Inhalants are chemicals commonly found in household items that produce chemical vapors that can be inhaled for a psychoactive effect.
“Huffing” describes the action of inhaling vapors with an inhalant-soaked rag in the mouth.
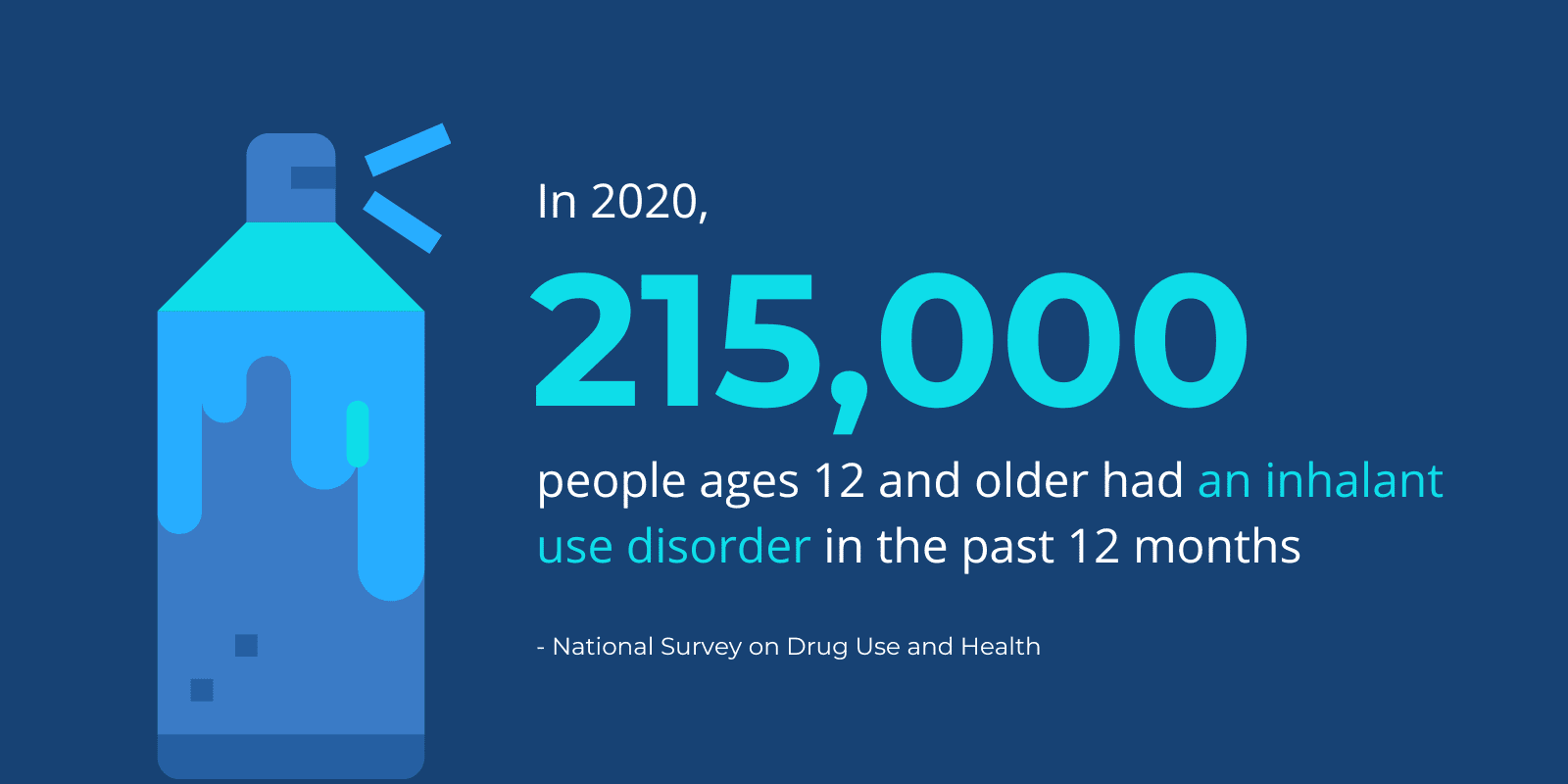
According to the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health, about 215,000 people ages 12 and older had an inhalant use disorder in the past 12 months.
