid psychopathologies with ADHD are anxiety disorders, depression, bipolar disorders, personality disorders, and substance use disorders.
The DSM-5 guidelines include the severity of ADHD as mild, moderate, or severe.
A person with mild ADHD, formerly known as ADD, may have symptoms that are not very obvious or mistaken for other mental health conditions like anxiety or depression.
Some adults with mild ADHD may not know they have it, but they most likely recognize that everyday tasks can be difficult to complete.
A person with mild ADHD may be easily distracted, make careless mistakes, or have difficulty finishing tasks that feel challenging.
If you think you may have mild ADD, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional to get a diagnosis and care.
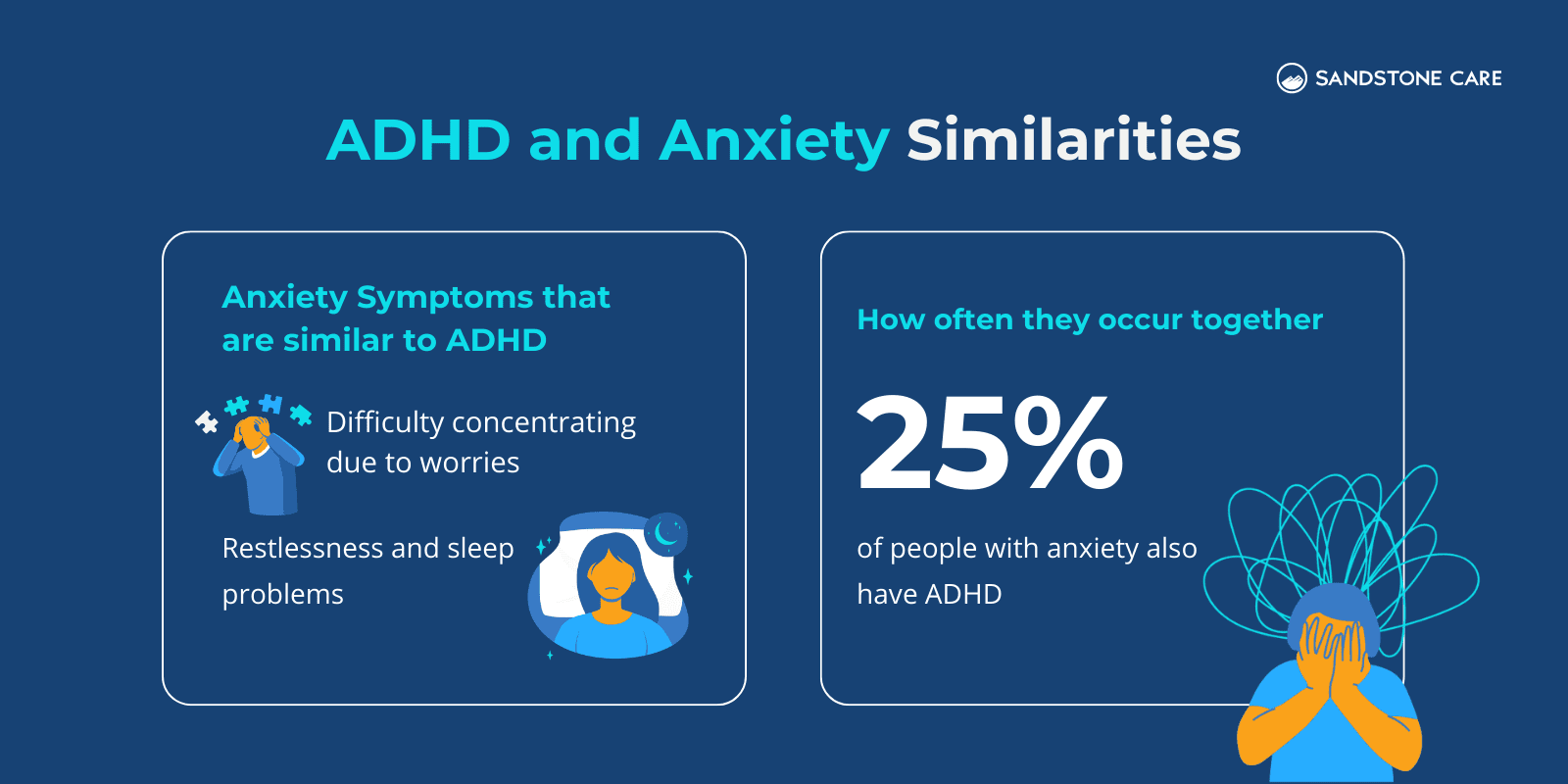
Some symptoms of ADHD share similarities with those of anxiety.