Teenagers and young people are at a time in their lives where they are going through many changes and transitioning into new stages of their life.
Some believe part of growing up is experimenting, and one of the most common substances young people start with are inhalants.
Young people may also use substances for other reasons, possibly from peer pressure, to fit in, or as an unhealthy coping mechanism.
Many young people don’t recognize the dangers of inhalants and huffing because they are found in everyday household items, so they assume they can’t be as dangerous as illicit drugs. However, inhalant use can be hazardous and fatal, even after just one time.
Huffing is a slang term for inhalants breathed in through the mouth.
An inhalant is a substance that produces chemical vapors which can be inhaled to produce a psychoactive effect.
Inhalants can be categorized into four different groups, including:
People use inhalants in different ways, including sniffing, snorting, bagging, or huffing.
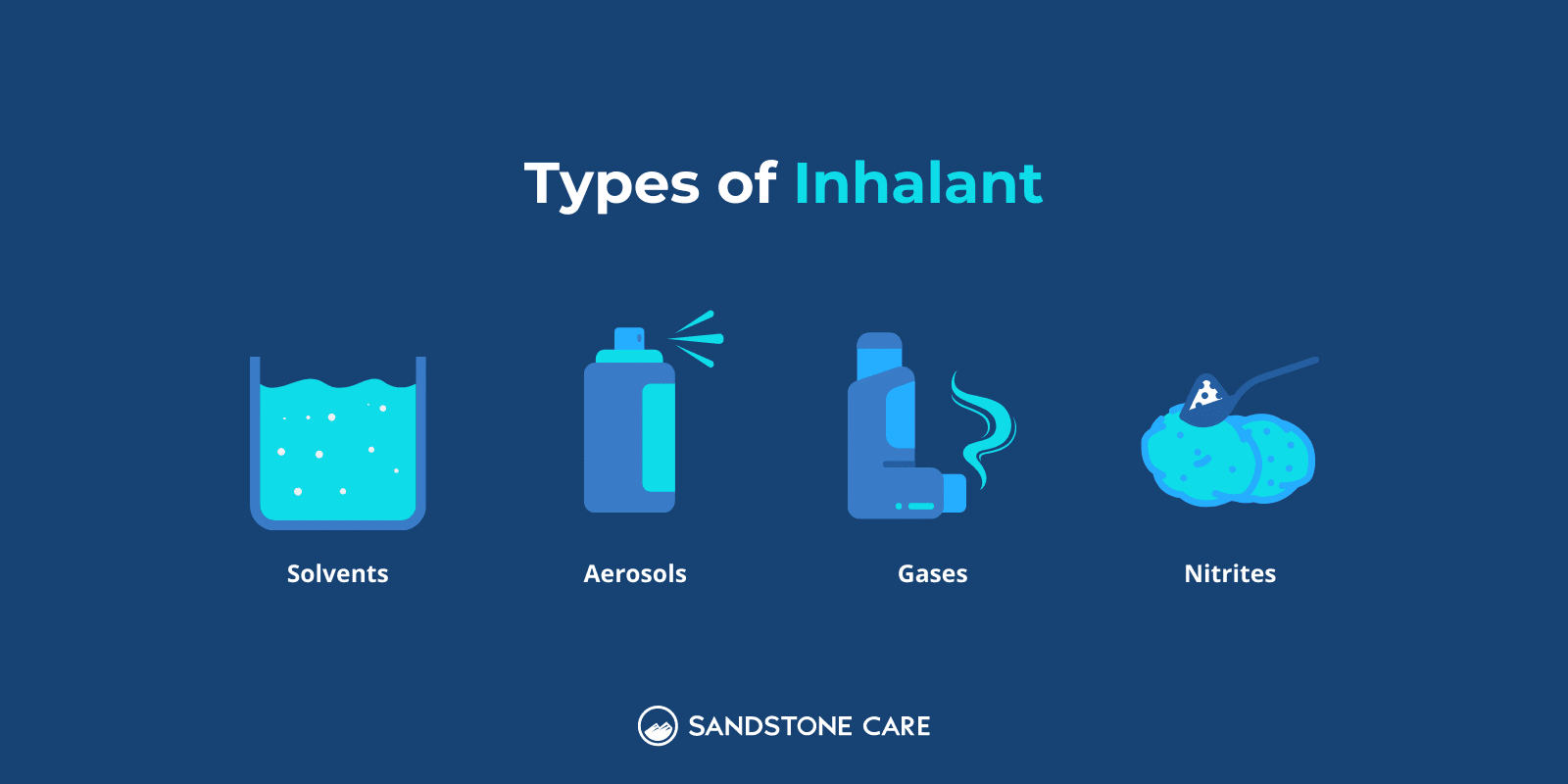
Different products that can be used as inhalants can include:
Huffing paint can be addictive, especially with repeated use.
People who try to quit using inhalants may experience withdrawal symptoms such as:

Young people are especially vulnerable to developing addictions because their brains are still going through major development through their mid-twenties.
Substance use disorder forms when an individual continues using a substance despite its negative effects on their life and well-being. The most severe form of a substance use disorder is addiction.
People who regularly use inhalants can build a tolerance over time.
Tolerance can be described as a person’s response to a drug, where the body adapts to the drug, so a person needs more and more of it to achieve the same effects.
When someone builds a tolerance, it doesn’t necessarily mean they are addicted; however, addiction can follow shortly after.
Inhalant-related disorders refer to a category of disorders that include inhalant intoxication and inhalant use disorder which involve substances that produce a high through inhaling.
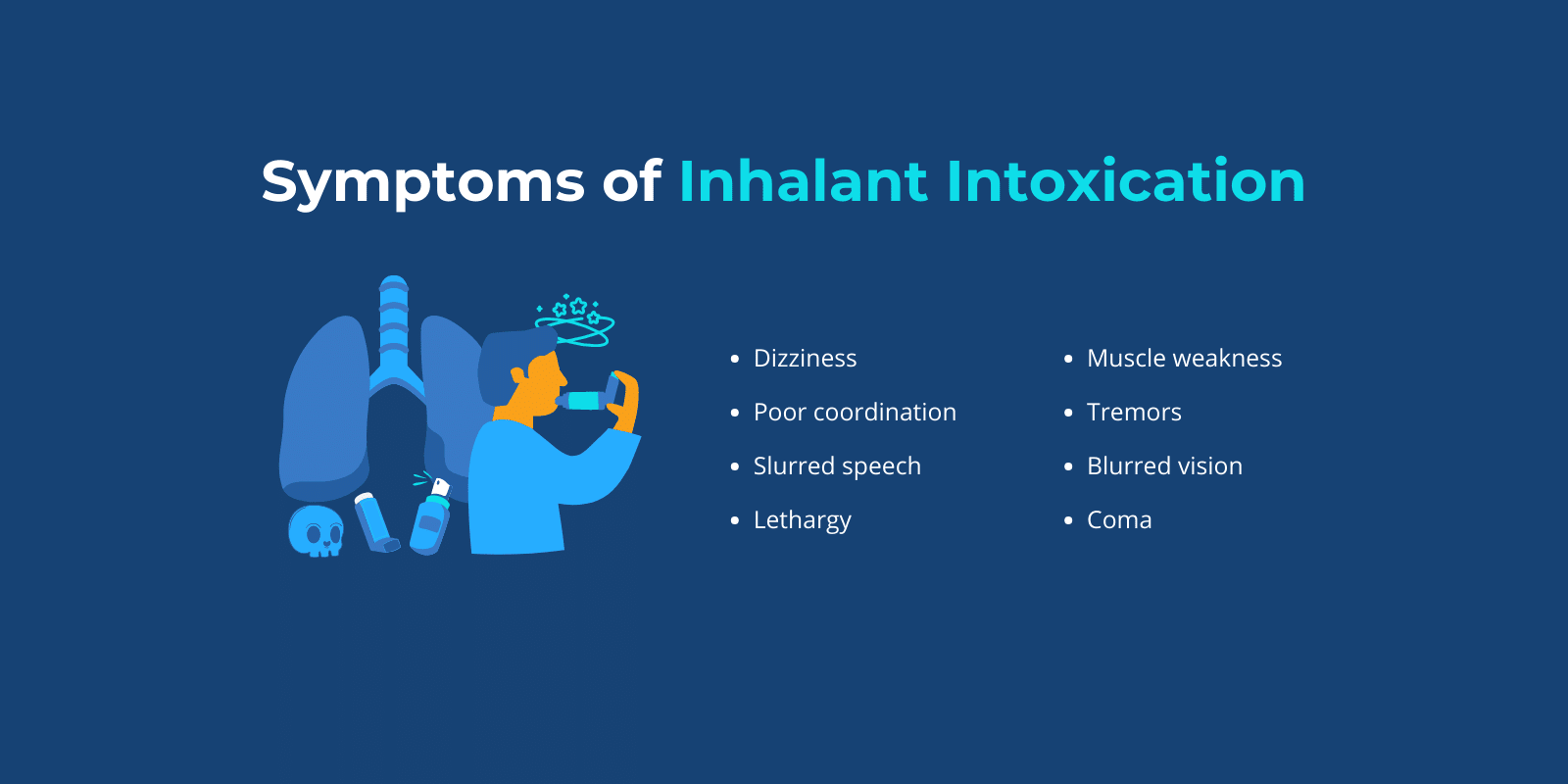
Inhalant intoxication happens when a person is exposed to a high dose of inhalants.