With anxiety disorders, a person experiences worry and anxiety that does not go away and can worsen over time.
A person with an anxiety disorder can have difficulty concentrating because they are fixated on the present worry.
They may also experience restlessness and sleep problems, which are similar to symptoms of ADHD.
According to the International Journal of Psychiatry in Clinical Practice, “ADHD and anxiety disorders are among the most common psychiatric disorders with a 25% comorbidity rate with each other”.
It is not uncommon for a person with ADHD to have anxiety as well. Treating these disorders can be a little more complex and usually involves a mix of cognitive-behavioral treatment approaches and medication.
Depression is a mood disorder that impacts the way a person feels, thinks, and acts.
Common symptoms of depression can include anxiousness, sad mood, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, and difficulty sleeping.
Sometimes, a person with ADHD may be misdiagnosed with depression because many symptoms of inattentive ADHD are internal and can be hard to spot.
Often, ADHD in women is misdiagnosed with depression.
There is a misconception that people with ADHD are lazy.
However, people who may be considered lazy often don’t make an effort or don’t have the desire to get certain things done.
But, individuals with ADHD usually try hard to complete certain things but may have difficulty doing so. This can make them feel frustrated with themselves and lead to low self-esteem.
Being lazy and having ADHD are two completely different things.
Having ADHD does not mean you are lazy, and being lazy does not mean you have ADHD.
Hyperactivity, impulsivity, and inattentiveness can all be symptoms of both ADHD and autism.
While they both share some similar symptoms, autism is different because individuals may have challenges with communication, interaction, and repetitive behaviors.
“Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a developmental disability caused by differences in the brain,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
According to Frontiers in Psychiatry, “50 to 70% of individuals with autism spectrum disorder also present with comorbid attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)”.
Attention impairment is commonly reported in individuals with autism spectrum disorder, and there is a discussion on whether this symptom is ADHD itself or just another trait of ASD.
FAQ
Our goal is to provide the most helpful information. Please reach out to us if you have any additional questions. We are here to help in any way we can.
Part of managing the symptoms of ADHD is identifying and learning what your triggers are.
ADHD triggers can be different for everyone.
However, common triggers of ADHD symptoms can include:
When a person learns what triggers some of the symptoms of ADHD, they can learn how to find things that work for them and get rid of what doesn’t.
While ADHD may come with difficult symptoms to manage, ADHD also comes with gifts and benefits.
Individuals with ADHD can be creative, empathetic, conversational, and energetic.
Every person is unique, and individuals with ADHD have incredible strengths and talents that help make them who they are.
Individuals with ADHD also have great perseverance, strength, and determination. Everyday tasks can become difficult when you have ADHD, but they still work through it to succeed and reach their goals.
“Masking” ADHD means a person is hiding their ADHD symptoms from other people.
Sometimes, a person is trying to seem “normal” or that they are not living with ADHD.
Living with ADHD can be hard, and sometimes it can feel easier to hide the symptoms from others.
However, the longer a person goes hiding their symptoms and not getting the help they need, the worse they can feel.
Acting like the symptoms are not there can lead to other health and life problems, and many people may face challenges in silence when they are in need of help and support.
ADHD can come from a number of different causes, which can include:
Scientists are also looking into other potential causes of ADHD, including alcohol and tobacco use during pregnancy, low birth weight, and premature delivery.
The best way to find out if you have undiagnosed ADHD is to reach out to a professional, like your healthcare provider, and receive a proper diagnosis.
Undiagnosed ADHD can be mistaken for other mental health conditions, and the longer it goes undiagnosed, the likeliness of worsened symptoms increases.


Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) can look very different for each individual. If you think you have ADHD it is best to seek help from a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.