Symptoms associated with inhalant intoxication can include:
Inhalant-use disorder is diagnosed when a problematic pattern of intoxication develops from repeated inhalant use or causes significant impairment or distress.
Inhalant-use disorder can be diagnosed when at least two of the following symptoms are present over 12 months:
The main age group affected by inhalant abuse are teens and young people.
Inhalant abuse may start in young people because of its accessibility. It can also be much cheaper and easier to hide. Many abused inhalants are common household products, making them much easier to obtain than other substances.
Many young people struggle with mental health conditions and large amounts of stress in their teenage and young adult years. They may turn to substances like inhalants as a way to escape or cope.
A person may be more likely to abuse inhalants if they have a history of:
It can be hard to tell if someone is huffing as inhalants are very easy to hide.
However, there are warning signs that you can look out for if you believe a loved one is huffing.
A person who is huffing may display changes in their behavior, mood, and sleeping or eating patterns. More specifically, they may show changes in their appearance, with paint on their face, hands, or clothes.
The discovery of empty spray containers and paper or plastic bags can be a big indicator of huffing. You also may be able to smell chemical odors on their clothing or breath.
If you are unsure if a loved one is struggling with inhalant use, seek professional help.
Warning signs that a person may be using inhalants or huffing include:

4 warning signs of inhalant abuse can include:
Routine urine drug screenings do not detect inhalants, so a clinical diagnosis has to come from experienced medical professionals.
Elevated liver enzymes from lab results or specific urine tests can help detect inhalant use if abused over a long period.’
Being open with your child about huffing can help prevent or get a person to treatment if they struggle with inhalant use.
When talking to your kid about huffing, it is important to educate them about the effects and dangers that come with huffing. Many kids may be unaware of how serious inhalant use is.
Be open to answering any questions, and ensure they are in a safe space to talk about things and be comfortable opening up.
Talking to your kid about substance abuse may seem uncomfortable or intimidating, but they are important conversations.
If a loved one is struggling with inhalant use, it is important to:

Some side effects that come from inhalant intoxication include:
Huffing paint can cause suffocation if a person cuts off oxygen, commonly through bagging. Asphyxiation may also happen if the inhalant replaces too much oxygen in the lungs.
Huffing paint can also lead to overdose and, in some cases, become fatal.

Inhalant use can have negative effects on a person’s mental health.
Research shows that inhalant users show high rates of mental illnesses such as depression, anxiety, and personality disorders.
Inhalant use can also contribute to self-harming behaviors as well as suicidal thoughts.
Inhalant use can take a toll on a young person’s mental and emotional health and worsen over time if left untreated.
If you or a loved one are experiencing suicidal thoughts, seek help or call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 988.
Psychosis describes conditions that affect the mind, where a person loses some sense of reality.
Some research suggests that certain inhalants may cause psychosis over prolonged use.
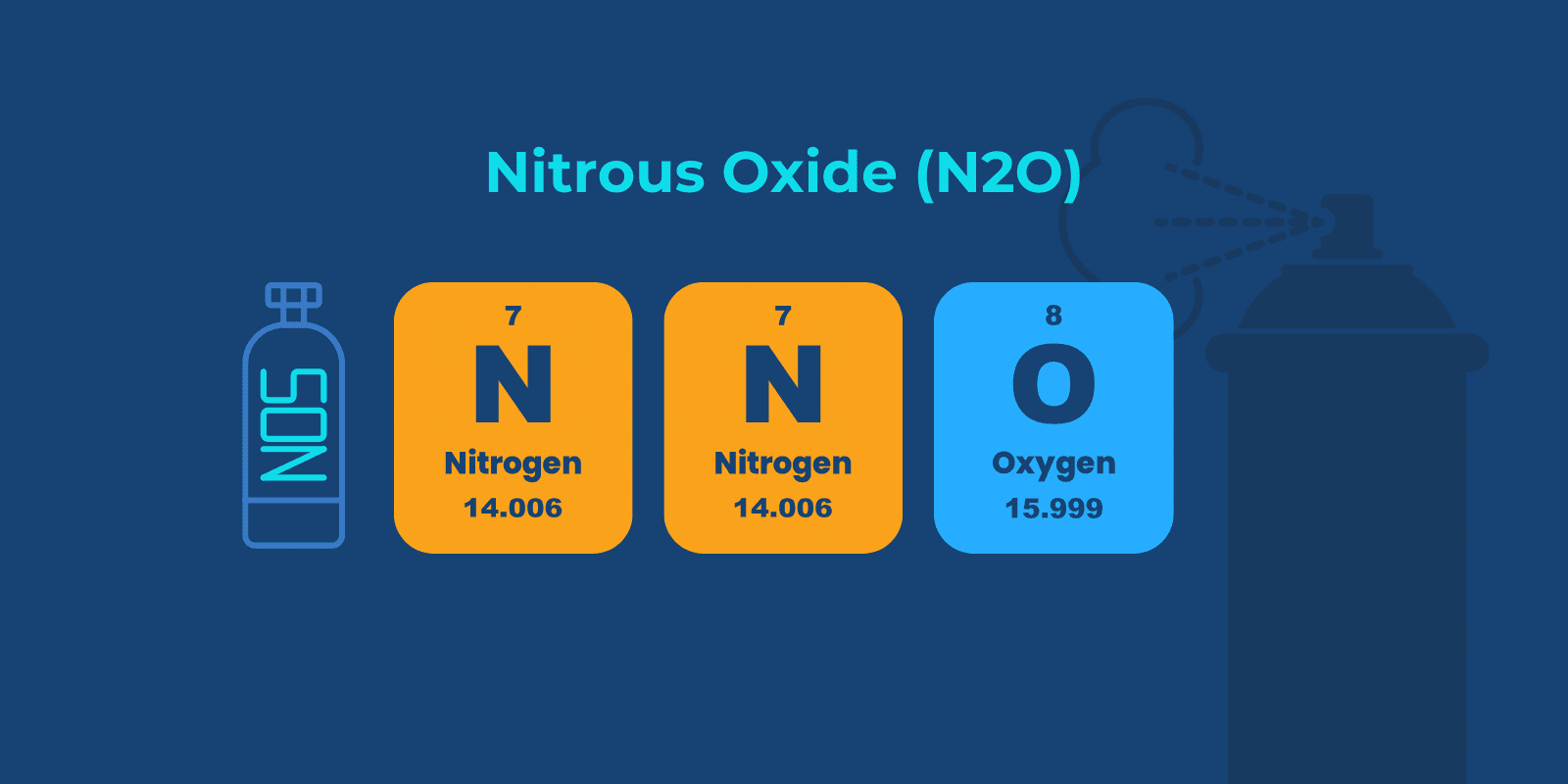
Nitrous oxide, also known as “laughing gas,” slows down the brain and body’s responses.
Nitrous oxide can cause a calm, euphoric feeling and is used sometimes to treat pain or as a mild sedative.
While its use is considered safe in the medical setting, it is important to know recreational use’s side effects and dangers.
Side effects of nitrous oxide can include dizziness, nausea, vomiting, headache, excessive shivering, disorientation, loss of balance, impaired memory and cognition, and weakness in the legs.
There is also a possibility a person can overdose on nitrous oxide. This happens when a person gets too much gas at once.
Overdose can cause symptoms such as chest tightness, difficulty breathing, hallucinations, psychosis, choking, and increased heart rate.
Inhalant overdose can be extremely dangerous, lead to seizures, or cause the heart to stop. First responders and emergency room doctors can try to treat overdose by treating these conditions.
If you think someone has overdosed on nitrous oxide, get help immediately and call 911.

Almost all inhalants, besides nitrates, produce a pleasurable effect by depressing the central nervous system.
Chronic exposure to inhalants can cause long-term damage to the brain and other major nervous system parts.
Prolonged inhalant use can also damage parts of the brain that play a role in cognition, movement, vision, and hearing.
People who use inhalants may also have hallucinations or delusions. Hallucinations are things created by the mind, such as visions, sounds, or smells that seem real but are not. Delusions are beliefs that are not based on reality.
Sudden sniffing death syndrome happens when the highly concentrated chemicals in inhalants induce irregular and rapid heart rhythms which lead to fatal heart failure.
Sudden sniffing death syndrome can happen after just one session of inhalant use, even in a healthy young person.
Sudden sniffing death syndrome is typically associated with butane, propane, and chemicals in aerosols.
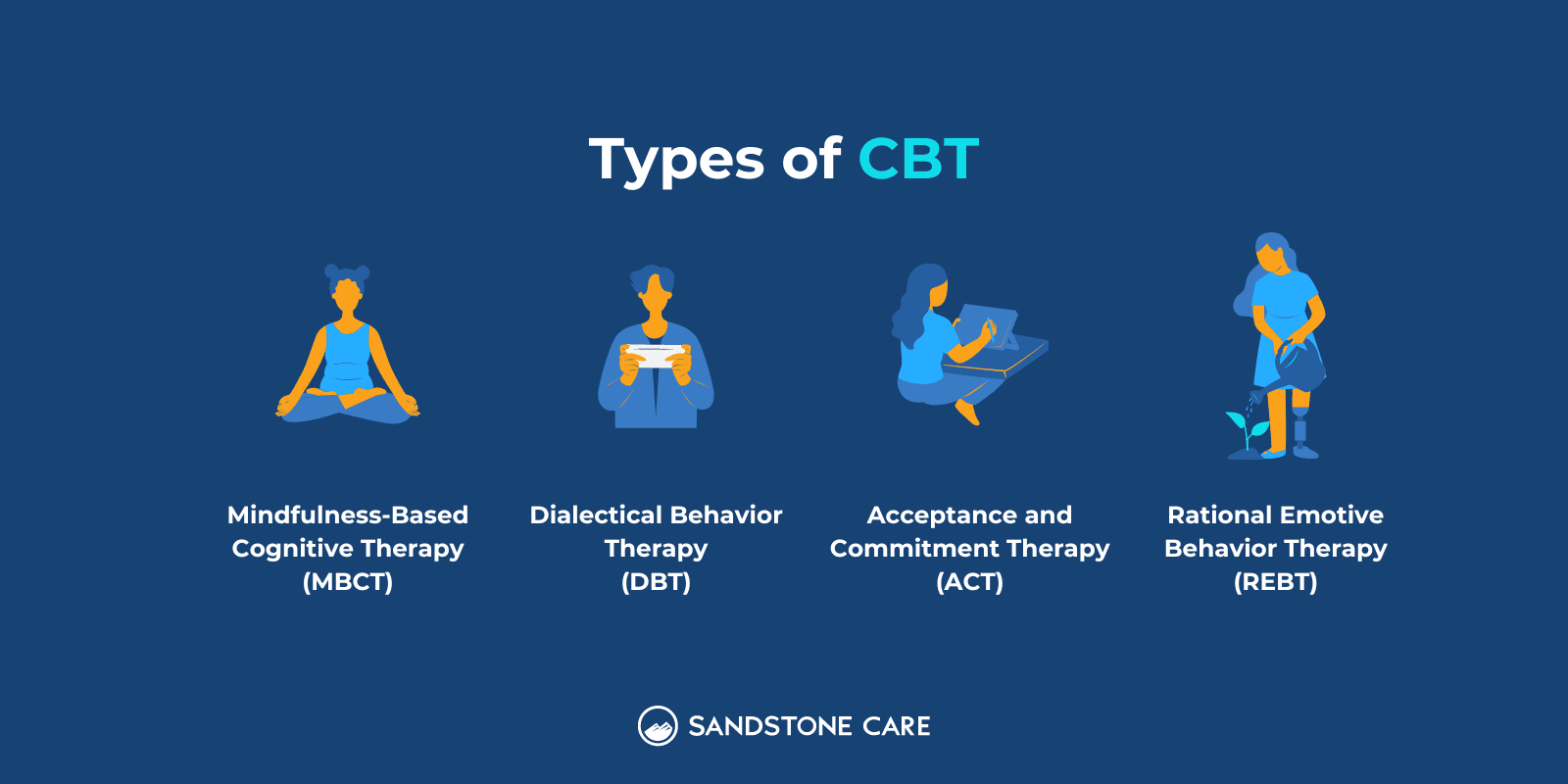
Treatment for inhalant abuse involves individual therapy, family therapy, and support groups.
The approach to treating inhalant use is typically similar to other substance use addiction treatments; however, finding a treatment that works for you and your family’s unique needs is important.
Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help teens and young adults struggling with inhalant use identify unhealthy thought and behavior patterns and teach them how to handle stressful situations.
Family therapy is another important aspect of inhalant treatment, especially for young people.
Motivational incentives may also be effective in helping young people engage in treatment and stay drug-free through vouchers or rewards for positive behaviors.
More research is needed to determine the most effective inhalant addiction treatment.
If you or a loved one are struggling with inhalant use or huffing, seek help from a health care professional.
Talk to a trusted adult if you are young and know somebody struggling with inhalant use.
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has a Behavioral Health Treatment Services Locator that can help you find treatment near you.
According to Drug and Alcohol Dependence, psychiatric disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and others, were highly prevalent among inhalant users.
Inhalants can cause significant damage to the central nervous system, which can cause disruptions in a person’s emotional and psychological mechanisms.
Research suggests that inhalants can also impact cognition and brain maturation.
Young people may huff aerosols such as air fresheners or deodorants, where they spray them into a towel and press the soaked towel against their nose or mouth. The fumes then create a high.
According to BMJ Case Reports, inhalation of deodorant spray has caused cardiac in a number of cases.
The main toxic chemical found in deodorant sprays is butane. Symptoms of butane intoxication can include:
The high that inhalants produce typically only lasts a few minutes.
However, some people may try to make the high last longer by repeatedly inhaling over several hours. Doing so can be extremely dangerous and result in serious negative consequences like an overdose.
Some people may try to inhale the gas from air dusters to achieve a high or sense of euphoria.
Air dusters are cans of compressed air used in households to clean dust and dirt. Air dusters can contain a variety of ingredients such as:
Inhaling air dusters can lead to serious negative side effects and, in some cases, become fatal.
Inhaling air dusters can cause side effects that include:
Other terms sometimes used to refer to the misuse of air dusters include huffing, dusting, can of sunshine, or sunshine can.
Huffing the bag refers to the action of pouring the substance into a bag and inhaling through the opening.
Almost any spray can be bagged, such as aerosol deodorant, air freshener, and hairspray.
Some people may do so by placing the bag over their mouth, while others place it over their whole head.
Placing a bad around the head puts individuals at increased risk of depriving, cutting off oxygen, and resulting in suffocation.
Finding plastic or paper bags along with empty aerosol spray cans can be a warning sign of bagging among young people.
“Whippets” is a slang term used for the recreational use of nitrous oxide.
The name originated from whipped cream aerosol containers, which a person cracks open to get the gas.
Young people may do whippets by breathing in the fumes while covering the user’s head with a bag, or face mask, or transferring to a balloon.
Whippet highs can impair an individual’s judgment and muscle control. Some people who have done whippets have experienced heart failure, suffocation, and seizures.
Warning signs of whippet use can include:


Inhalants are most abused among teens and young people, mainly because of their accessibility. Huffing can be extremely dangerous and fatal. Sandstone Care is here to support teens and young adults with mental health and substance use disorders.